首页 > 代码库 > 在Linux上使用软RAID模拟磁盘损坏实验
在Linux上使用软RAID模拟磁盘损坏实验
软RAID是在操作系统层面进行的RAID配置,也能对数据进行保护,实际生产环境中使用存储中磁盘阵列和硬RAID实现冗余的情况比较多。
此实验在虚拟机中完成,在系统中添加5块磁盘,每块磁盘512MB,利用这5块磁盘做RAID5实验,模拟磁盘损坏及替换磁盘,模拟停止RAID阵列及启动阵列,阵列中的数据情况。
1.添加磁盘,每块磁盘512MB,共5块,如图1所示。
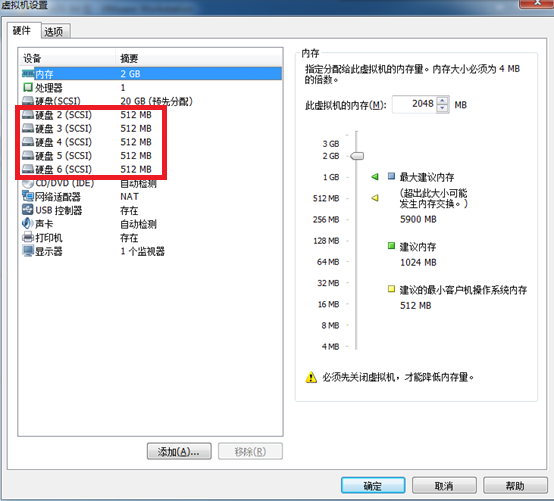 图1
图1
2.启动系统并查看磁盘
ll /dev/sd*
出现/dev/sdb,/dev/sdc,…/dev/sdf,如图2所示,说明系统已识别到新添加的5块磁盘。
 图2
图2
3.磁盘分区,以/dev/sdb为例(fdisk/dev/sdb),其它磁盘做相同操作。
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI orOSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x2646775b.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to writethem.
After that, of course, the previous content won‘t berecoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be correctedby w(rite)
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It‘s stronglyrecommended to
switch off the mode(command ‘c‘) and change display units to
sectors (command ‘u‘).
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition‘s system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-512, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-512, default 512):
Using default value 512
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list codes): fd
Changed system type of partition 1 to fd (Linux raidautodetect)
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l |more
注:Linux分区默认的类型编号为83,RAID的类型编号为fd,所以要将磁盘分区的类型改为fd。
5块磁盘全部分区完毕,如图3所示
 图3
图3
4.生成RAID5阵列
阵列名字为/dev/md0,组成阵列的磁盘有4块,分别为/dev/sdb1、/dev/sdc1、dev/sdd1、/dev/sde1。
mdadm –C /dev/md0 –l 5 –n 3 –x 1 /dev/sd[b-e]1

参数说明:
-C Create a new array
-l Set RAID level
-n Specify the number of active devices in the array
-x Specify the number of spare devices in the initial array
5.将阵列格式化,类型为ext4
mkfs –t ext4 /dev/md0

6.查看RAID信息
mdadm –D /dev/md0
从图4可知,阵列中共有4块磁盘,/dev/sdb1、/dev/sdc1、/dev/sdd1为active状态,/dev/sde1为spare状态。
 图4
图4
7.建立挂载点,并挂载。
mkdir /raid5
mount /dev/md0 /raid5

8.使用RAID设备

9.设置磁盘/dev/sdb1损坏
mdadm /dev/md0 –f /dev/sdb1

10.再次查看RAID信息
mdadm –D /dev/md0
从图5可知,/dev/sde1、/dev/sdc1、/dev/sdd1为active状态,/dev/sdb1为faulty状态。
 图5
图5
11.检查原阵列中的数据
cat /raid5/hello.txt

12.移除损坏的磁盘
mdadm /dev/md0 –r /dev/sdb1

13.向阵列中添加新的备用磁盘
mdadm /dev/md0 –a /dev/sdf1

14.查看添加备用磁盘后的RAID信息
mdadm –D /dev/md0
从图6可知,/dev/sde1、/dev/sdc1、/dev/sdd1为active状态,/dev/sdf1为spare状态。
处于faulty状态的/dev/sdb1已被移除。
 图6
图6
15.检查阵列中的数据
cat /raid5/hello.txt

16.卸载RAID设备,并停止RAID阵列
umount /dev/md0
mdadm -S /dev/md0

17.再启动RAID阵列,并查看启动阵列后的RAID信息
mdadm –A /dev/md0 /dev/sd[c-f]1
mdadm –D /dev/md0
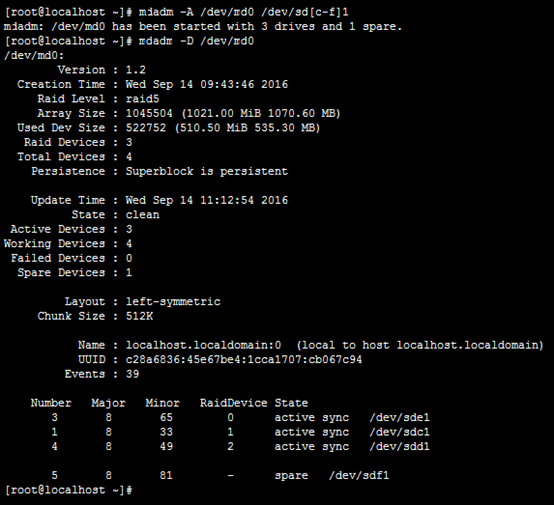
18.挂载RAID设备,并检查阵列中的数据
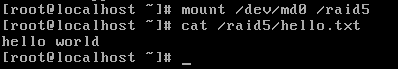
由图可知阵列中的数据没有受到影响,至此实验结束。
本文出自 “IT运维” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://itops.blog.51cto.com/2420369/1852672
在Linux上使用软RAID模拟磁盘损坏实验
