首页 > 代码库 > Nginx基础应用--------基于CentOS6源码安装
Nginx基础应用--------基于CentOS6源码安装
1. 背景
介绍:
Nginx是一款高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,能够选择高效的epoll(linux2.6内核)、kqueue(freebsd)、eventport(solaris10)作为网络I/O模型,能够支持高达50000个并发连接数的响应,而内存、CPU等系统资源消耗却非常低、运行非常稳定。
选择的理由:
* 支持高并发连接:nginx使用高效的多路复用模型(epoll/linux, kqueue/freebsd, eventport/solaris)
* 内存消耗少:在服务器3W并发连接下,开启10个Nginx进程消耗150MB内存(15MB*10)
* 成本低廉:购买F5 BIG-IP、NetScaler等负载均衡交换机需要几十万RMB,而开源Nginx替代这些商业设备。
* 其他理由:网络配置简单;支持rewrite重写规则,能够根据域名、URL的不同、将HTTP请求分到不同的后端服务器群组;内置的健康检查功能;节省带宽,支持GZIP压缩,可以添加浏览器本地缓存的Header头;支持热部署,能够在不间断服务的情况下、对软件版本进行升级
应用范围:
* Web服务: 设置多虚拟主机的服务并配合fast-cgi或tomcat支持动态网页
Nginx是近年来比较火的一个www服务的软件,与Apache和lighttpd以及tomcat等功能类似,但是nginx要比前者有着卓越的性能,比如:采用了epoll模型,内存消耗小等优点;
* 反向代理, 多虚拟主机的代理:
指以代理服务器来接受Internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给Internet上请求连接的客户端;
* 七层的负载均衡: 单多虚拟主机不同服务器之间的访问;
负载均衡是由多台服务器以对称的方式组成一个服务器集合,每台都是等价地位,通过某种负载分担技术,将外部发送来的请求均匀分配到对称结构中某一台服务器上,来接收到请求的服务器独立地回应客户的请求;
* 正向代理: 代理上网
代理内部网络对Internet的链接请求,客户机必须指定代理服务器,并将本来要直接发送到web服务器上的http请求发送到代理服务器中,由代理服务器请求并返回响应内容;
* 缓存服务
为proxy和fastcgi做缓存服务,提高访问速度,相当于squid功能;
2. 环境
[root@nginx ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.8 (Final) [root@nginx ~]# uname -r 2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64
3. 安装
* 临时关闭selinux(可选)
[root@nginx ~]# setenforce 0
* 关闭iptables(可选)
[root@nginx ~]# service iptables stop
* 创建www用户
[root@nginx ~]# useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin -M www
* 安装pcre库依赖
[root@nginx ~]# yum install pcre pcre-devel -y
* 安装ssl库依赖
[root@nginx ~]# yum install openssl openssl-devel -y
* 进入下载目录
cd /usr/local/src
* 下载nginx源码包
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.11.10.tar.gz
* 解压nginx源码包
tar zxvf nginx-1.11.10.tar.gz
* 进入nginx包目录
cd nginx-1.11.10
* 指定安装目录、用户、模块
[root@nginx ~]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.11.10 --user=www --group=www --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module
* 编译并安装
[root@nginx ~]# make && make install
* 做nginx软链接
[root@nginx ~]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.11.10 /usr/local/nginx
4. 创建启动脚本
* /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/sh
#
# nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: NGINX is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse # proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server
# processname: nginx
# config: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx
# pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
nginx="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(basename $nginx)
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
[ -f /etc/sysconfig/nginx ] && . /etc/sysconfig/nginx
lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx
make_dirs() {
# make required directories
user=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep "configure arguments:" | sed ‘s/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g‘ -`
if [ -z "`grep $user /etc/passwd`" ]; then
useradd -M -s /bin/nologin $user
fi
options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep ‘configure arguments:‘`
for opt in $options; do
if [ `echo $opt | grep ‘.*-temp-path‘` ]; then
value=http://www.mamicode.com/`echo $opt | cut -d "=" -f 2`
if [ ! -d "$value" ]; then
# echo "creating" $value
mkdir -p $value && chown -R $user $value
fi
fi
done
}
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] || exit 5 [ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6
make_dirs echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
return $retval
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc $prog -QUIT retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
configtest || return $?
stop
sleep 1
start
}
reload() {
configtest || return $?
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc $nginx -HUP RETVAL=$?
echo
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0 $1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0 $1
;;
restart|configtest)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7 $1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload ;;
status)
rh_status ;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 0 ;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}"
exit 2
esac* 改变nginx脚本文件权限
[root@nginx ~]# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/nginx
* 添加进service管理服务并设置开机启动
[root@nginx ~]# chkconfig --add nginx [root@nginx ~]# chkconfig nginx on
5. 服务启动测试
[root@nginx ~]# service nginx start
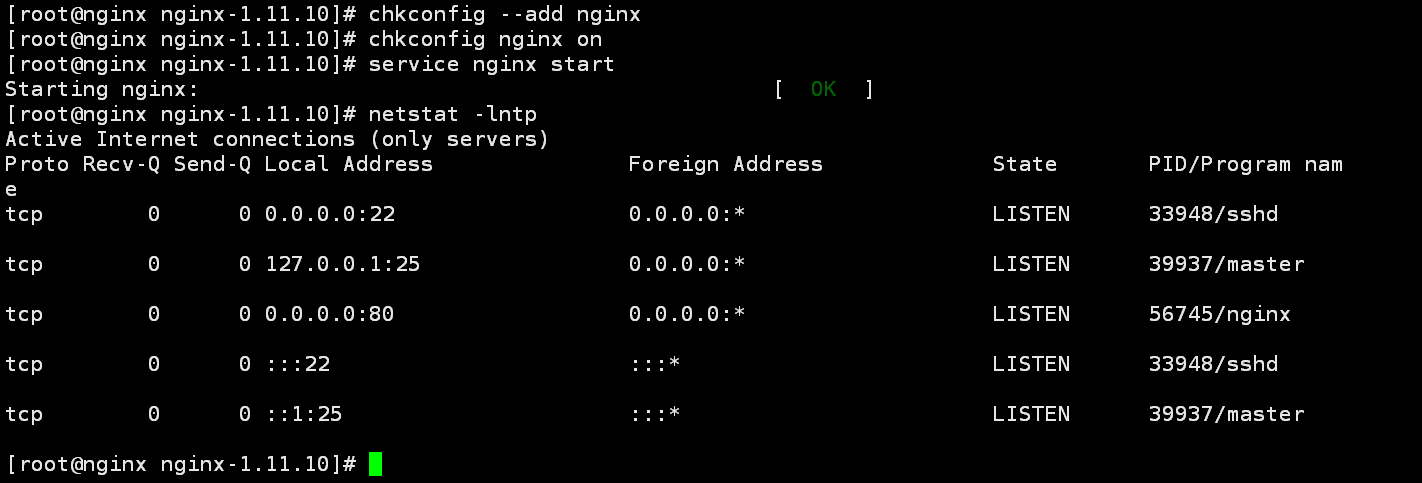
可以看到80默认的80端口nginx已经开始监听
6. 访问测试
* 通过浏览器测试, 此nginx宿主机ip为192.168.222.128
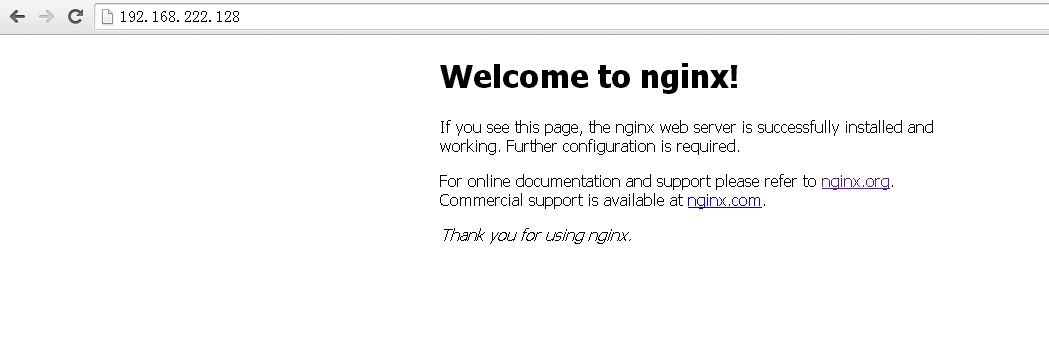
访问成功,nginx已经成功返回页面
7. 总结
以需求驱动技术,技术本身没有优略之分,只有业务之分。
本文出自 “sea” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://lisea.blog.51cto.com/5491873/1907590
Nginx基础应用--------基于CentOS6源码安装
