首页 > 代码库 > android XML布局和子View按比例布局
android XML布局和子View按比例布局
首先按照程序的目录结构大致分析:
res/layout/ 这个目录存放的就是布局用的xml文件,一般默认为main.xml
res/values/ 这个目录存放的是一堆常量的xml文件
res/drawable/ 存放的是一些图片什么的,当然图标也在这里
下面主要对layout下的xml文件做个介绍,顺便也把布局的方法总结一下:
·文件的开头
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
这是在说明xml版本及字符编码
·紧接着到了关键的部分:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/ android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</LinearLayout>
其中开头的"LinearLayout"是布局的方式,可以有很多种,最常用的应该就是Linear了,其他的布局方法等下在后面总结。
接着android:layout_width(height)="wrap_content"是在设置这部分布局的宽高,也可以是绝对值,当然设置为绝对值时要标上单位。
·在<LinearLayout ...>和</LinearLayout>就之间可以添加控件了,比如要添加一个名字为btn的Button控件,并且Button上显示的文字是"Test!",可以这样写:
<Button id="@+id/btn"
android:text="Test!"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
开头id后面的就是控件名称,在用于添加事件Listener时会用到,而下几行的android:xxx就是设置控件的属性了,这些属性在Android的文档中都有,不需要特别去记,一般现查就可以了。
·有一点要说明的是,布局方法可以嵌套,有点像java中的Container,可以非常方便的把界面“堆”出来。
布局方式的简单说明:
查了Android文档发现布局确实很多,只列出两个我自己认为较常用的:
·LinearLayout线性的布局方式,要么上下,要么左右的添加控件,很常用;
·GridView中文翻译过来是网格布局,控件按照顺序依次填到每个格子里就好了,出来的界面会很整齐,较常用;
具体的几个布局如下:
@ <1> LinearLayout(线性布局)提供了控件水平垂直排列的模型,同时可以通过设置子控件的weight布局参数控制各个控件在布局中的相对大小。水平(vertical)垂直(horizontal)
fill-parent:占满整个屏幕,wrap-content:刚好适合控件内容的大小
对齐方式gravity取值:
top:不改变大小,位置置于容器的顶部
bottom:不改变大小,位置置于容器的底部
left:不改变大小,位置置于容器的左边
right:不改变大小,位置置于容器的右边
center_vertical:不改变大小,位置置于容器的纵向中央部分
center_horizontal:不改变大小,位置置于容器的横向中央部分
center:不改变大小,位置置于容器的横向和纵向的中央部分
fill_vertical:可能的话,纵向延伸可以填满容器
fiil_horizontal:可能的话,横向延伸可以填满容器
fiil:可能的话,纵向和横向延伸填满容器
@<2> AbsoluteLayout(坐标布局)可以让子元素指定准确的x/y坐标值,并显示在屏幕上。(0, 0)为左上角,当向下或向右移动时,坐标值将变大。AbsoluteLayout没有页边框,允许元素之间互相重叠(尽管不推荐)。我们通常不推荐使用AbsoluteLayout,除非你有正当理由要使用它,因为它使界面代码太过刚性,以至于在不同的设备上可能不能很好地工作。
Android:layout_x/layout_y=”56px”确定控件位置
@<3> RelativeLayout(相对布局)允许子元素指定他们相对于其它元素或父元素的位置(通过ID指定)。因此,你可以以右对齐,或上下,或置于屏幕中央的形式来排列两个元素。元素按顺序排列,因此如果第一个元素在屏幕的中央,那么相对于这个元素的其它元素将以屏幕中央的相对位置来排列。如果使用XML来指定这个layout,在你定义它之前,被关联的元素必须定义。
Android:layout_centerInparent, 将当前控件放置于起父控件的横向和纵向的中央部分 Android:layout_centerHorizontal, 使当前控件置于父控件横向的中央部分
Android:layout_centerVertival, 使当前控件置于父控件纵向的中央部分
Android:layout_alignParentLeft, 使当前控件的左端和父控件左端对齐
Android:layout_alignParentRight, 使当前控件的右端和父控件右端对齐
Android:layout_alignParentTop, 使当前控件的顶端和父控件顶端对齐
Android:layout_alignParentBottom,使当前控件的底端和父控件底端对齐
上述属性只能设置Bool类型的值,“true”或“false”
Android:layout_below/layout_above/ layout_toLeftOf/ layout_toRightOf =“@id/”使当前控件置于给出id的空间的下方/上方/左边/右边
Android:layout_marginBottom/layout_marginLeft/layo ut_marginRight/layout_marginTop=”30px”使当前控件底部/左边/右边/顶部空出相应像素空间
@<4> FrameLayout(单帧布局)是最简单的一个布局对象。它被定制为你屏幕上的一个空白备用区域,之后你可以在其中填充一个单一对象— 比如,一张你要发布的图片。所有的子元素将会固定在屏幕的左上角;你不能为FrameLayout中的一个子元素指定一个位置。后一个子元素将会直接在前一个子元素之上进行覆盖填充,把它们部份或全部挡住(除非后一个子元素是透明的)。
Android:src=http://blog.soso.com/qz.q/”@drawable/”属性指定所需图片的文件位置,用ImageView显示图片时,也应当用android:src指定要显示的图片
@<5> TableLayout(表格布局)以行列的形式管理子控件,每一行为一个TableRow的对象,TableRow也可以添加子控件
android:collapseColumns=“n”隐藏TableLayout里面的TableRow的列n
android:stretchColumns=“n” 设置列n为可延伸的列
android:shrinkColumns=“n” 设置列n为可收缩的列
Android:src=http://blog.soso.com/qz.q/”@drawable/”属性指定所需图片的文件位置,用ImageView显示图片时,也应当用android:src指定要显示的图片
--------------前一部分为复制粘贴他人--------------------
在android线性布局中要实现其子控件按一定比例排列 需要用到weight属性:
??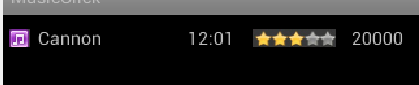
图片中 是3个TextView加一个ImageView 其中比例是2:1:1:1
第一个TextView占用了总宽度的2/5余下的占用了1/5,当TextView中的内容过多,并且高度设置为:wrap_content时将会分多行显示,而设置为fill_parent时,则有部分字被隐藏。
要实现此布局:是在所有View都包含在LinearLayout中,并且要将layaout_width设置为fill_parent,oriantatioan设置为horizontal,其子View的layout_width都设置为0dip,让后设置按所占比例设置weight值。
代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll_listview"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="10dip"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:gravity="center"
>
<TextView android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text=" Cannon"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/music_icon"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:gravity="left"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/time"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="12:01"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<ImageView android:id="@+id/difficult"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src=http://www.mamicode.com/"@drawable/five_star"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/record"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="20000"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
</LinearLayout>
如果需要设置为垂直方向按比例分配,则改动相应的Height为Odip。
首先按照程序的目录结构大致分析:
res/layout/ 这个目录存放的就是布局用的xml文件,一般默认为main.xml
res/values/ 这个目录存放的是一堆常量的xml文件
res/drawable/ 存放的是一些图片什么的,当然图标也在这里
下面主要对layout下的xml文件做个介绍,顺便也把布局的方法总结一下:
·文件的开头
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
这是在说明xml版本及字符编码
·紧接着到了关键的部分:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/ android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</LinearLayout>
其中开头的"LinearLayout"是布局的方式,可以有很多种,最常用的应该就是Linear了,其他的布局方法等下在后面总结。
接着android:layout_width(height)="wrap_content"是在设置这部分布局的宽高,也可以是绝对值,当然设置为绝对值时要标上单位。
·在<LinearLayout ...>和</LinearLayout>就之间可以添加控件了,比如要添加一个名字为btn的Button控件,并且Button上显示的文字是"Test!",可以这样写:
<Button id="@+id/btn"
android:text="Test!"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
开头id后面的就是控件名称,在用于添加事件Listener时会用到,而下几行的android:xxx就是设置控件的属性了,这些属性在Android的文档中都有,不需要特别去记,一般现查就可以了。
·有一点要说明的是,布局方法可以嵌套,有点像java中的Container,可以非常方便的把界面“堆”出来。
布局方式的简单说明:
查了Android文档发现布局确实很多,只列出两个我自己认为较常用的:
·LinearLayout线性的布局方式,要么上下,要么左右的添加控件,很常用;
·GridView中文翻译过来是网格布局,控件按照顺序依次填到每个格子里就好了,出来的界面会很整齐,较常用;
具体的几个布局如下:
@ <1> LinearLayout(线性布局)提供了控件水平垂直排列的模型,同时可以通过设置子控件的weight布局参数控制各个控件在布局中的相对大小。水平(vertical)垂直(horizontal)
fill-parent:占满整个屏幕,wrap-content:刚好适合控件内容的大小
对齐方式gravity取值:
top:不改变大小,位置置于容器的顶部
bottom:不改变大小,位置置于容器的底部
left:不改变大小,位置置于容器的左边
right:不改变大小,位置置于容器的右边
center_vertical:不改变大小,位置置于容器的纵向中央部分
center_horizontal:不改变大小,位置置于容器的横向中央部分
center:不改变大小,位置置于容器的横向和纵向的中央部分
fill_vertical:可能的话,纵向延伸可以填满容器
fiil_horizontal:可能的话,横向延伸可以填满容器
fiil:可能的话,纵向和横向延伸填满容器
@<2> AbsoluteLayout(坐标布局)可以让子元素指定准确的x/y坐标值,并显示在屏幕上。(0, 0)为左上角,当向下或向右移动时,坐标值将变大。AbsoluteLayout没有页边框,允许元素之间互相重叠(尽管不推荐)。我们通常不推荐使用AbsoluteLayout,除非你有正当理由要使用它,因为它使界面代码太过刚性,以至于在不同的设备上可能不能很好地工作。
Android:layout_x/layout_y=”56px”确定控件位置
@<3> RelativeLayout(相对布局)允许子元素指定他们相对于其它元素或父元素的位置(通过ID指定)。因此,你可以以右对齐,或上下,或置于屏幕中央的形式来排列两个元素。元素按顺序排列,因此如果第一个元素在屏幕的中央,那么相对于这个元素的其它元素将以屏幕中央的相对位置来排列。如果使用XML来指定这个layout,在你定义它之前,被关联的元素必须定义。
Android:layout_centerInparent, 将当前控件放置于起父控件的横向和纵向的中央部分 Android:layout_centerHorizontal, 使当前控件置于父控件横向的中央部分
Android:layout_centerVertival, 使当前控件置于父控件纵向的中央部分
Android:layout_alignParentLeft, 使当前控件的左端和父控件左端对齐
Android:layout_alignParentRight, 使当前控件的右端和父控件右端对齐
Android:layout_alignParentTop, 使当前控件的顶端和父控件顶端对齐
Android:layout_alignParentBottom,使当前控件的底端和父控件底端对齐
上述属性只能设置Bool类型的值,“true”或“false”
Android:layout_below/layout_above/ layout_toLeftOf/ layout_toRightOf =“@id/”使当前控件置于给出id的空间的下方/上方/左边/右边
Android:layout_marginBottom/layout_marginLeft/layo ut_marginRight/layout_marginTop=”30px”使当前控件底部/左边/右边/顶部空出相应像素空间
@<4> FrameLayout(单帧布局)是最简单的一个布局对象。它被定制为你屏幕上的一个空白备用区域,之后你可以在其中填充一个单一对象— 比如,一张你要发布的图片。所有的子元素将会固定在屏幕的左上角;你不能为FrameLayout中的一个子元素指定一个位置。后一个子元素将会直接在前一个子元素之上进行覆盖填充,把它们部份或全部挡住(除非后一个子元素是透明的)。
Android:src=http://blog.soso.com/qz.q/”@drawable/”属性指定所需图片的文件位置,用ImageView显示图片时,也应当用android:src指定要显示的图片
@<5> TableLayout(表格布局)以行列的形式管理子控件,每一行为一个TableRow的对象,TableRow也可以添加子控件
android:collapseColumns=“n”隐藏TableLayout里面的TableRow的列n
android:stretchColumns=“n” 设置列n为可延伸的列
android:shrinkColumns=“n” 设置列n为可收缩的列
Android:src=http://blog.soso.com/qz.q/”@drawable/”属性指定所需图片的文件位置,用ImageView显示图片时,也应当用android:src指定要显示的图片
--------------前一部分为复制粘贴他人--------------------
在android线性布局中要实现其子控件按一定比例排列 需要用到weight属性:
??
图片中 是3个TextView加一个ImageView 其中比例是2:1:1:1
第一个TextView占用了总宽度的2/5余下的占用了1/5,当TextView中的内容过多,并且高度设置为:wrap_content时将会分多行显示,而设置为fill_parent时,则有部分字被隐藏。
要实现此布局:是在所有View都包含在LinearLayout中,并且要将layaout_width设置为fill_parent,oriantatioan设置为horizontal,其子View的layout_width都设置为0dip,让后设置按所占比例设置weight值。
代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll_listview"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingTop="10dip"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:gravity="center"
>
<TextView android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text=" Cannon"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/music_icon"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:gravity="left"
android:paddingLeft="5dip"
/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/time"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="12:01"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<ImageView android:id="@+id/difficult"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src=http://www.mamicode.com/"@drawable/five_star"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/record"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="20000"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
/>
</LinearLayout>
如果需要设置为垂直方向按比例分配,则改动相应的Height为Odip。
android XML布局和子View按比例布局
