首页 > 代码库 > 从零开始部署httpd2.2之四 配置虚拟主机
从零开始部署httpd2.2之四 配置虚拟主机
一、 配置www.aaa.com:
vim/etc/httpd/conf.d/www.aaa.com.conf

ErrorLog"|/usr/sbin/rotatelogs -l /var/logs/httpd/aaa.com-error_%Y%m%d_log86400"
CustomLog"|/usr/sbin/rotatelogs /var/log/httpd/aaa.com-access_log 100M"combined
cp /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf{,.bk} //先备份
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf //配置https



httpd -t //配置后检查一下
service httpd reload //重载配置
测试:

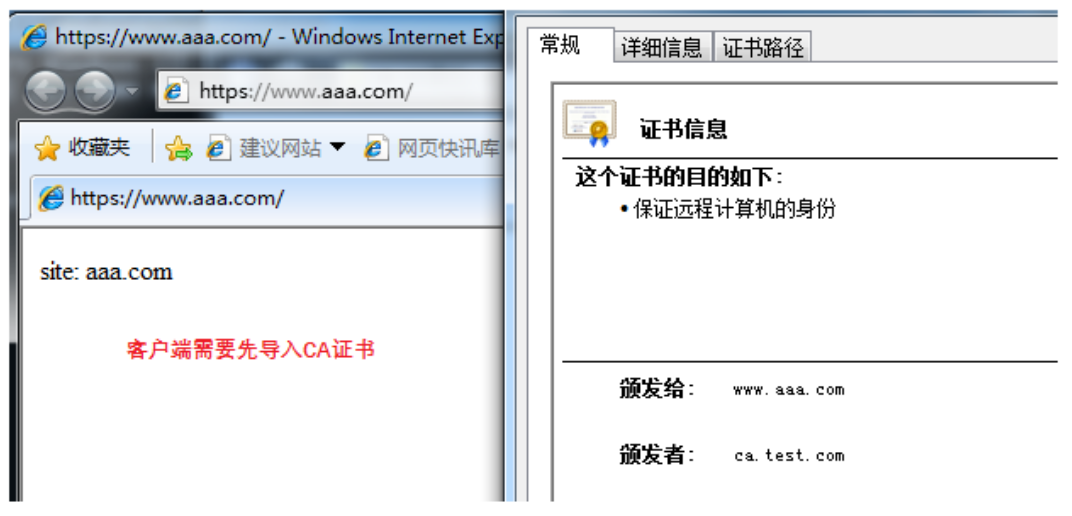
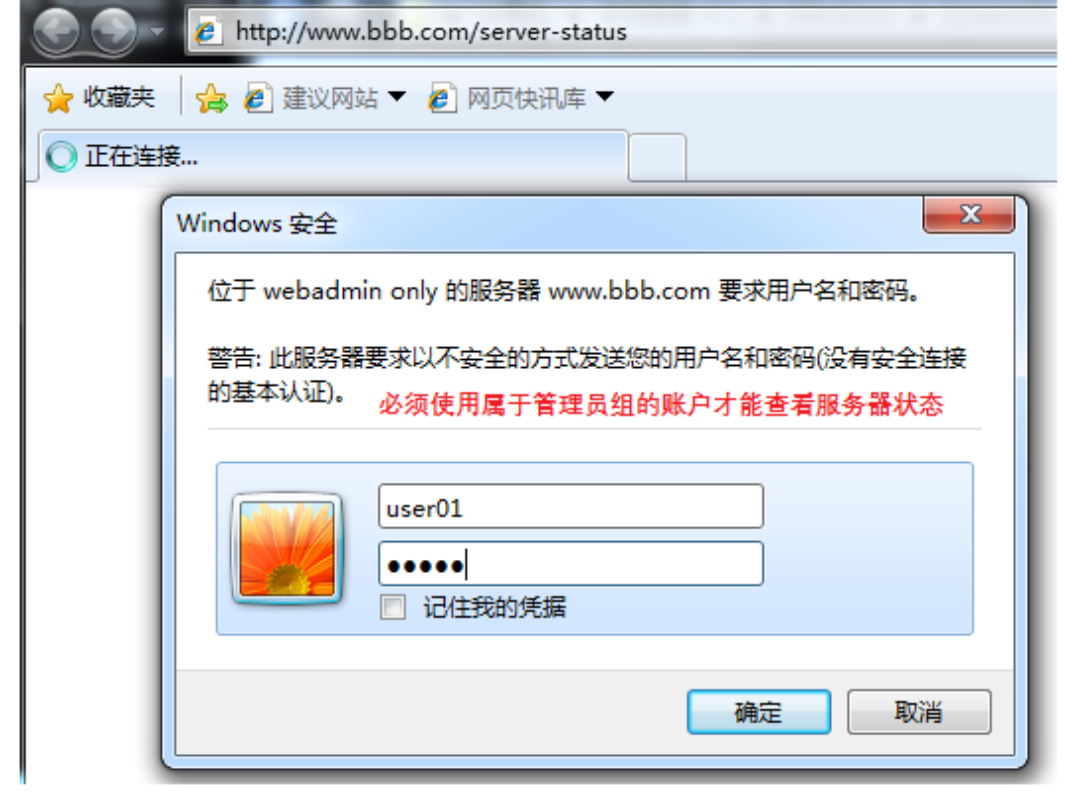
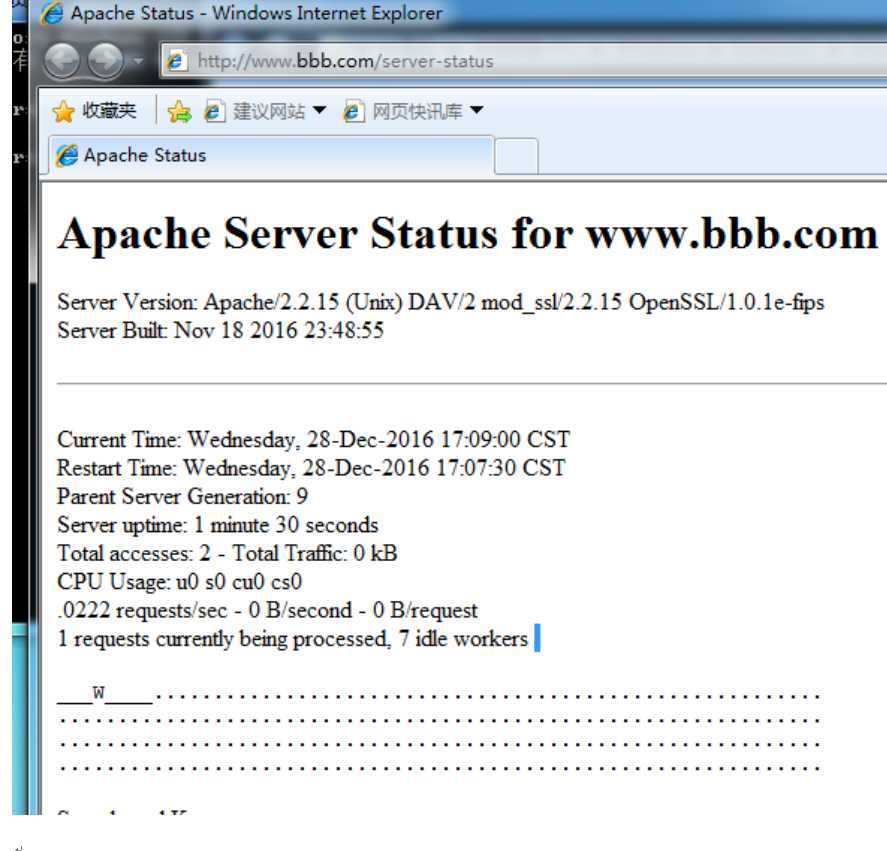
二、配置www.bbb.com:
htpasswd -c -m/etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswd user01
//创建用户密码文件,并创建第一个用户

htpasswd -m/etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswd user02 //创建第二个用户
htpasswd -m/etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswd user03 //创建第三个用户
htpasswd -m /etc/httpd/conf.d/.htpasswduser04 //创建第四个用户
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/.htgroup //编辑组文件
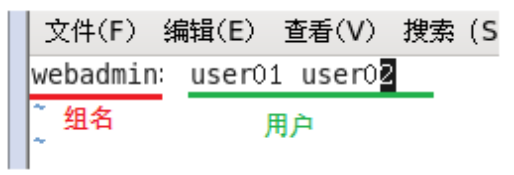
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.bbb.com.conf
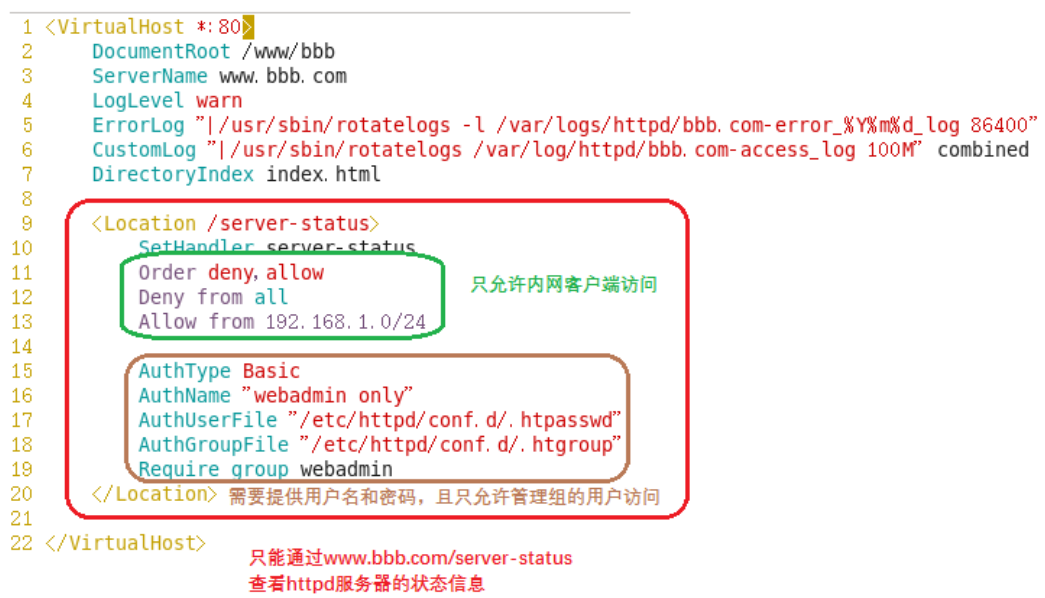

httpd -t //配置后检查一下
service httpd reload //重载配置
测试:
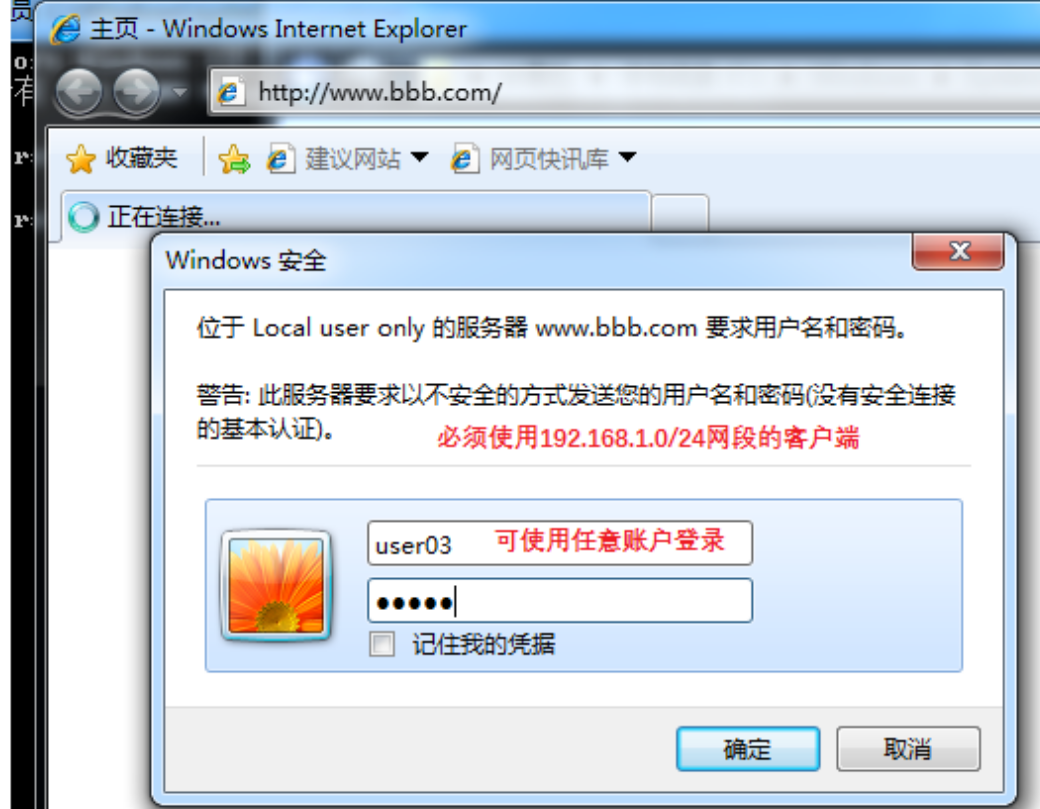
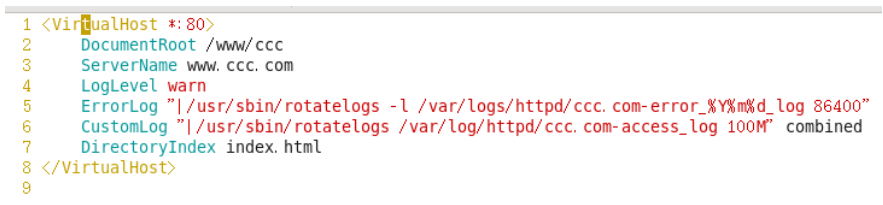
三、配置www.ccc.com:
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/www.ccc.com.conf
httpd -t //配置后检查一下
service httpd reload //重载配置
测试:

附,/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf:
#
#This is the Apache server configuration file providing SSL support.
# Itcontains the configuration directives to instruct the server how to
#serve pages over an https connection. For detailing information about these
#directives see <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_ssl.html>
#
# DoNOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding
#what they do. They‘re here only as hintsor reminders. If you are unsure
#consult the online docs. You have been warned.
#
LoadModulessl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
#
#When we also provide SSL we have to listen to the
# theHTTPS port in addition.
#
Listen443
##
## SSL Global Context
##
## All SSL configuration in this context appliesboth to
## the main server and all SSL-enabled virtualhosts.
##
# Pass Phrase Dialog:
# Configure the pass phrase gathering process.
# The filtering dialog program (`builtin‘ is ainternal
# terminal dialog) has to provide the passphrase on stdout.
SSLPassPhraseDialog builtin
# Inter-Process Session Cache:
# Configure the SSL Session Cache: First themechanism
# to use and second the expiring timeout (inseconds).
SSLSessionCache shmcb:/var/cache/mod_ssl/scache(512000)
SSLSessionCacheTimeout 300
# Semaphore:
# Configure the path to the mutual exclusionsemaphore the
# SSL engine uses internally for inter-processsynchronization.
SSLMutexdefault
# Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG):
# Configure one or more sources to seed thePRNG of the
# SSL library. The seed data should be of goodrandom quality.
# WARNING! On some platforms /dev/randomblocks if not enough entropy
# is available. This means you then cannot usethe /dev/random device
# because it would lead to very longconnection times (as long as
# it requires to make more entropy available).But usually those
# platforms additionally provide a/dev/urandom device which doesn‘t
# block. So, if available, use this oneinstead. Read the mod_ssl User
# Manual for more details.
SSLRandomSeedstartup file:/dev/urandom 256
SSLRandomSeedconnect builtin
#SSLRandomSeedstartup file:/dev/random 512
#SSLRandomSeedconnect file:/dev/random 512
#SSLRandomSeedconnect file:/dev/urandom 512
#
# Use"SSLCryptoDevice" to enable any supported hardware
#accelerators. Use "openssl engine -v" to list supported
#engine names. NOTE: If you enable anaccelerator and the
#server does not start, consult the error logs and ensure
#your accelerator is functioning properly.
#
SSLCryptoDevicebuiltin
#SSLCryptoDeviceubsec
##
##SSL Virtual Host Context
##
<VirtualHost*:443>
DirectoryIndexindex.html
DocumentRoot/www/aaa
ServerNamewww.aaa.com
#General setup for the virtual host, inherited from global configuration
#DocumentRoot"/var/www/html"
#ServerNamewww.example.com:443
# Useseparate log files for the SSL virtual host; note that LogLevel
# isnot inherited from httpd.conf.
ErrorLoglogs/aaa.com-error_log
CustomLoglogs/aaa.com-access_log combined
LogLevelwarn
# SSL Engine Switch:
# Enable/Disable SSL for this virtual host.
SSLEngineon
# SSL Protocol support:
#List the enable protocol levels with which clients will be able to
#connect. Disable SSLv2 access bydefault:
SSLProtocolall -SSLv2
# SSL Cipher Suite:
#List the ciphers that the client is permitted to negotiate.
# Seethe mod_ssl documentation for a complete list.
SSLCipherSuiteDEFAULT:!EXP:!SSLv2:!DES:!IDEA:!SEED:+3DES
# Server Certificate:
#Point SSLCertificateFile at a PEM encoded certificate. If
# thecertificate is encrypted, then you will be prompted for a
#pass phrase. Note that a kill -HUP willprompt again. A new
#certificate can be generated using the genkey(1) command.
SSLCertificateFile/etc/httpd/ssl/www.aaa.com.crt
# Server Private Key:
# If the key is not combined with thecertificate, use this
# directive to point at the key file. Keep in mind that if
# you‘ve both a RSA and a DSA private key youcan configure
# both in parallel (to also allow the use ofDSA ciphers, etc.)
SSLCertificateKeyFile/etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.key
# Server Certificate Chain:
# Point SSLCertificateChainFile at a filecontaining the
# concatenation of PEM encoded CA certificateswhich form the
# certificate chain for the servercertificate. Alternatively
# the referenced file can be the same asSSLCertificateFile
# when the CA certificates are directlyappended to the server
# certificate for convinience.
#SSLCertificateChainFile/etc/pki/tls/certs/server-chain.crt
# Certificate Authority (CA):
# Set the CA certificate verification pathwhere to find CA
# certificates for client authentication oralternatively one
# huge file containing all of them (file mustbe PEM encoded)
#SSLCACertificateFile/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
# Client Authentication (Type):
# Client certificate verification type anddepth. Types are
# none, optional, require and optional_no_ca. Depth is a
# number which specifies how deeply to verifythe certificate
# issuer chain before deciding the certificateis not valid.
#SSLVerifyClientrequire
#SSLVerifyDepth 10
# Access Control:
# With SSLRequire you can do per-directoryaccess control based
# on arbitrary complex boolean expressionscontaining server
# variable checks and other lookupdirectives. The syntax is a
# mixture between C and Perl. See the mod_ssl documentation
# for more details.
#<Location/>
#SSLRequire( %{SSL_CIPHER} !~ m/^(EXP|NULL)/ \
# and %{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_O} eq"Snake Oil, Ltd." \
# and %{SSL_CLIENT_S_DN_OU} in{"Staff", "CA", "Dev"} \
# and %{TIME_WDAY} >= 1 and%{TIME_WDAY} <= 5 \
# and %{TIME_HOUR} >= 8 and%{TIME_HOUR} <= 20 ) \
# or %{REMOTE_ADDR} =~m/^192\.76\.162\.[0-9]+$/
#</Location>
# SSL Engine Options:
# Set various options for the SSL engine.
# o FakeBasicAuth:
# Translate the client X.509 into a BasicAuthorisation. This means that
# the standard Auth/DBMAuth methods can beused for access control. The
# user name is the `one line‘ version of theclient‘s X.509 certificate.
# Note that no password is obtained from theuser. Every entry in the user
# file needs this password: `xxj31ZMTZzkVA‘.
# o ExportCertData:
# This exports two additional environmentvariables: SSL_CLIENT_CERT and
# SSL_SERVER_CERT. These contain thePEM-encoded certificates of the
# server (always existing) and the client(only existing when client
# authentication is used). This can be usedto import the certificates
# into CGI scripts.
# o StdEnvVars:
# This exports the standard SSL/TLS related`SSL_*‘ environment variables.
# Per default this exportation is switchedoff for performance reasons,
# because the extraction step is anexpensive operation and is usually
# useless for serving static content. So oneusually enables the
# exportation for CGI and SSI requests only.
# o StrictRequire:
# This denies access when"SSLRequireSSL" or "SSLRequire" applied even
# under a "Satisfy any" situation,i.e. when it applies access is denied
# and no other module can change it.
# o OptRenegotiate:
# This enables optimized SSL connectionrenegotiation handling when SSL
# directives are used in per-directorycontext.
#SSLOptions+FakeBasicAuth +ExportCertData +StrictRequire
<Files~ "\.(cgi|shtml|phtml|php3?)$">
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</Files>
<Directory"/var/www/cgi-bin">
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</Directory>
# SSL Protocol Adjustments:
# The safe and default but still SSL/TLSstandard compliant shutdown
# approach is that mod_ssl sends the closenotify alert but doesn‘t wait for
# the close notify alert from client. When youneed a different shutdown
# approach you can use one of the followingvariables:
# o ssl-unclean-shutdown:
# This forces an unclean shutdown when theconnection is closed, i.e. no
# SSL close notify alert is send or allowedto received. This violates
# the SSL/TLS standard but is needed forsome brain-dead browsers. Use
# this when you receive I/O errors becauseof the standard approach where
# mod_ssl sends the close notify alert.
# o ssl-accurate-shutdown:
# This forces an accurate shutdown when theconnection is closed, i.e. a
# SSL close notify alert is send and mod_sslwaits for the close notify
# alert of the client. This is 100% SSL/TLSstandard compliant, but in
# practice often causes hanging connectionswith brain-dead browsers. Use
# this only for browsers where you know thattheir SSL implementation
# works correctly.
# Notice: Most problems of broken clients arealso related to the HTTP
# keep-alive facility, so you usuallyadditionally want to disable
# keep-alive for those clients, too. Usevariable "nokeepalive" for this.
# Similarly, one has to force some clients touse HTTP/1.0 to workaround
# their broken HTTP/1.1 implementation. Usevariables "downgrade-1.0" and
# "force-response-1.0" for this.
SetEnvIfUser-Agent ".*MSIE.*" \
nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown \
downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0
# Per-Server Logging:
# The home of a custom SSL log file. Use thiswhen you want a
# compact non-error SSL logfile on a virtualhost basis.
</VirtualHost>
从零开始部署httpd2.2之四 配置虚拟主机
