首页 > 代码库 > 网络地址转换(NAT)
网络地址转换(NAT)
网络地址转换(NAT)
实验01: 网络地址转换(NAT)
实验目标: 通过使用少量的公有IP 地址代表较多的私有IP 地址
实验环境:
借助于NAT,私有(保留)地址的"内部"网络通过路由器发送数据包时,私有地址被转换成合法的IP地址,一个局域网只需使用少量IP地址(甚至是1个)即可实现私有地址网络内所有计算机与Internet的通信需求。
这种通过使用少量的公有IP 地址代表较多的私有IP 地址的方式,将有助于减缓可用IP地址空间的枯竭。而且还能够有效地避免来自网络外部的攻击,隐藏并保护网络内部的计算机。
实验拓扑图:
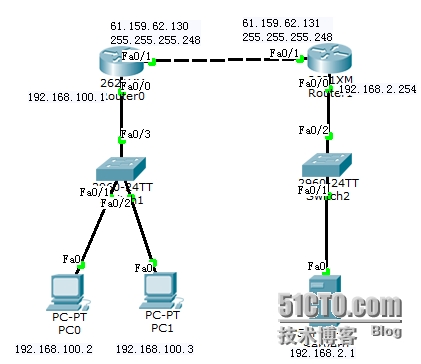
实验步骤:
一. 配置IP地址
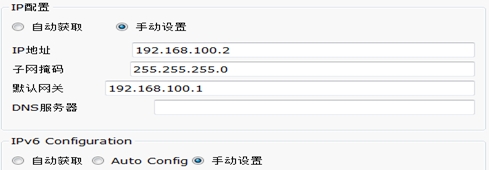
1. 配置PC0 IP地址
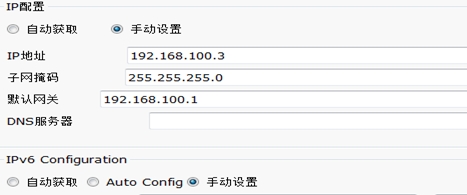
2. 配置PC1 IP地址
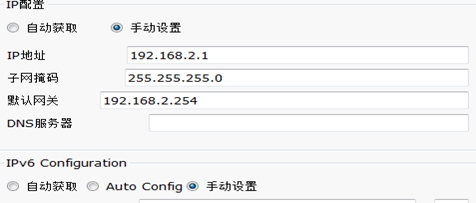
3.配置server服务器地址
二、 配置路由IP地址
1.配置R1端口IP地址,以及默认路由
1) Router#configure terminal
2) Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
3) Router(config-if)#no shutdown
4) Router(config-if)#exit
5) Router(config)#interface f0/1
6) Router(config-if)#ip address 61.159.62.130 255.255.255.248
7) Router(config-if)#no shutdown
8) Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 f0/1
2. 配置R2端口IP地址
1) Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
2) Router(config)#interface f0/0
3) Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.254 255.255.255.0
4) Router(config-if)#no shutdown
5) Router(config)#interface f0/1
6) Router(config-if)#ip address 61.159.62.131 255.255.255.248
7) Router(config-if)#no shutdown
三、静态NAT配置
1. 在R1上将192.168.100.2映射到61.159.62.129,将
192.168.100.3映射到61.159.62.132
1) Router(config)#ip nat inside source static 192.168.100.2 61.159.62.129
2) Router(config)#ip nat inside source static 192.168.100.3 61.159.62.132
2. 在R1上配置NAT内、外端口
3) Router(config)#interface f0/0
4) Router(config-if)#ip nat inside
5) Router(config-if)#exit
6) Router(config)#interface f0/1
7) Router(config-if)#ip nat outside
3.在PC1测试
1) PC>ping 192.168.2.1(服务器IP地址)
2) Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
3) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
4) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
5) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
6) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
7) Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
8) Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
9) Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
10) Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
4. 测试PC2试
1) PC>ping 192.168.2.1(服务器IP地址)
2) Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
3) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
4) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
5) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
6) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
7) Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
8) Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
9) Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
10) Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
5. 在路由上测试
1) Router#show ip nat translations
2) Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
3) --- 61.159.62.129 192.168.100.2 --- ---
4) --- 61.159.62.131 192.168.100.3 --- ---
5) Router#show ip nat translations
6) Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
7) icmp 61.159.62.129:21 192.168.100.2:21 192.168.2.1:21 192.168.2.1:21
8) icmp 61.159.62.129:22 192.168.100.2:22 192.168.2.1:22 192.168.2.1:22
9) icmp 61.159.62.129:23 192.168.100.2:23 192.168.2.1:23 192.168.2.1:23
10) icmp 61.159.62.129:24 192.168.100.2:24 192.168.2.1:24 192.168.2.1:24
11) icmp 61.159.62.131:1 192.168.100.3:1 192.168.2.1:1 192.168.2.1:1
12) icmp 61.159.62.131:2 192.168.100.3:2 192.168.2.1:2 192.168.2.1:2
13) icmp 61.159.62.131:3 192.168.100.3:3 192.168.2.1:3 192.168.2.1:3
14) icmp 61.159.62.131:4 192.168.100.3:4 192.168.2.1:4 192.168.2.1:4
15) icmp 61.159.62.131:5 192.168.100.3:5 192.168.2.1:5 192.168.2.1:5
16) icmp 61.159.62.131:6 192.168.100.3:6 192.168.2.1:6 192.168.2.1:6
17) icmp 61.159.62.131:7 192.168.100.3:7 192.168.2.1:7 192.168.2.1:7
18) --- 61.159.62.129 192.168.100.2 --- ---
19) --- 61.159.62.131 192.168.100.3 --- ---
问题和经验:
IP地址的对应关系是一对一,而且是不变的,借助静态转换,能实现外部网络对内部网络中某些特设定服务器的访问。
四、动态NAT配置
1. 标准访问控制列表移除,其他配置保留
1) no ip nat inside source static 192.168.100.2 61.159.62.129
2) no ip nat inside source static 192.168.100.3 61.159.62.131
2.R1上配置包括内网所有IP地址的ACL
1) Router(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.255
3.置合法的IP地址池
Router(config)#ip nat pool nsd 61.159.62.132 61.159.62.34 netmask 255.255.255.248
4. 关联ACL和合法的IP地址池
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool nsd
5. 在R1上配置NAT内、外端口
1) Router(config)#interface f0/0
2) Router(config-if)#ip nat inside
3) Router(config-if)#exit
4) Router(config)#interface f0/1
5) Router(config-if)#ip nat outside
6. PC1测试
1) PC>ping 192.168.2.1(服务器IP地址)
2) Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
3) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
4) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
5) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
6) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
7) Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
8) Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
9) Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
10) Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
7. PC2测试
1) PC>ping 192.168.2.1(服务器IP地址)
2) Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
3) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
4) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
5) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
6) Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=126
7) Ping statistics for 192.168.2.1:
8) Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
9) Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximu
8. 在路由上测试
1) Router#show ip nat translations
2) Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
3) icmp 61.159.62.129:21 192.168.100.2:21 192.168.2.1:21 192.168.2.1:21
4) icmp 61.159.62.129:22 192.168.100.2:22 192.168.2.1:22 192.168.2.1:22
5) icmp 61.159.62.129:23 192.168.100.2:23 192.168.2.1:23 192.168.2.1:23
6) icmp 61.159.62.129:24 192.168.100.2:24 192.168.2.1:24 192.168.2.1:24
问题和经验:
IP地址的对应关系是不确定的,而是随机的,所有被受权访问互联网的私有地址可随机转换为任何指定的合法的外部IP地址。(内部网络同时访问Internet的主机数少于配置的合法地址集中的IP个数时适用)
五.端口多路复用(PAT)
1.R1上配置包括内网所有IP地址的ACL
Router(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.255
2.ACL和路由器连接互联网的端口
该命令最后加上的overload表示复用。
ip nat inside source list 1 interface f0/1 overload
3. R1上配置NAT内、外端口
1) Router(config)#interface f0/0
2) Router(config-if)#ip nat inside
3) Router(config-if)#exit
4) Router(config)#interface f0/1
5) Router(config-if)#ip nat outside
结构验证:
Router#show ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
icmp 61.159.62.130:25 192.168.100.2:25 192.168.2.1:25 192.168.2.1:25
icmp 61.159.62.130:26 192.168.100.2:26 192.168.2.1:26 192.168.2.1:26
icmp 61.159.62.130:27 192.168.100.2:27 192.168.2.1:27 192.168.2.1:27
icmp 61.159.62.130:28 192.168.100.2:28 192.168.2.1:28 192.168.2.1:28
icmp 61.159.62.130:10 192.168.100.3:10 192.168.2.1:10 192.168.2.1:10
icmp 61.159.62.130:11 192.168.100.3:11 192.168.2.1:11 192.168.2.1:11
icmp 61.159.62.130:12 192.168.100.3:12 192.168.2.1:12 192.168.2.1:12
icmp 61.159.62.130:9 192.168.100.3:9 192.168.2.1:9 192.168.2.1:9
问题和经验:
通过改变外出数据包的源IP地址和源端口并进行端口转换,内部网络的所有主机均可共享一个合法IP地址实现互联网的访问,节约IP。
