首页 > 代码库 > java常见类之String类
java常见类之String类
1.字符串概述
字符串:就是由多个字符组成的一串字符,也可以看成是字符数组。
String类代表字符串,java程序中的字符串字面值,如"abc"等都作为此类的实例实现。
字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
2.String的构造方法
public String() 空构造
public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串
public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length) 把字节数组的指定索引长度的字节转换成字符串
public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转换成字符串
public String(char[] values,int offset,int count) 把字符数组的指定索引长度的字符转换成字符串
public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串
package cn;
/**
* 字符串:就是由多个字符组成的一串字符,也可以看成是字符数组
* 通过查看API,我们可以知道
* 字符串字面值"abc"也可以看成是一个字符串对象。
* 字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
*
* 构造方法:
* public String() 空构造
* public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串
* public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
把字节数组的指定索引长度的字节转换成字符串
* public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转换成字符串
* public String(char[] values,int offset,int count)
把字符数组的指定索引长度的字符转换成字符串
* public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串
*
* 字符串的方法:
* public int length()获取字符串的长度
*/
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public String() 空构造
String s1 = new String();
System.out.println("s1:"+s1);//s1:
//public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[]{97,98,99};
String s2 = new String(bytes1);
System.out.println("s2:"+s2);//s2:abc
//public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
// 把字节数组的指定索引长度的字节转换成字符串
byte[] bytes2 = new byte[]{97,98,99,100};
String s3 = new String(bytes2,1,2);
System.out.println("s3:"+s3);//s3:bc
//public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转换成字符串
char[] char1 = new char[]{‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘};
String s4 = new String(char1);
System.out.println("s4:"+s4);//s4:abc
//public String(char[] values,int offset,int count)
// 把字符数组的指定索引长度的字符转换成字符串
char[] char2 = new char[]{‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘};
String s5 = new String(char2,1,2);
System.out.println("s5:"+s5);//s5:bc
//public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串
String s6 = new String("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("s6:"+s6);//s6:HelloWorld
}
}
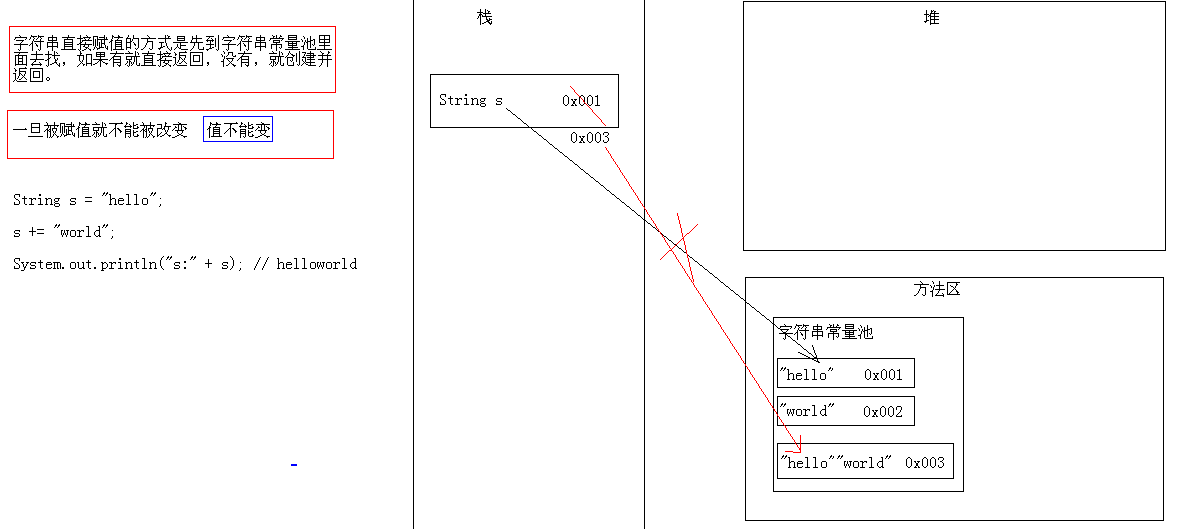
3.字符串的特点:一旦被声明,就不能被改变
package com;
/**
* 字符串的特点:一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
* 指的是字符串"hello"不可以改变 吗,而不是变量s
*
* 字符串直接赋值的方式是先到字符串常量池里面去找,
* 如果有就直接返回,没有,就创建并返回。
*
*/
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
s += "world";
System.out.println("s:"+s);//s:helloworld
}
}
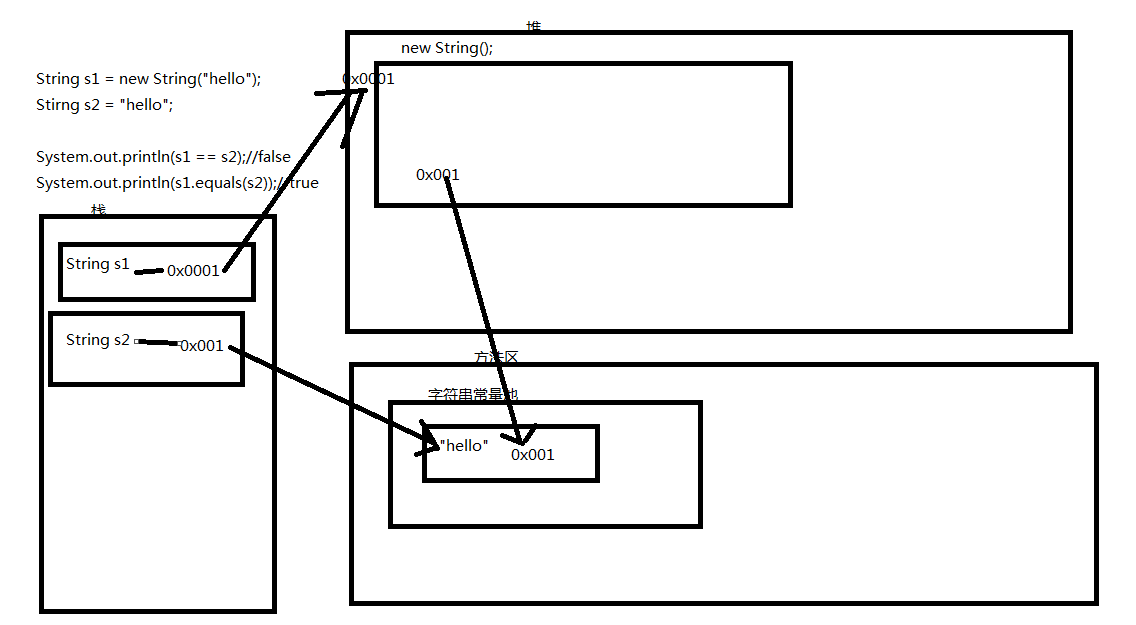
4.String直接赋值和创建对象方式的区别
package com;
/**
* String s1 = "hello";和 String s2 = new String("hello")的区别
* 前者会创建2个对象,后者会创建一个对象。
*
* ==在基本类型中,比较的是值是否相等。在引用类型中,比较的是地址值是否相等。
* equals()在Object类中比较的是地址值是否相等。
* 但是String重写了equals()方法,所以在String比较的是内容是否相等。
*/
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
}
}
5.练习
package com;
/**
* 看程序写结果
*/
public class StringDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
String s3 = new String("hello");
String s4 = "hello";
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = "hello";
System.out.println(s5 == s6 );//true
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));//true
}
}package com;
/**
* 看程序,写结果
* 字符串如果是变量相加,先开辟空间,再拼接
* 字符串如果是常量相加,是先相加,然后再在常量池中寻找,如果有就直接返回,否则,就创建
*/
public class StringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s1.hashCode()+s2.hashCode());
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());
/**
* s3 就相当于是s3.hashCode()
* 而s1 + s2 就相当于s1.hashCode() + s2.hashCode()
* 当然不一样了
*/
System.out.println(s3 == s1 + s2);//false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s1 + s2));//true
System.out.println(s3 == "hello"+"world");//true
System.out.println(s3.equals("hello"+"world"));//true
/**
* 通过反编译,看源码,我们知道这里已经做好了处理
*/
System.out.println(s3=="helloworld");
System.out.println(s3.equals("helloworld"));
}
}6.String类的判断功能
public boolean equals(Object obj) 判断两个字符串的内容是否相等,区分大小写
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断两个字符串是否相等,不区分大小写
public contains(String str) 判断大的字符串中是否包含有小的字符串
public boolean stratsWith(String str) 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
pubilc booelan endsWithd(String str) 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
public boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串的内容是否为空
package cn;
/**
* String类的判断功能
* public boolean equals(Object obj) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,区分大小写
* public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,不区分大小写
* public contains(String str) 判断大的字符串中是否包含小的字符串
* public boolean startsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串开开头
* public boolean endsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串结尾
* public boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串的内容是否为空
*
*/
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s1 = "helloworld";
String s2 = "helloworld";
String s3 = "helloWorld";
//public boolean equals(Object obj) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,区分大小写
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
//public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,不区分大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));//true
//public contains(String str) 判断大的字符串中是否包含小的字符串
System.out.println(s1.contains("hello"));//true
System.out.println(s1.contains("hw"));//false
//public boolean startsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串开开头
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("hello"));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("h"));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("world"));//false
//public boolean endsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串结尾
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("world"));//true
//public boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串是否为空
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());//false
String s4 = "";
System.out.println(s4.isEmpty());//true
String s5 = null;
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
* 因为s5的对象不存在,它怎么可以调用方法呢??
*/
//System.out.println(s5.isEmpty());
}
}7.练习
package cn;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次机会
*
* 分析:
* 1.定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
* 2.键盘录入用户名和密码。
* 3.比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
* 4.给三次机会,用循环改进,用for循环
*/
public class StringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
String username = "admin";
String password = "admin";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
//键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
//比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if(username.equals(name) && password.equals(pwd)){
//如果都相同,则登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else{
//如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if((2-i) == 0){//如果是第0次,那么就
System.out.println("抱歉,帐号被锁定。");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败,你还有"+(2-i)+"次机会");
}
}
}
}
}改进
package cn;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次机会,如果登录成功,就可以玩猜数字了
*
* 分析:
* 1.定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
* 2.键盘录入用户名和密码。
* 3.比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
* 4.给三次机会,用循环改进,用for循环
*/
public class StringDemo1 {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
String username = "admin";
String password = "admin";
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
//键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
//比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if(username.equals(name) && password.equals(pwd)){
flag = true;
//如果都相同,则登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else{
//如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if((2-i) == 0){//如果是第0次,那么就
System.out.println("抱歉,帐号被锁定。");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败,你还有"+(2-i)+"次机会");
}
}
}
if(flag){
GuessNumberGame.start();
}
}
}
package cn;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 创建猜数字的小游戏
*/
public class GuessNumberGame {
private GuessNumberGame(){}
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void start(){
//产生一个随机数
int number = (int)(Math.random() * 100 ) + 1 ;
System.out.println(number);
while(true){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要猜的数据(1-100):");
int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
//判断
if(guessNumber > number){
System.out.println("你猜的数据"+guessNumber+"大了");
}else if (guessNumber < number){
System.out.println("你猜的数据"+guessNumber+"小了");
}else{
System.out.println("恭喜你,猜中了");
break;
}
}
}
}8.String类的获取功能
public int length() 获取字符串的长度
public char charAt(int index) 获取指定索引位置上的字符
为什么这里是int类型,而不是char类型?
因为:‘a‘和97是可以相互转换的,即97就是代表‘a‘
public int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(String str) 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)返回指定字符在此支付串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(Sring str,itn fromIndex) 返回指定字符串在此字符串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
public String subString(int start) 从指定位置开始截取的字符串
public String subString(int strat,int end) 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束时截取的字符串
package cn;
/**
* String类的获取功能
* public int length() 获取字符串的长度
* public char charAt(int index) 获取指定索引位置上的字符
* 为什么这里是int类型,而不是char类型?
* 因为:‘a‘和97是可以相互转换的,即97就是代表‘a‘
* public int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
* public int indexOf(String str) 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
* public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)返回指定字符在此支付串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
* public int indexOf(Sring str,itn fromIndex) 返回指定字符串在此字符串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
* public String subString(int start) 从指定位置开始截取的字符串
* public String subString(int strat,int end) 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束时截取的字符串
*/
public class StringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串
String s = "helloworld";
//public int length() 获取字符串的长度
System.out.println("s的长度是:"+s.length());//s的长度是:10
//public char charAt(int index) 获取指定索引位置上的字符
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));//h
//public int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("l出现第一次的索引"+s.indexOf(‘l‘));//l出现第一次的索引2
//public int indexOf(String str) 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("hello第一次出现的索引"+s.indexOf("hello"));//hello第一次出现的索引0
//public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)返回指定字符在此支付串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:"+s.indexOf(‘l‘, 4));//l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:8
System.out.println("l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:"+s.indexOf(‘k‘, 4));//l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:-1
System.out.println("l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:"+s.indexOf(‘l‘, 40));//l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:-1
//public int indexOf(Sring str,itn fromIndex) 返回指定字符串在此字符串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("or从第2个索引位置开始出现的第一个索引位置:"+s.indexOf("or", 2));//or从第2个索引位置开始出现的第一个索引位置:6
//public String subString(int start) 从指定位置开始截取的字符串
System.out.println("截取world:"+s.substring(5));//截取world:world
System.out.println("截取helloworld:"+s.substring(0));//截取helloworld:helloworld
//public String subString(int strat,int end) 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束时截取的字符串
System.out.println("截取wo:"+s.substring(5, 7));//截取wo:wo
}
}9.练习
package cn;
/**
* 需求:遍历获取字符串中的每一个字符
*
*/
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "helloworld";
//第一种实现方法
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
System.out.print(ch+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//第二种实现方法
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]+" ");
}
}
}package cn;
/**
* 需求:统计一个字符串中大写字母字符、小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数(不考虑其他字符)
* 举例:
* "Hello123World"
* 结果:
* 大写字符 2个
* 小写字符 8个
* 数字字符 3个
*
*
*/
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello123World";
int maxCharacterSum = 0;
int minCharacterSum = 0;
int numSum = 0;
//方法一:将字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
if(chs[i] >= ‘a‘ && chs[i] <= ‘z‘){
minCharacterSum ++;
}else if(chs[i] >= ‘A‘ && chs[i] <= ‘Z‘){
maxCharacterSum ++;
}else if(chs[i] >= ‘0‘ && chs[i] <= ‘9‘){
numSum ++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字符的总数:"+maxCharacterSum);
System.out.println("小写字符的总数:"+minCharacterSum);
System.out.println("数字字符的总数:"+numSum);
//第二中实现
maxCharacterSum = 0;
minCharacterSum = 0;
numSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if(ch >= ‘a‘ && ch <= ‘z‘){
minCharacterSum ++;
}else if(ch >= ‘A‘ && ch <= ‘Z‘){
maxCharacterSum ++;
}else if(ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘){
numSum ++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字符的总数:"+maxCharacterSum);
System.out.println("小写字符的总数:"+minCharacterSum);
System.out.println("数字字符的总数:"+numSum);
}
}10.String类的转换功能
public byte[] getBytes() 字符串转换为字节数组
public char[] toCharArray() 字符串转换为字符数组
public static String valueOf(char[] chs) 将字符数组转换为字符串
public static String valueOf(int i) 将int类型的数值转换为字符串
public String toLowerCase() 将字符串转换为小写
public String toUpperCase() 将字符串转换为大写
public String concat(String str) 字符串的拼接
package cn;
/**
* String类的转换功能
*
* public byte[] getBytes() 字符串转换为字节数组
* public char[] toCharArray() 字符串转换为字符数组
* public static String valueOf(char[] chs) 将字符数组转换为字符串
* public static String valueOf(int i) 将int类型的数值转换为字符串
* public String toLowerCase() 将字符串转换为小写
* public String toUpperCase() 将字符串转换为大写
* public String concat(String str) 字符串的拼接
*
*/
public class StringDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串对象
String s = "javaSE";
//public byte[] getBytes() 字符串转换为字节数组
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.print(bytes[i]+" ");//106 97 118 97 83 69
}
System.out.println();
//public char[] toCharArray() 字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
System.out.print(chs[i]+" ");//j a v a S E
}
System.out.println();
// public static String valueOf(char[] chs) 将字符数组转换为字符串
String ss = String.valueOf(chs);
System.out.println(ss);//javaSE
System.out.println();
//public static String valueOf(int i) 将int类型的数值转换为字符串
int num = 100;
System.out.println(s.valueOf(num));//100
System.out.println();
System.out.println("转换小写:"+s.toLowerCase());//转换小写:javase
System.out.println("转换大写:"+s.toUpperCase());//转换大写:JAVASE
System.out.println();
System.out.println(s.concat("javaEE"));//javaSEjavaEE
}
}11.练习
package cn;
/**
* 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转换为大写
* 举例:
* helloWORLD
* 结果
* HelloWORLD
*/
public class StringTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloWORLD";
str = str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+str.substring(1);
System.out.println(str);//HelloWORLD
}
}
package cn;
/**
* 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转换为大写,其余为小写
* 举例:
* helloWORLD
* 结果
* Helloworld
*/
public class StringTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloWORLD";
str = str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+str.substring(1).toLowerCase();
System.out.println(str);//Helloworld
}
}12.
本文出自 “11831428” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://11841428.blog.51cto.com/11831428/1859607
java常见类之String类
