首页 > 代码库 > Head First设计模式之原型模式
Head First设计模式之原型模式
用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。
原型模式是一种比较简单的模式,也非常容易理解,实现一个接口,重写一个方法即完成了原型模式。在实际应用中,原型模式很少单独出现。经常与其他模式混用,他的原型类Prototype也常用抽象类来替代。
二、结构图
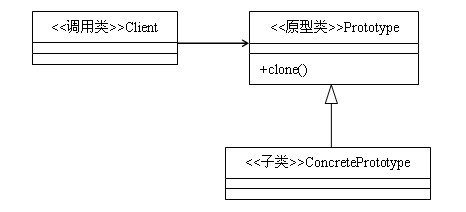
原型模式主要用于对象的复制,它的核心是就是类图中的原型类Prototype。Prototype类需要具备以下两个条件:
- 实现Cloneable接口。在java语言有一个Cloneable接口,它的作用只有一个,就是在运行时通知虚拟机可以安全地在实现了此接口的类上使用clone方法。在java虚拟机中,只有实现了这个接口的类才可以被拷贝,否则在运行时会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常。
- 重写Object类中的clone方法。Java中,所有类的父类都是Object类,Object类中有一个clone方法,作用是返回对象的一个拷贝,但是其作用域protected类型的,一般的类无法调用,因此,Prototype类需要将clone方法的作用域修改为public类型。
三、实现
namespace DesignPatterns.Prototype{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<string> executors = new List<string>(); executors.Add("张三"); executors.Add("李四"); Plan plan = new Plan(); plan.SetName("重构前端登录界面"); plan.SetLevel(1); plan.SetStartdate(DateTime.Parse("2017-08-07")); plan.SetEnddate(DateTime.Parse("2017-08-09")); plan.SetExecutors(executors); Plan plan2 = plan.Clone(); plan2.SetName("后端接口改造"); plan2.SetLevel(2); plan2.SetStartdate(DateTime.Parse("2017-08-10")); plan2.SetEnddate(DateTime.Parse("2017-08-12")); Console.WriteLine("地址是否一样?" + (plan == plan2)); Console.WriteLine("plan.getName() == plan2.getName() " + (plan.GetName() == plan2.GetName())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getLevel() == plan2.getLevel() " + (plan.GetLevel() == plan2.GetLevel())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getStartdate() == plan2.getStartdate() " + (plan.GetStartdate() == plan2.GetStartdate())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getEnddate() == plan2.getEnddate() " + (plan.GetEnddate() == plan2.GetEnddate())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getExecutors() == plan2.getExecutors() " + (plan.GetExecutors() == plan2.GetExecutors())); Console.WriteLine("plan:" + plan.toString()); Console.WriteLine("plan2:" + plan2.toString()); //plan任务比较重,在给plan添加一个人 executors.Add("王五"); plan.SetExecutors(executors); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("地址是否一样?" + (plan == plan2)); Console.WriteLine("plan.getName() == plan2.getName() " + (plan.GetName() == plan2.GetName())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getLevel() == plan2.getLevel() " + (plan.GetLevel() == plan2.GetLevel())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getStartdate() == plan2.getStartdate() " + (plan.GetStartdate() == plan2.GetStartdate())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getEnddate() == plan2.getEnddate() " + (plan.GetEnddate() == plan2.GetEnddate())); Console.WriteLine("plan.getExecutors() == plan2.getExecutors() " + (plan.GetExecutors() == plan2.GetExecutors())); Console.WriteLine("plan:" + plan.toString()); Console.WriteLine("plan2:" + plan2.toString()); } } /** * 计划 * 【浅拷贝】 */ public class Plan { //计划名称 private string _name; //任务级别 private int _level; //开始时间 private DateTime _startdate; //截止时间 private DateTime _enddate; //执行人员 private List<string> _executors = new List<string>(); public Plan Clone() { return this; } public string GetName() { return _name; } public void SetName(string name) { this._name = name; } public DateTime GetStartdate() { return _startdate; } public void SetStartdate(DateTime startdate) { this._startdate = startdate; } public DateTime GetEnddate() { return _enddate; } public void SetEnddate(DateTime enddate) { this._enddate = enddate; } public List<string> GetExecutors() { return _executors; } public void SetExecutors(List<string> executors) { this._executors = executors; } public int GetLevel() { return _level; } public void SetLevel(int level) { this._level = level; } public string toString() { return "[name=" + _name + ", level=" + _level + ", startdate=" + _startdate + ", enddate=" + _enddate + ", executors=" + _executors + "]"; } }}
四、适用场景
1、资源优化场景。
2、类初始化需要消化非常多的资源,这个资源包括数据、硬件资源等。
3、性能和安全要求的场景。
4、通过 new 产生一个对象需要非常繁琐的数据准备或访问权限,则可以使用原型模式。
5、一个对象多个修改者的场景。
6、一个对象需要提供给其他对象访问,而且各个调用者可能都需要修改其值时,可以考虑使用原型模式拷贝多个对象供调用者使用。
7、在实际项目中,原型模式很少单独出现,一般是和工厂方法模式一起出现,通过 clone 的方法创建一个对象,然后由工厂方法提供给调用者。
注意事项:与通过对一个类进行实例化来构造新对象不同的是,原型模式是通过拷贝一个现有对象生成新对象的。浅拷贝实现 Cloneable,重写,深拷贝是通过实现 Serializable 读取二进制流。
五、优缺点
优点:
1、对客户端隐藏具体的实现类型:原型模式的客户端,只知道原型接口的类型,并不知道具体的实现类型,从而减少了客户端对这些具体实现类型的依赖。
2、在运行时动态改变具体的实现类型:原型模式可以在运行期间,由客户来注册符合原型接口的实现类型,也可以动态的改变具体的实现类型,看起来接口没有任何变化,但其实运行的已经是另外一个类实例了。因为克隆一个原型就类似于实例化一个类。
缺点:
深度克隆方法实现会比较困难:原型模式最大的缺点就在于每个原型的子类都必须实现clone的操作,尤其在包含引用类型的对象时,clone方法会比较麻烦,必须要能够递归的让所有的相关对象都要正确的实现克隆。
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/JsonShare/p/7300124.html
http://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/prototype-pattern.html
欢迎阅读本系列文章:Head First设计模式之目录
Head First设计模式之原型模式
