首页 > 代码库 > java学习笔记--类ArrayList和LinkedList的实现
java学习笔记--类ArrayList和LinkedList的实现
在集合Collection下的List中有两个实现使用的很频繁,一个是ArrayList,另一个是LinkedList,在学习中肯定都会有这样的疑问:什么时候适合使用ArrayList,什么时候用LinkedList?这时,我们就需要了解ArrayList和LinkedList的底层的实现,下面,为了更好的了解它们具体是怎样实现的,我们来写自己的ArrayList 和LinkedList。
ArrayList底层是基于数组实现的,数组在内存中是存储在连续的存储单元中,在数据查找的时候比较快,适用于不常进行插入数据和需要频繁的查找数据的操作,下面,我们将其实现(为了方便理解,不使用泛型,用Object存储数据):
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 顺序存储结构:类ArrayList的实现
* @author liuzb
* 2017年8月8日 下午2:58:59
*/
public class SequenceStroeLinearList{
/**
* 用于存储容器中实际存储的元素个数
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* 底层用于存储数据的容器
*/
private Object[] container;
/**
* 在顺序存储结构中,用于初始化
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_CONTAINER = {};
/**
* 构造器,用于初始化存储数据的容器
*/
public SequenceStroeLinearList(){
this.container = EMPTY_CONTAINER;
}
/**
* 构造器,用于初始化存储数据的容器
*/
public SequenceStroeLinearList(int minCapactiy) {
if(minCapactiy > 0) {
container = new Object[minCapactiy];
}else if(minCapactiy == 0) {
container = EMPTY_CONTAINER;
}else {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
/**
* 向容器中添加一个元素
* @param index 添加元素位置
* @param element 待添加元素
*/
public void insert(int index ,Object element) {
//要向一个数组中插入数据:1、数组的长度够不够 2、插入位置合不合法
//如果插入位置不合法,抛出索引越界异常
if(index > container.length || index <0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}else {
//插入位置合法
//如果是在尾部插入数据
if(index == container.length) {
container = Arrays.copyOf(container, ++size);
container[index] = element;
}else {
//如果不是在尾部插入数据,先用临时变量存储容器中的内容
Object[] temp = container;
//1、container指向一个新容器
container = new Object[size+1];
//将原数组的下标从0到index的元素复制到扩容后的容器中
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, container, 0, index);
//2、将index及其以后位置的数据整体向后移位
for(int i = size ; i > index ; i--) {
container[i] = temp[i-1];
}
//3、插入数据
container[index] = element;
//4、元素个数加一
++size;
}
}
}
/**
* 向容器中添加数据
* @param obj 需要添加的对象
*/
public void add(Object obj) {
insert(size,obj);
}
/**
* 容器中实际存储的元素个数
* @return
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* 获取指定索引位置的对象
* @param index 指定位置的索引
* @return 指定位置的对象
*/
public Object get(int index) {
if(index <0 || index > size) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return container[index];
}
/**
* 获取指定对象的索引
* @param obj 需要获取索引的对象
* @return 索引
*/
public int indexOf(Object obj) {
int index = -1;
for(int i = 0; i<size ; i++) {
if(container[i].equals(obj)) {
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
/**
* 容器中是否包含某个元素
* @param obj
* @return false 不包含 true 包含
*/
public boolean contains(Object obj) {
return indexOf(obj) == -1 ? false :true;
}
/**
* 从容器中移除指定索引的元素
* @param index 需要移除元素的索引
* @return 移除
*/
public boolean remove(Integer index) {
boolean flag = true;
// 非法索引,抛出异常
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
flag = false;
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("移除指定索引元素失败,索引值非法");
} else {
// 索引合法
for (int i = index; i < size-1; i++) {
//将index到size的元素依次往前移位
container[i] = container[i + 1];
}
// 将末尾元素值赋为 null
container[size-1] = null;
// 元素个数减一
-- size;
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 移除指定元素
* @param obj 需要移除的元素
* @return true :移除成功 false:移除失败
*/
public boolean remove(Object obj){
if(contains(obj)) {
remove(indexOf(obj));
return true;
}
return false;
}
}在实现中,用到了util包下面的Arrays帮助类,此处也可以使用System.arrayCpy()。
写好该类后,对该类进行测试:
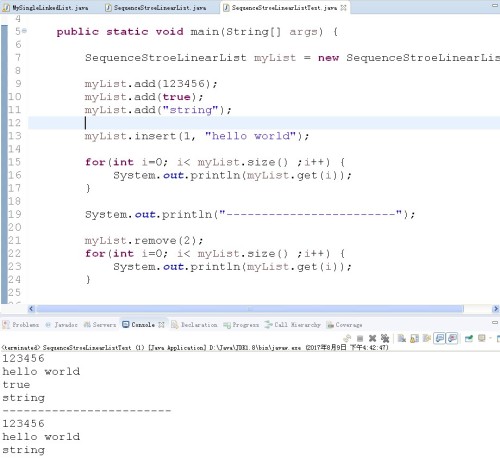
从实现结果看,我们基本实现了ArrayList的功能,此处重要的两个方法是插入数据和移除数据,当然本程序也有bug,就是remove方法。
LinkedList底层是基于链表实现的,在数据插入和删除时速度较快,适用于频繁进行插入和删除的操作,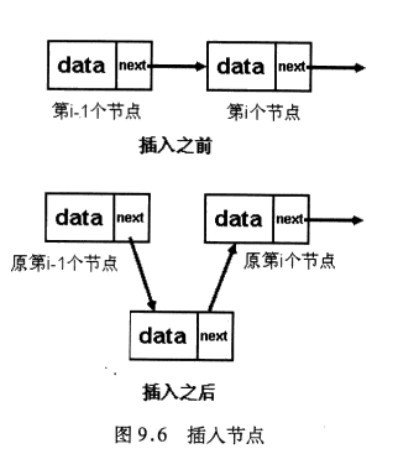 这里我们实现一个单链表:
这里我们实现一个单链表:
/**
* 自定义链式存储列表 :单链表
* @author liuzb
* 2017年8月9日 上午11:24:07
*/
public class MySingleLinkedList {
/**
* 单链表中的首节点
*/
private Node header;
/**
* 单链表中的尾节点
*/
private Node tail;
/**
* 单链表中实际存储元素的个数
*/
private int size;
/**
* 内部类,用于封装节点需要的数据和下一个节点的地址
* @author liuzb
* 2017年8月9日 上午11:24:43
*/
private class Node{
/**
* 当前链表存储的数据
*/
private Object data;
/**
* 当前节点存储的下一个节点的地址
*/
private Node next;
/**
* 无参构造器,用于节点的初始化
*/
public Node() {
}
/**
* 有参构造器,用于节点的初始化
* @param date 节点存储的值
* @param next 节点中保存的下一个节点的地址
*/
public Node(Object data,Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
/**
* 获取当前节点的存储的值
* @return 节点值
*/
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
}
/**
* 单链表头插入法
* @param item 需要存储的数据
*/
public void addHeader(Object item) {
//定义一个节点
Node node = null;
//如果原链表是空表
if(size == 0) {
//构建一个新的节点,节点的下一个节点指向null
node = new Node(item,null);
//头结点和尾节点都指向新节点
header = node;
tail = header;
}else {
//如果原链表不是空表,定义一个新节点,新节点的下一个节点指向原来的头结点
node = new Node(item,header);
//新节点变成了头结点
header = node;
}
//元素的个数加一
size ++;
}
/**
* 单链表为插入法
* @param item 需要出入的元素
*/
public void addLast(Object item) {
//创建一个新节点
Node node = new Node(item,null);
// 如果原来的链表是空表
if(size == 0) {
//单链表的头结点和尾节点都指向新节点
tail = header = node;
}else {
//原来的尾节点的下一个节点指向新节点
tail.next = node;
//新节点变成了尾节点
tail = node;
}
//链表的元素个数加一
size ++;
}
/**
* 向单链表中添加元素
* @param item 待添加的元素
* @return
*/
public void add(Object item) {
//方法中默认使用尾插入法插入元素
addLast(item);
}
/**
* 移除指定位置的元素
* @param index 需要移除元素的索引
* @return true:移除成功 false:移除失败
*/
public boolean remove(int index) {
boolean flag = false;
//如果索引非法,抛出异常
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("移除元素的索引越界");
} else {
//如果移除的是头结点
if (index == 0) {
//原头结点的下一个节点变成了头结点
header = header.next;
}else if(index == size-1) {
//如果删除的是尾节点,先获取原尾节点的前一个节点
Node node = getNodeByIndex(index-1);
//将原尾节点的前一个节点存储的下一个节点地址信息置为null
node.next = null;
//原尾节点的前一个节点变成了尾节点
tail = node;
}else {
//删除的既不是头结点,也不是尾节点,将需要删除的数据先暂时存储
Node removeNode = getNodeByIndex(index);
//获取需要删除数据的前一个节点
Node node = getNodeByIndex(index - 1);
//将前一个节点的下一个节点指向需要删除的节点的下一个节点
node.next = removeNode.next;
}
//元素个数减一
size -- ;
flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 获取指定索引的节点
* @param index 需要获取的节点的索引值
* @return 节点对象
*/
public Node getNodeByIndex(int index) {
Node current = header;
for(int i = 0;i < size && current != null;i++) {
if(index == i) {
return current;
}
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取单链表中元素个数
* @return 元素个数
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* 获取指定索引的节点值
* @param index 需要获取的节点的索引
* @return 节点值
*/
public Object get(int index) {
//索引非法,抛出异常
if(index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("无法获取该节点的值");
}
return getNodeByIndex(index).getData();
}
/**
* 向链表指定位置插入数据
* @param index 待插入位置
* @param item 待插入数据
* @return true 插入成功 false 插入失败
*/
public boolean insert(int index,Object item) {
boolean flag = true;
if(index < 0 || index >size) {
flag = false;
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
//如果插入到头结点前
if(index == 0) {
header = new Node(item,header);
}else if(index == size) {
//插入到尾节点后
//定义一个新的节点
Node node = new Node(item,null);
//尾节点的下一个节点指向新节点
tail.next = node;
//新节点变成了尾节点
tail = node;
}else {
//在首节点和尾节点之间插入节点
//获取出入位置的节点
Node indexNode = getNodeByIndex(index);
//定义新节点,新节点的下一个节点指向原插入位置的节点
Node newNode = new Node(item,indexNode);
//获取插入位置的前一个节点
Node node = getNodeByIndex(index-1);
//插入位置的前一个节点的下一个节点指向新节点
node.next = newNode;
}
//元素个数加一
size ++ ;
return flag;
}
}写好代码后,对代码进行测试:
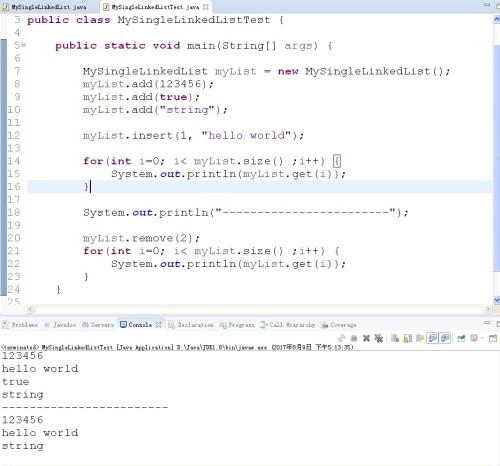
以上是个人拙见,如有错误,请指出,谢谢!
本文出自 “刘紫兵的博客” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://zibing.blog.51cto.com/8177516/1954864
java学习笔记--类ArrayList和LinkedList的实现
声明:以上内容来自用户投稿及互联网公开渠道收集整理发布,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任,若内容有误或涉及侵权可进行投诉: 投诉/举报 工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
