首页 > 代码库 > nagios安装部署
nagios安装部署
安装说明:
系统:
[root@1-138 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
nagios主机安装:
nagios-cn nagios-plugins
被监控linux主机安装
nrpe和nagios-plugins
修改nagios监控主机的语言编码为UTF8:
vi /etc/sysconfig/i18n
LANG="zh_CN.UTF8"
nagios监控主机安装操作过程中ssh工具也要为UTF8
安装路径:/usr/local/nagios
1. 准备软件包
1)基础包安装
安装基础软件包,确保后面安装不报错,键入命令:
wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
rpm -Uvh epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
yum -y install httpd openssl-devel gcc glibc glibc-commongd gd-devel php-gd rrdtool-perl rrdtool rrdtool-devel rrdtool-ruby php
2)下载程序包
中文Nagios下载
http://sourceforge.net/projects/nagios-cn/(此处选择中文安装)
Nagios插件包
http://www.nagios.org/download/
nagios-plugins-2.1.1.tar.gz
Nagiso监控服务器上安装操作过程
1)建立一个帐号
创建一个名为nagios的帐号并给定登录口令
useradd nagios
passwd nagios
创建一个用户组名为nagcmd用于从Web接口执行外部命令。将nagios用户和apache用户都加到这个组中。
groupadd nagcmd
usermod -G nagcmd nagios
usermod -G nagcmd apache
2)编译与安装Nagios
tar xvpf nagios-cn-3.2.3.tar
cd nagios-cn-3.2.3
运行Nagios配置脚本并使用先前开设的用户及用户组:
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --with-nagios-user=nagios--with-nagios-group=nagios --with-command-group=nagcmd
编译Nagios程序包源码
make all
安装二进制运行程序、初始化脚本、配置文件样本并设置运行目录权限
make install
make install-init
make install-config
make install-commandmode
不要现在执行nagios,下面还有一些需要配置。
定制配置
样式配置文件已经安装在/usr/local/nagios/etc目录,修改联系人为下一步中的管理员并更改email地址。
#vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
3)配置WEB接口
安装Nagios的WEB配置文件到Apache的conf.d目录下
make install-webconf
[root@1-138 nagios-cn-3.2.3]# make install-webconf
/usr/bin/install -c -m 644 sample-config/httpd.conf/etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf
*** Nagios/Apache conf file installed ***
创建一个nagiosadmin的用户用于Nagios的WEB接口登录。记下你所设置的登录口令。之后登录用到。
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users admin
重启Apache服务以使设置生效。
service httpd restart
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/cgi.cfg
修改所有nagiosadmin为admin
:0,$s/nagiosadmin/admin/g
:g/nagiosadmin/s//admin/g
4)编译并安装Nagios插件
tar xzf nagios-plugins-1.4.15.tar.gz
cd nagios-plugins-1.4.15
编译并安装插件
./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios--with-nagios-group=nagios
make
make install
5)启动Nagios
把Nagios加入到服务列表中以使之在系统启动时自动启动
chkconfig --add nagios
chkconfig nagios on
chkconfig httpd on
service httpd restart
验证Nagios的样例配置文件
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v/usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
出现如下提示表示正确
Total Warnings: 0
Total Errors: 0
这个命令后面经常会用到,但这么长的命令很难输入也难记,因此我将其添加为别名,方法如下:
#vi /etc/bashrc
最最后添加如下一行:
alias nagc=‘/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v/usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg‘
如果没有报错,可以启动Nagios服务
service nagios start
登录Nagios
安装已经完成,你可以使用barlow用户以及之前设置的密码通过http://Nagios_IP/nagios/地址登录Nagios后台。

nrpe监控远程Linux主机
监控linux本地主机时,我们可以直接更改配置文件进行监控,如果需要监控的主机与nagios不在同一机器上,即监控远程linux主机时,我们需要借助NRPE插件实现。
nrpe工作原理图
![O]~3PRZ$_)3XI)EYIG[@1}9.jpg 技术分享](http://s5.51cto.com/wyfs02/M02/86/8E/wKiom1fD177TY_UQAADK4XFuFuY195.jpg)
这里是被动监控模式
1.Nagois主机端安装nrpe
之前已经将nagios 运行起来了,现在要做的事情是: 安装check_nrpe 插件
下载地址
https://sourceforge.net/projects/nagios/files/nrpe-2.x/
tar -zxvf nrpe-2.12.tar.gz
cd nrpe-2.12
./configure
make all
make install-plugin
只运行这一步就行了,因为只需要check_nrpe 插件
1. 被监控机器的安装操作
1)增加用户
groupadd nagios
useradd nagios -g nagios -M -s /bin/false
passwd nagios
安装支持:
yum install openssl-devel -y
2)安装nagios-plugin插件
tar zvxf nagios-plugins-1.4.15.tar.gz
cd nagios-plugins-1.4.15
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --exec-prefix=/usr/local/nagios--enable-redhat-pthread-workaround
make
make install
3)修改目录权限
chown -R nagios:nagios /usr/local/nagios
chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec/
4)安装nrpe
tar zxvf nrpe-2.12.tar.gz
cd nrpe-2.12
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios --exec-prefix=/usr/local/nagios
make all
(1) 安装check_nrpe 这个插件
make install-plugin
(2) 安装deamon
make install-daemon
(3) 安装配置文件
make install-daemon-config
监控脚本目录/usr/local/nagios/libexec
配置NRPE以守护进程运行
1、更改vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg文件,设置允许nagios服务器连接,如nagios服务器的ip为192.168.1.138:
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,192.168.1.138
6) 启动nrpe
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg -d
7) 查看NRPE 是否已经启动
netstat -nltp |grep nrpe
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5163/nrpe
8) 测试NRPE 是否则正常工作
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1
NRPE v2.15
nagios服务器的操作
测试监控机check_nrpe 与被监控机运行的nrpedaemon 之间的通信.
登陆监控机
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 被监控IP
NRPE v2.8.1
看到已经正确返回了NRPE 的版本信息,说明一切正常.
遇到的错误:
[root@1-138 soft]# /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe-H 192.168.1.139
CHECK_NRPE: Error - Could not complete SSL handshake.
提示:被监控端没有运行监控端访问
为监控远程主机定义host和service
配置主配置文件
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
添加如下两行
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/hosts.cfg
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg
注释掉下面这行
#cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/localhost.cfg
1、定义check_nrpe命令
在文件/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg后面增加:
# ‘check_nrpe‘ command definition
define command{
command_name check_nrpe
command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -t 30 -c$ARG1$
}
2、创建/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/hosts.cfg (需提前在nagios.cfg中定义)
host定义示例:
define host{
use linux-server #==>templates.cfg模板里面定义的名字
host_name 1-139 #===>被监控的远程主机名
address 192.168.1.139 #===>被监控的远程主机的ip
}
define host{
use linux-server
host_name 1-138
address 192.168.1.138
}
define hostgroup{ #==>定义主机组
hostgroup_name linux-server
members 1-138,1-139
}
3、创建服务:vi/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg (需提前在nagios.cfg中定义)
如定义监控远程主机磁盘空间示例(其他服务语法相同):
define service{
use generic-service
host_name remotehost
service_description sda磁盘空间
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
}
语法检测:
[root@1-138 objects]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig
Running configuration check... OK
之后重载nagios配置文件使其生效
# service nagios reload
打开web页面,主机正常
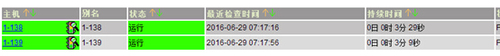
显示服务

在被监控端检测
定义服务的脚本在这里,就是被监控端的脚本
vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
command[check_users]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_users-w 5 -c 10
command[check_load]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load-w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
command[check_disk]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10%-p /dev/sda1
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs-w 5 -c 10 -s Z
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs-w 150 -c 200
客户端的监控的执行程序都放在这个路径里面
[root@1-139 libexec]# ll /usr/local/nagios/libexec
总用量 6044
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 180543 6月 29 05:27check_apt
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 2309 6月 29 05:27 check_breeze
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 183476 6月 29 05:27check_by_ssh
lrwxrwxrwx 1 nagios nagios 9 6月 29 05:27 check_clamd -> check_tcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 138790 6月 29 05:27check_cluster
-r-xr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 177359 6月 29 05:27check_dhcp
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 178454 6月 29 05:27check_dig
-rwxr-xr-x 1 nagios nagios 195857 6月 29 05:27 check_disk
服务端测试
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.1.139 -c check_disk
客户端本地测试
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 127.0.0.1 -c check_disk
或者
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p/dev/sda1
下面是主动模式
在服务端测试
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_http -I 192.168.1.138==》url监控原理
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_tcp -H 192.168.1.139 -p22 ==》端口监控原理
基于url和端口的监控,这两种用法工作用得最多
1.对于域名url地址blog.abc.com.org 的监控
2.监听任意端口例如:80,25,8080,873
=======被动模式nagios检测密码文件脚本check_passwd=============
在客户端开发插件
[root@1-139 ~]# md5sum /etc/passwd
ca634e937faed5583b7d675ed3f5e528 /etc/passwd
[root@1-139 ~]# md5sum /etc/passwd >/etc/passwd.md5
[root@1-139 ~]#md5sum -c /etc/passwd.md5
/etc/passwd: OK
vim /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_passwd
#!/bin/sh
char=`md5sum -c /etc/passwd.md5 2>/dev/null |grep"OK" |wc -l`
if [ $char -eq 1 ];then
echo"passwd is ok!"
exit 0
else
echo"passwd is changed!"
exit 2
fi
[root@1-139 libexec]# chown -R nagios.nagios check_passwd
[root@1-139 libexec]# chmod +x check_passwd
Vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg
添加
command[check_passwd]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_passwd
重启nrpe
pkill nrpe
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/nrpe.cfg–d
在服务端设置
先检测一下
[root@1-138 objects]#/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H 192.168.1.139 -c check_passwd
passwd is ok!
然后添加服务
Vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/services.cfg
define service{
use generic-service
host_name 1-139
service_description check_passwd
check_command check_nrpe!check_passwd
}
[root@1-138 objects]# /etc/init.d/nagios checkconfig
Running configuration check... OK.
[root@1-138 objects]# /etc/init.d/nagios reload
本文出自 “比尔运维笔记” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://chenshoubiao.blog.51cto.com/6159058/1843910
nagios安装部署
