首页 > 代码库 > 源码编译安装LNMP架构环境
源码编译安装LNMP架构环境
源码编译安装LNMP架构环境
OS版本:2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64
Nginx版本:nginx-1.6.1
mariadb版本:mariadb-10.0.13
php版本:php-5.4.26
1、安装编译安装所需系统环境
~]# yum groupinstall "Development Tools" "Server Platform Development" -y
2、编译安装nginx-1.6.1
# yum -y install pcre-devel openssl-devel zlib-devel
# tar -xf nginx-1.6.1.tar.gz
# cd nginx-1.6.1
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --user=nginx --group=nginx --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-debug
# make && make install
账号添加,否则开启会报错(nginx: [emerg] getpwnam("nginx") failed)
~]# useradd -r -M nginx
~]# id nginx
uid=498(nginx) gid=498(nginx) 组=498(nginx)
修改配置文件中servername从localhost修改为ip地址启动nginx测试
~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
~]# ss -tnlp | grep nginx
LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* users:(("n ginx",3939,6),("nginx",3940,6))
编写一个nginx启动脚本
~]# vim /etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/sh
#
# nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse \
# proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server
# processname: nginx
# config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx
# pidfile: /var/run/nginx/nginx.pid
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
nginx="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(basename $nginx)
sysconfig="/etc/sysconfig/$prog"
lockfile="/var/lock/nginx.lock"
pidfile="/var/run/nginx/${prog}.pid"
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
[ -f $sysconfig ] && . $sysconfig
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] || exit 5
[ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
return $retval
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc -p $pidfile $prog
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
configtest_q || return 6
stop
start
}
reload() {
configtest_q || return 6
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc -p $pidfile $prog -HUP
echo
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
configtest_q() {
$nginx -t -q -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
# Upgrade the binary with no downtime.
upgrade() {
local oldbin_pidfile="${pidfile}.oldbin"
configtest_q || return 6
echo -n $"Upgrading $prog: "
killproc -p $pidfile $prog -USR2
retval=$?
sleep 1
if [[ -f ${oldbin_pidfile} && -f ${pidfile} ]]; then
killproc -p $oldbin_pidfile $prog -QUIT
success $"$prog online upgrade"
echo
return 0
else
failure $"$prog online upgrade"
echo
return 1
fi
}
# Tell nginx to reopen logs
reopen_logs() {
configtest_q || return 6
echo -n $"Reopening $prog logs: "
killproc -p $pidfile $prog -USR1
retval=$?
echo
return $retval
}
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0
$1
;;
restart|configtest|reopen_logs)
$1
;;
force-reload|upgrade)
rh_status_q || exit 7
upgrade
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7
$1
;;
status|status_q)
rh_$1
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 7
restart
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|reload|configtest|status|force-reload|upgrade|restart|reopen_logs}" exit 2
esac
~]# service nginx start
正在启动 nginx: [确定]
~]# service nginx status
nginx (pid 1171 1169) 正在运行...
设置开机启动
~]# chkconfig --add nginx
~]# chkconfig --list nginx
nginx 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:关闭 3:关闭 4:关闭 5:关闭 6:关闭
~]# chkconfig nginx on
~]# chkconfig --list nginx
nginx 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
3、mariadb编译安装
首先安装mariadb编译安装所需的cmake、ncurses-devel
~]# yum -y install cmake ncurses-devel
(1)创建数据存放目录
~]# mkdir -pv /data/mydata
mkdir: 已创建目录 "/data"
mkdir: 已创建目录 "/data/mydata"
(2)创建mysql用户,并授予数据文件mysql账户权限
~]# groupadd mysql
~]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin -g mysql -M mysql
~]# id mysql
uid=500(mysql) gid=500(mysql) 组=500(mysql)
~]# chown -R mysql.mysql /data/mydata
(3)安装mariadb
解压mariadb
~]# tar -xf mariadb-10.0.13.tar.gz
编译安装mariadb
mariadb-10.0.13]# cmake . -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql -DMYSQL_DATADIR=/data/mydata -DSYSCONFDIR=/etc -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_ARCHIVE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_BLACKHOLE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1 -DWITH_READLINE=1 -DWITH_SSL=system -DWITH_ZLIB=system -DWITH_LIBWRAP=0 -DMYSQL_UNIX_ADDR=/tmp/mysql.sock -DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8 -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8_general_ci
mariadb-10.0.13]# make -j 4 && make install
(4)配置mariadb
初始化数据库
~]# cd /usr/local/mysql/
mysql]# scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --datadir=/data/mydata
mysql]# ls /data/mydata/
aria_log.00000001 ibdata1 ib_logfile1 performance_schema
aria_log_control ib_logfile0 mysql test
设置配置文件,修改datadir指定目录项和socket所指定文件
[mysqld]
datadir=/data/mydata
socket=/tmp/mysql.sock
user=mysql
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
symbolic-links=0
[mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
设置启动脚本
mysql]# cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld
mysql]# chkconfig --add mysqld
mysql]# chkconfig --list mysqld
启动并查看服务
mysql]# service mysqld start
Starting MySQL. SUCCESS!
~]# ss -tnlp | grep 3306
LISTEN 0 128 :::3306 :::* users:(("mysqld",65174,
16))
设置环境变量
~]# vim /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
export PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH
~]# source /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh
导出头文件
~]# ln -sv /usr/local/mysql/include/ /usr/local/include/mysql
"/usr/local/include/mysql" -> "/usr/local/mysql/include/"
导出库文件
mysql]# vim /etc/ld.so.conf.d/mysql.conf
/usr/local/mysql/lib
mysql]# ldconfig -v
mysql]# ldconfig -p |grep mysql
libmysqlclient_r.so.16 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/lib64/mysql/libmysqlclient_r.so.16
libmysqlclient.so.18 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/mysql/lib/libmysqlclient.so.18
libmysqlclient.so.16 (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/lib64/mysql/libmysqlclient.so.16
libmysqlclient.so (libc6,x86-64) => /usr/local/mysql/lib/libmysqlclient.so
使用mysql_secure_installation脚本来进行安全配置
[root@localhost mysql]# mysql_secure_installation
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_secure_installation: line 379: find_mysql_client: command not fou
nd
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we‘ll need the current
password for the root user. If you‘ve just installed MariaDB, and
you haven‘t set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n]
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from ‘localhost‘. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named ‘test‘ that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you‘ve completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
4、编译安装php
编译安装前安装所需要包
~]# yum -y install libxml2-devel
安装bzip2-devel
php-5.4.26]# yum -y install bzip2-devel
~]# wget ftp://mcrypt.hellug.gr/pub/crypto/mcrypt/libmcrypt/libmcrypt-2.5.7.tar.gz
~]# tar -xf libmcrypt-2.5.7.tar.gz
~]# cd libmcrypt-2.5.7
libmcrypt-2.5.7]# ./configure
libmcrypt-2.5.7]# make && make install
解压并进行编译安装,nginx是通过php-fpm连接php的,编译时需添加--enable-fpm
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php5 --with-mysql=mysqlnd --with-openssl --with-mysqli=mysqlnd --enable-mbstring --with-freetype-dir --with-jpeg-dir --with-png-dir --with-zlib --with-libxml-dir=/usr --enable-xml --enable-sockets --enable-fpm --with-mcrypt --with-config-file-path=/etc --with-config-file-scan-dir=/etc/php.d --with-bz2
再次编译没有问题,进行安装
php-5.4.26]# make -j 4 && make install
拷贝配置文件至/etc目录
php-5.4.26]# cp php.ini-production /etc/php.ini
拷贝php-fpm配置文件,并同时取消pid选项的注释
cp /usr/local/php5/etc/php-fpm.conf.default /usr/local/php5/etc/php-fpm.conf
php-5.4.26]# vim /usr/local/php5/etc/php-fpm.conf
pid = /usr/local/php5/var/run/php-fpm.pid
添加服务脚本
fpm]# pwd
/root/php-5.4.26/sapi/fpm
fpm]# cp init.d.php-fpm /etc/rc.d/init.d/php-fpm
~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/php-fpm
~]# chkconfig --add php-fpm
启动php-fpm
~]# service php-fpm start
~]# ps aux | grep fpm
root 14881 0.0 0.3 68920 3928 ? Ss 09:51 0:00 php-fpm: master process (/usr/local/php5/etc/php-fpm.conf) nobody 14882 0.0 0.3 68920 3460 ? S 09:51 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
nobody 14883 0.0 0.3 68920 3460 ? S 09:51 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
root 14885 0.0 0.0 103260 872 pts/1 S+ 09:51 0:00 grep f
5、修改nginx.conf文件,支持php
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm index.php; 添加支持index.php
}
location ~ \.php$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf; 这边要注意的是直接include fastcgi.conf即可,老版本的使用方法是fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;再include。参考http://gxl-ct001.iteye.com/blog/2270522
}
修改完成后重启nginx
service nginx restart
停止 nginx: [确定]
正在启动 nginx: [确定]
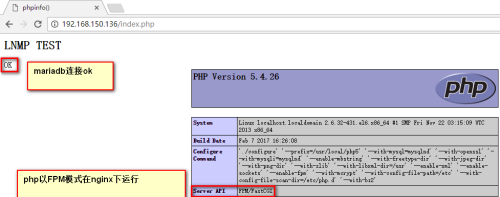
6、编写测试页进行测试
vim /usr/local/nginx/html/index.php
<h1>LNMP TEST</h1>
<?php
$conn = mysql_connect(‘localhost‘,‘root‘,‘oracleadmin‘); 测试连接mariadb是否ok
if ($conn)
echo "OK";
else
echo "Failure";
phpinfo(); 测试nginx使用php是否ok
?>
本文出自 “Open World” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://voidyao000.blog.51cto.com/12458042/1896064
源码编译安装LNMP架构环境