首页 > 代码库 > 编写PHP框架,深入了解MVC运行流程
编写PHP框架,深入了解MVC运行流程
1 什么是MVC
MVC模式(Model-View-Controller)是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式,把软件系统分为三个基本部分:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。
PHP中MVC模式也称Web MVC,从上世纪70年代进化而来。MVC的目的是实现一种动态的程序设计,便于后续对程序的修改和扩展简化,并且使程序某一部分的重复利用成为可能。除 此之外,此模式通过对复杂度的简化,使程序结构更加直观。软件系统通过对自身基本部份分离的同时,也赋予了各个基本部分应有的功能。
MVC各部分的职能:
- 模型Model – 管理大部分的业务逻辑和所有的数据库逻辑。模型提供了连接和操作数据库的抽象层。
- 控制器Controller - 负责响应用户请求、准备数据,以及决定如何展示数据。
- 视图View – 负责渲染数据,通过HTML方式呈现给用户。
一个典型的Web MVC流程:
- Controller截获用户发出的请求;
- Controller调用Model完成状态的读写操作;
- Controller把数据传递给View;
- View渲染最终结果并呈献给用户。
2 为什么要自己开发MVC框架
网络上有大量优秀的MVC框架可供使用,本教程并不是为了开发一个全面的、终极的MVC框架解决方案,而是将它看作是一个很好的从内部学习PHP的机会,在此过程中,你将学习面向对象编程和MVC设计模式,并学习到开发中的一些注意事项。
更重要的是,你可以完全控制你的框架,并将你的想法融入到你开发的框架中。虽然不一定是做好的,但是你可以按照你的方式去开发功能和模块。
3 开始开发自己的MVC框架
3.1 目录准备
在开始开发前,让我们先来把项目建立好,假设我们建立的项目为 todo,MVC的框架可以命名为 FastPHP,那么接下来的第一步就是把目录结构先设置好。
虽然在这个教程中不会使用到上面的所有的目录,但是为了以后程序的可拓展性,在一开始就把程序目录设置好使非常必要的。下面就具体说说每个目录的作用:
- application – 应用代码
- config – 程序配置或数据库配置
- fastphp - 框架核心目录
- public – 静态文件
- runtime - 临时数据目录
- scripts – 命令行工具
3.2 代码规范
在目录设置好以后,我们接下来就要来规定一下代码的规范:
- MySQL的表名需小写,如:item,car
- 模块名(Models)需首字母大写,,并在名称后添加“Model”,如:ItemModel,CarModel
- 控制器(Controllers)需首字母大写,,并在名称中添加“Controller”,如:ItemController,CarController
- 视图(Views)部署结构为“控制器名/行为名”,如:item/view.php,car/buy.php
上述的一些规则是为了能在程序中更好的进行互相的调用。接下来就开始真正的PHP MVC编程了。
3.3 重定向
将所有的数据请求都重定向 index.php 文件,在 todo 目录下新建一个 .htaccess 文件,文件内容为:
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c> RewriteEngine On # 确保请求路径不是一个文件名或目录 RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d # 重定向所有请求到 index.php?url=PATHNAME RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?url=$1 [PT,L] </IfModule>
- 程序有一个单一的入口;
- 除静态程序,其他所有程序都重定向到 index.php 上;
- 可以用来生成利于SEO的URL,想要更好的配置URL,后期可能会需要URL路由,这里先不做介绍了。
3.4 入口文件
做完上面的操作,就应该知道我们需要做什么了,没错!在 public 目录下添加 index.php 文件,文件内容为:
<?php // 应用目录为当前目录 define(‘APP_PATH‘, __DIR__.‘/‘); // 开启调试模式 define(‘APP_DEBUG‘, true); // 网站根URL define(‘APP_URL‘, ‘http://localhost/fastphp‘); // 加载框架 require ‘./fastphp/FastPHP.php‘;
3.5 配置文件和主请求
在 index.php 中,我们对 fastphp 文件夹下的 FastPHP.php 发起了请求,那么 FastPHP.php 这个启动文件中到底会包含哪些内容呢?

<?php // 初始化常量 defined(‘FRAME_PATH‘) or define(‘FRAME_PATH‘, __DIR__.‘/‘); defined(‘APP_PATH‘) or define(‘APP_PATH‘, dirname($_SERVER[‘SCRIPT_FILENAME‘]).‘/‘); defined(‘APP_DEBUG‘) or define(‘APP_DEBUG‘, false); defined(‘CONFIG_PATH‘) or define(‘CONFIG_PATH‘, APP_PATH.‘config/‘); defined(‘RUNTIME_PATH‘) or define(‘RUNTIME_PATH‘, APP_PATH.‘runtime/‘); // 包含配置文件 require APP_PATH . ‘config/config.php‘; //包含核心框架类 require FRAME_PATH . ‘Core.php‘; // 实例化核心类 $fast = new Core; $fast->run();
先来看看config文件下的 config .php 文件,该文件的主要作用是设置一些程序的配置项及数据库连接等,主要内容为:
<?php /** 变量配置 **/ define(‘DB_NAME‘, ‘todo‘); define(‘DB_USER‘, ‘root‘); define(‘DB_PASSWORD‘, ‘root‘); define(‘DB_HOST‘, ‘localhost‘);
应该说 config.php 涉及到的内容并不多,不过是一些基础数据库的设置,再来看看 fastphp下的共用框架入口文件 Core.php 应该怎么写。

<?php /** * FastPHP核心框架 */ class Core { // 运行程序 function run() { spl_autoload_register(array($this, ‘loadClass‘)); $this->setReporting(); $this->removeMagicQuotes(); $this->unregisterGlobals(); $this->Route(); } // 路由处理 function Route() { $controllerName = ‘Index‘; $action = ‘index‘; if (!empty($_GET[‘url‘])) { $url = $_GET[‘url‘]; $urlArray = explode(‘/‘, $url); // 获取控制器名 $controllerName = ucfirst($urlArray[0]); // 获取动作名 array_shift($urlArray); $action = empty($urlArray[0]) ? ‘index‘ : $urlArray[0]; //获取URL参数 array_shift($urlArray); $queryString = empty($urlArray) ? array() : $urlArray; } // 数据为空的处理 $queryString = empty($queryString) ? array() : $queryString; // 实例化控制器 $controller = $controllerName . ‘Controller‘; $dispatch = new $controller($controllerName, $action); // 如果控制器存和动作存在,这调用并传入URL参数 if ((int)method_exists($controller, $action)) { call_user_func_array(array($dispatch, $action), $queryString); } else { exit($controller . "控制器不存在"); } } // 检测开发环境 function setReporting() { if (APP_DEBUG === true) { error_reporting(E_ALL); ini_set(‘display_errors‘,‘On‘); } else { error_reporting(E_ALL); ini_set(‘display_errors‘,‘Off‘); ini_set(‘log_errors‘, ‘On‘); ini_set(‘error_log‘, RUNTIME_PATH. ‘logs/error.log‘); } } // 删除敏感字符 function stripSlashesDeep($value) { $value = is_array($value) ? array_map(‘stripSlashesDeep‘, $value) : stripslashes($value); return $value; } // 检测敏感字符并删除 function removeMagicQuotes() { if ( get_magic_quotes_gpc()) { $_GET = stripSlashesDeep($_GET ); $_POST = stripSlashesDeep($_POST ); $_COOKIE = stripSlashesDeep($_COOKIE); $_SESSION = stripSlashesDeep($_SESSION); } } // 检测自定义全局变量(register globals)并移除 function unregisterGlobals() { if (ini_get(‘register_globals‘)) { $array = array(‘_SESSION‘, ‘_POST‘, ‘_GET‘, ‘_COOKIE‘, ‘_REQUEST‘, ‘_SERVER‘, ‘_ENV‘, ‘_FILES‘); foreach ($array as $value) { foreach ($GLOBALS[$value] as $key => $var) { if ($var === $GLOBALS[$key]) { unset($GLOBALS[$key]); } } } } } // 自动加载控制器和模型类 static function loadClass($class) { $frameworks = FRAME_PATH . $class . ‘.class.php‘; $controllers = APP_PATH . ‘application/controllers/‘ . $class . ‘.class.php‘; $models = APP_PATH . ‘application/models/‘ . $class . ‘.class.php‘; if (file_exists($frameworks)) { // 加载框架核心类 include $frameworks; } elseif (file_exists($controllers)) { // 加载应用控制器类 include $controllers; } elseif (file_exists($models)) { //加载应用模型类 include $models; } else { /* 错误代码 */ } } }
下面重点讲解主请求方法 callHook(),首先我们想看看我们的 URL 会这样:
yoursite.com/controllerName/actionName/queryString
callHook()的作用就是,从全局变量 GE
controller、action和
queryString。
例如,URL链接为:todo.com/item/view/1/first-item,那么
- $controller 就是:item
- $action 就是:view
- 查询字符串Query String就是:array(1, first-item)
分割完成后,会实例化一个新的控制器:$controller.‘Controller‘(其中“.”是连字符),并调用其方法 $action。
3.6 控制器/Controller基类
接下来的操作就是在 fastphp 中建立程序所需的基类,包括控制器、模型和视图的基类。
新建控制器基类为 Controller.class.php,控制器的主要功能就是总调度,具体具体内容如下:

<?php /** * 控制器基类 */ class Controller { protected $_controller; protected $_action; protected $_view; // 构造函数,初始化属性,并实例化对应模型 function __construct($controller, $action) { $this->_controller = $controller; $this->_action = $action; $this->_view = new View($controller, $action); } // 分配变量 function assign($name, $value) { $this->_view->assign($name, $value); } // 渲染视图 function __destruct() { $this->_view->render(); } }
Controller 类实现所有控制器、模型和视图(View类)的通信。在执行析构函数时,我们可以调用 render() 来显示视图(view)文件。
3.7 模型Model基类
新建模型基类为 Model.class.php,模型基类 Model.class.php 代码如下:

<?php class Model extends Sql { protected $_model; protected $_table; function __construct() { // 连接数据库 $this->connect(DB_HOST, DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, DB_NAME); // 获取模型名称 $this->_model = get_class($this); $this->_model = rtrim($this->_model, ‘Model‘); // 数据库表名与类名一致 $this->_table = strtolower($this->_model); } function __destruct() { } }
考虑到模型需要对数据库进行处理,所以单独建立一个数据库基类 Sql.class.php,模型基类继承 Sql.class.php,代码如下:

<?php class Sql { protected $_dbHandle; protected $_result; // 连接数据库 public function connect($host, $user, $pass, $dbname) { try { $dsn = sprintf("mysql:host=%s;dbname=%s;charset=utf8", $host, $dbname); $this->_dbHandle = new PDO($dsn, $user, $pass, array(PDO::ATTR_DEFAULT_FETCH_MODE => PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)); } catch (PDOException $e) { exit(‘错误: ‘ . $e->getMessage()); } } // 查询所有 public function selectAll() { $sql = sprintf("select * from `%s`", $this->_table); $sth = $this->_dbHandle->prepare($sql); $sth->execute(); return $sth->fetchAll(); } // 根据条件 (id) 查询 public function select($id) { $sql = sprintf("select * from `%s` where `id` = ‘%s‘", $this->_table, $id); $sth = $this->_dbHandle->prepare($sql); $sth->execute(); return $sth->fetch(); } // 根据条件 (id) 删除 public function delete($id) { $sql = sprintf("delete from `%s` where `id` = ‘%s‘", $this->_table, $id); $sth = $this->_dbHandle->prepare($sql); $sth->execute(); return $sth->rowCount(); } // 自定义SQL查询,返回影响的行数 public function query($sql) { $sth = $this->_dbHandle->prepare($sql); $sth->execute(); return $sth->rowCount(); } // 新增数据 public function add($data) { $sql = sprintf("insert into `%s` %s", $this->_table, $this->formatInsert($data)); return $this->query($sql); } // 修改数据 public function update($id, $data) { $sql = sprintf("update `%s` set %s where `id` = ‘%s‘", $this->_table, $this->formatUpdate($data), $id); return $this->query($sql); } // 将数组转换成插入格式的sql语句 private function formatInsert($data) { $fields = array(); $values = array(); foreach ($data as $key => $value) { $fields[] = sprintf("`%s`", $key); $values[] = sprintf("‘%s‘", $value); } $field = implode(‘,‘, $fields); $value = implode(‘,‘, $values); return sprintf("(%s) values (%s)", $field, $value); } // 将数组转换成更新格式的sql语句 private function formatUpdate($data) { $fields = array(); foreach ($data as $key => $value) { $fields[] = sprintf("`%s` = ‘%s‘", $key, $value); } return implode(‘,‘, $fields); } }
应该说,Sql.class.php 是框架的核心部分。为什么?因为通过它,我们创建了一个 SQL 抽象层,可以大大减少了数据库的编程工作。虽然 PDO 接口本来已经很简洁,但是抽象之后框架的可灵活性更高。
3.8 视图View类
视图类 View.class.php 内容如下:

<?php /** * 视图基类 */ class View { protected $variables = array(); protected $_controller; protected $_action; function __construct($controller, $action) { $this->_controller = $controller; $this->_action = $action; } /** 分配变量 **/ function assign($name, $value) { $this->variables[$name] = $value; } /** 渲染显示 **/ function render() { extract($this->variables); $defaultHeader = APP_PATH . ‘application/views/header.php‘; $defaultFooter = APP_PATH . ‘application/views/footer.php‘; $controllerHeader = APP_PATH . ‘application/views/‘ . $this->_controller . ‘/header.php‘; $controllerFooter = APP_PATH . ‘application/views/‘ . $this->_controller . ‘/footer.php‘; // 页头文件 if (file_exists($controllerHeader)) { include ($controllerHeader); } else { include ($defaultHeader); } // 页内容文件 include (APP_PATH . ‘application/views/‘ . $this->_controller . ‘/‘ . $this->_action . ‘.php‘); // 页脚文件 if (file_exists($controllerFooter)) { include ($controllerFooter); } else { include ($defaultFooter); } } }
这样我们的核心的PHP MVC框架就编写完成了,下面我们开始编写应用来测试框架功能。
4 应用
4.1 数据库部署
在 SQL 中新建一个 todo 数据库,使用下面的语句增加 item 数据表并插入2条记录:
CREATE DATABASE `todo` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; USE `todo`; CREATE TABLE `item` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL auto_increment, `item_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `item` VALUES(1, ‘Hello World.‘); INSERT INTO `item` VALUES(2, ‘Lets go!‘);
4.2 部署模型
然后,我们还需要在 models 目录中创建一个 ItemModel.php 模型,内容如下:
<?php class ItemModel extends Model { /* 业务逻辑层实现 */ }
4.3 部署控制器
在 controllers 目录下创建一个 ItemController.php 控制器,内容如下:

<?php class ItemController extends Controller { // 首页方法,测试框架自定义DB查询 public function index() { $items = (new ItemModel)->selectAll(); $this->assign(‘title‘, ‘全部条目‘); $this->assign(‘items‘, $items); } // 添加记录,测试框架DB记录创建(Create) public function add() { $data[‘item_name‘] = $_POST[‘value‘]; $count = (new ItemModel)->add($data); $this->assign(‘title‘, ‘添加成功‘); $this->assign(‘count‘, $count); } // 查看记录,测试框架DB记录读取(Read) public function view($id = null) { $item = (new ItemModel)->select($id); $this->assign(‘title‘, ‘正在查看‘ . $item[‘item_name‘]); $this->assign(‘item‘, $item); } // 更新记录,测试框架DB记录更新(Update) public function update() { $data = array(‘id‘ => $_POST[‘id‘], ‘item_name‘ => $_POST[‘value‘]); $count = (new ItemModel)->update($data[‘id‘], $data); $this->assign(‘title‘, ‘修改成功‘); $this->assign(‘count‘, $count); } // 删除记录,测试框架DB记录删除(Delete) public function delete($id = null) { $count = (new ItemModel)->delete($id); $this->assign(‘title‘, ‘删除成功‘); $this->assign(‘count‘, $count); } }
4.4 部署视图
在 views 目录下新建 header.php 和 footer.php 两个页头页脚模板,内容如下。
header.php,内容:

<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title><?php echo $title ?></title>
<style>
.item {
width:400px;
}
input {
color:#222222;
font-family:georgia,times;
font-size:24px;
font-weight:normal;
line-height:1.2em;
color:black;
}
a {
color:blue;
font-family:georgia,times;
font-size:20px;
font-weight:normal;
line-height:1.2em;
text-decoration:none;
}
a:hover {
text-decoration:underline;
}
h1 {
color:#000000;
font-size:41px;
letter-spacing:-2px;
line-height:1em;
font-family:helvetica,arial,sans-serif;
border-bottom:1px dotted #cccccc;
}
h2 {
color:#000000;
font-size:34px;
letter-spacing:-2px;
line-height:1em;
font-family:helvetica,arial,sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1><?php echo $title ?></h1>
footer.php,内容:

</body> </html>
然后,在 views/item 创建以下几个视图文件。
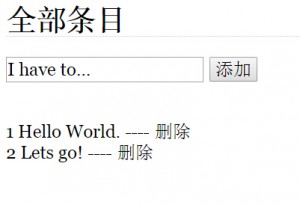
index.php,浏览数据库内 item 表的所有记录,内容:

<form action="<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/add" method="post">
<input type="text" value="http://www.mamicode.com/点击添加" onclick="this.value=http://www.mamicode.com/‘‘" name="value">
<input type="submit" value="http://www.mamicode.com/添加">
</form>
<br/><br/>
<?php $number = 0?>
<?php foreach ($items as $item): ?>
<a class="big" href="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/view/<?php echo $item[‘id‘] ?>" title="点击修改">
<span class="item">
<?php echo ++$number ?>
<?php echo $item[‘item_name‘] ?>
</span>
</a>
----
<a class="big" href="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/delete/<?php echo $item[‘id‘]?>">删除</a>
<br/>
<?php endforeach ?>
add.php,添加记录,内容:

<a class="big" href="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/index">成功添加<?php echo $count ?>条记录,点击返回</a>
view.php,查看单条记录,内容:

<form action="<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/update" method="post">
<input type="text" name="value" value="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo $item[‘item_name‘] ?>">
<input type="hidden" name="id" value="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo $item[‘id‘] ?>">
<input type="submit" value="http://www.mamicode.com/修改">
</form>
<a class="big" href="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/index">返回</a>
update.php,更改记录,内容:

<a class="big" href="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/index">成功修改<?php echo $count ?>项,点击返回</a>
delete.php,删除记录,内容:

<a href="http://www.mamicode.com/<?php echo APP_URL ?>/item/index">成功删除<?php echo $count ?>项,点击返回</a>
4.5 应用测试
这样,在浏览器中访问 todo 程序:http://localhost/todo/item/index/,就可以看到效果了。
编写PHP框架,深入了解MVC运行流程

