首页 > 代码库 > 2017-4-30-Train:Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2)
2017-4-30-Train:Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2)
The country of Byalechinsk is running elections involving n candidates. The country consists of m cities. We know how many people in each city voted for each candidate.
The electoral system in the country is pretty unusual. At the first stage of elections the votes are counted for each city: it is assumed that in each city won the candidate who got the highest number of votes in this city, and if several candidates got the maximum number of votes, then the winner is the one with a smaller index.
At the second stage of elections the winner is determined by the same principle over the cities: the winner of the elections is the candidate who won in the maximum number of cities, and among those who got the maximum number of cities the winner is the one with a smaller index.
Determine who will win the elections.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100) — the number of candidates and of cities, respectively.
Each of the next m lines contains n non-negative integers, the j-th number in the i-th line a**ij (1 ≤ j ≤ n, 1 ≤ i ≤ m, 0 ≤ a**ij ≤ 109) denotes the number of votes for candidate j in city i.
It is guaranteed that the total number of people in all the cities does not exceed 109.
Output
Print a single number — the index of the candidate who won the elections. The candidates are indexed starting from one.
Examples
input
3 31 2 32 3 11 2 1
output
2
input
3 410 10 35 1 62 2 21 5 7
output
1
Note
Note to the first sample test. At the first stage city 1 chosen candidate 3, city 2 chosen candidate 2, city 3 chosen candidate 2. The winner is candidate 2, he gained 2 votes.
Note to the second sample test. At the first stage in city 1 candidates 1 and 2 got the same maximum number of votes, but candidate 1 has a smaller index, so the city chose candidate 1. City 2 chosen candidate 3. City 3 chosen candidate 1, due to the fact that everyone has the same number of votes, and 1 has the smallest index. City 4 chosen the candidate 3. On the second stage the same number of cities chose candidates 1 and 3. The winner is candidate 1, the one with the smaller index.
Means:
有n个候选人和m个城市,现在要从m个城市中的选票中选取得票最高的候选人,如果在一个城市中两个候选人得到的票数是相同的且是最高的,那么标号小的候选人获胜,如果m个城市中选出的候选人的中有票数最高且相同的,依旧选标号最小的。
Solve:
直接记录每次一哪个最高然后最后直接判断?个中哪个最高就好了

1 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:36777216") 2 3 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define LSON id << 1 , l , mid 6 #define RSON id << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r 7 #define ROOT 1 , 1 , n 8 #define CLR(x , y) memset(x , y , sizeof(x)) 9 #define LOWBIT(x) x & (-x)10 #define FORN(i , a , n) for(int i = (a) ; i <= (n) ; ++i)11 #define FORP(i , n , a) for(int i = (n) ; i >= (a) ; --i)12 #define CASE(x) printf("Case %d: ", x)13 #define SFD(x) scanf("%lf" , &x)14 #define SFC(x) scanf(" %c" , &x)15 #define SFS(x) scanf(" %s" , x)16 #define SFI(x) scanf("%d" , &x)17 #define SFI64(x) scanf("%I64d" , &x)18 #define PFF(x) printf("%f" , x)19 #define PFD(x) printf("%lf" , x)20 #define PFI(x) printf("%d" , x)21 #define PFC(x) printf("%c" , x)22 #define PFS(x) printf("%s" , x)23 #define PFI64(x) printf("%I64d" , x)24 #define SPACE printf(" ")25 #define PUT puts("")26 #define LPUP(i , j , k) for(int i = j ; i <= k ; ++i)27 #define LPDW(i , j , k) for(int i = j ; i >= k ; --i)28 #define PB(x) push_back(x)29 #define ALL(A) A.begin(), A.end()30 #define SZ(A) int((A).size())31 #define LBD(A, x) (lower_bound(ALL(A), x) - A.begin())32 #define UBD(A, x) (upper_bound(ALL(A), x) - A.begin())33 #define LOCAL34 static const double PI = acos(-1.0);35 static const double EPS = 1e-8;36 static const int INF = 0X3fffffff;37 typedef __int64 LL;38 typedef double DB;39 template<class T> inline40 T read(T &x)41 {42 x = 0;43 int f = 1 ; char ch = getchar();44 while (ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘) {if (ch == ‘-‘) f = -1; ch = getchar();}45 while (ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘) {x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘; ch = getchar();}46 x *= f;47 }48 49 /************************Little Pea****************************/50 51 static const int MAXN = 110;52 LL vis[MAXN];53 int main()54 {55 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE56 freopen("D:\\系统优化\\Desktop\\littlepea\\in.data" , "r" , stdin);57 #endif58 int n , m;59 LL x;60 read(n);read(m);61 LPUP(i , 1 , m)62 {63 LL mx = -1;64 int pos = -1;65 LPUP(j , 1 , n)66 {67 read(x);68 if(x > mx)69 {70 mx = x;71 pos = j;72 }73 }74 ++vis[pos];75 }76 LL mx = -1;77 int pos = -1;78 LPUP(i , 1 , n)79 {80 if(vis[i] > mx)81 {82 pos = i;83 mx = vis[i];84 }85 }86 PFI(pos);87 88 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE89 fclose(stdin), fclose(stdout);90 #endif91 }
One day Misha and Andrew were playing a very simple game. First, each player chooses an integer in the range from 1 to n. Let‘s assume that Misha chose number m, and Andrew chose number a.
Then, by using a random generator they choose a random integer c in the range between 1 and n (any integer from 1 to n is chosen with the same probability), after which the winner is the player, whose number was closer to c. The boys agreed that if m and a are located on the same distance from c, Misha wins.
Andrew wants to win very much, so he asks you to help him. You know the number selected by Misha, and number n. You need to determine which value of a Andrew must choose, so that the probability of his victory is the highest possible.
More formally, you need to find such integer a (1 ≤ a ≤ n), that the probability that 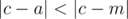 is maximal, where c is the equiprobably chosen integer from 1 to n (inclusive).
is maximal, where c is the equiprobably chosen integer from 1 to n (inclusive).
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 109) — the range of numbers in the game, and the number selected by Misha respectively.
Output
Print a single number — such value a, that probability that Andrew wins is the highest. If there are multiple such values, print the minimum of them.
Examples
input
3 1
output
2
input
4 3
output
2
Note
In the first sample test: Andrew wins if c is equal to 2 or 3. The probability that Andrew wins is 2 / 3. If Andrew chooses a = 3, the probability of winning will be 1 / 3. If a = 1, the probability of winning is 0.
In the second sample test: Andrew wins if c is equal to 1 and 2. The probability that Andrew wins is 1 / 2. For other choices of a the probability of winning is less.


1 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:36777216") 2 3 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define LSON id << 1 , l , mid 6 #define RSON id << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r 7 #define ROOT 1 , 1 , n 8 #define CLR(x , y) memset(x , y , sizeof(x)) 9 #define LOWBIT(x) x & (-x)10 #define FORN(i , a , n) for(int i = (a) ; i <= (n) ; ++i)11 #define FORP(i , n , a) for(int i = (n) ; i >= (a) ; --i)12 #define CASE(x) printf("Case %d: ", x)13 #define SFD(x) scanf("%lf" , &x)14 #define SFC(x) scanf(" %c" , &x)15 #define SFS(x) scanf(" %s" , x)16 #define SFI(x) scanf("%d" , &x)17 #define SFI64(x) scanf("%I64d" , &x)18 #define PFF(x) printf("%f" , x)19 #define PFD(x) printf("%lf" , x)20 #define PFI(x) printf("%d" , x)21 #define PFC(x) printf("%c" , x)22 #define PFS(x) printf("%s" , x)23 #define PFI64(x) printf("%I64d" , x)24 #define SPACE printf(" ")25 #define PUT puts("")26 #define LPUP(i , j , k) for(int i = j ; i <= k ; ++i)27 #define LPDW(i , j , k) for(int i = j ; i >= k ; --i)28 #define PB(x) push_back(x)29 #define ALL(A) A.begin(), A.end()30 #define SZ(A) int((A).size())31 #define LBD(A, x) (lower_bound(ALL(A), x) - A.begin())32 #define UBD(A, x) (upper_bound(ALL(A), x) - A.begin())33 #define LOCAL34 static const double PI = acos(-1.0);35 static const double EPS = 1e-8;36 static const int INF = 0X3fffffff;37 typedef __int64 LL;38 typedef double DB;39 template<class T> inline40 T read(T &x)41 {42 x = 0;43 int f = 1 ; char ch = getchar();44 while (ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘) {if (ch == ‘-‘) f = -1; ch = getchar();}45 while (ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘) {x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘; ch = getchar();}46 x *= f;47 }48 49 /************************Little Pea****************************/50 51 int n , m;52 int main()53 {54 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE55 freopen("D:\\系统优化\\Desktop\\littlepea\\in.data" , "r" , stdin);56 #endif57 read(n);read(m);58 if(n == 1 && m == 1)59 {60 puts("1");61 return 0;62 }63 int mid = n >> 1;64 if(m > mid)65 {66 PFI(m - 1);67 }68 else69 {70 PFI(m + 1);71 }72 73 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE74 fclose(stdin), fclose(stdout);75 #endif76 }
C. Replacement(模拟)
Daniel has a string s, consisting of lowercase English letters and period signs (characters ‘.‘). Let‘s define the operation of replacementas the following sequence of steps: find a substring ".." (two consecutive periods) in string s, of all occurrences of the substring let‘s choose the first one, and replace this substring with string ".". In other words, during the replacement operation, the first two consecutive periods are replaced by one. If string s contains no two consecutive periods, then nothing happens.
Let‘s define f(s) as the minimum number of operations of replacement to perform, so that the string does not have any two consecutive periods left.
You need to process m queries, the i-th results in that the character at position x**i (1 ≤ x**i ≤ n) of string s is assigned value c**i. After each operation you have to calculate and output the value of f(s).
Help Daniel to process all queries.
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300 000) the length of the string and the number of queries.
The second line contains string s, consisting of n lowercase English letters and period signs.
The following m lines contain the descriptions of queries. The i-th line contains integer x**i and c**i (1 ≤ x**i ≤ n, c**i — a lowercas English letter or a period sign), describing the query of assigning symbol c**i to position x**i.
Output
Print m numbers, one per line, the i-th of these numbers must be equal to the value of f(s) after performing the i-th assignment.
Examples
input
10 3.b..bz....1 h3 c9 f
output
431
input
4 4.cc.2 .3 .2 a1 a
output
1311
Note
Note to the first sample test (replaced periods are enclosed in square brackets).
The original string is ".b..bz....".
after the first query f(hb..bz....) = 4 ("hb[..]bz...." → "hb.bz[..].." → "hb.bz[..]." → "hb.bz[..]" → "hb.bz.")
after the second query f(hbс.bz....) = 3 ("hbс.bz[..].." → "hbс.bz[..]." → "hbс.bz[..]" → "hbс.bz.")
after the third query f(hbс.bz..f.) = 1 ("hbс.bz[..]f." → "hbс.bz.f.")
Note to the second sample test.
The original string is ".cc.".
after the first query: f(..c.) = 1 ("[..]c." → ".c.")
after the second query: f(....) = 3 ("[..].." → "[..]." → "[..]" → ".")
after the third query: f(.a..) = 1 (".a[..]" → ".a.")
after the fourth query: f(aa..) = 1 ("aa[..]" → "aa.")

Code:

1 #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:36777216") 2 3 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define LSON id << 1 , l , mid 6 #define RSON id << 1 | 1 , mid + 1 , r 7 #define ROOT 1 , 1 , n 8 #define CLR(x , y) memset(x , y , sizeof(x)) 9 #define LOWBIT(x) x & (-x) 10 #define FORN(i , a , n) for(int i = (a) ; i <= (n) ; ++i) 11 #define FORP(i , n , a) for(int i = (n) ; i >= (a) ; --i) 12 #define CASE(x) printf("Case %d: ", x) 13 #define SFD(x) scanf("%lf" , &x) 14 #define SFC(x) scanf(" %c" , &x) 15 #define SFS(x) scanf(" %s" , x) 16 #define SFI(x) scanf("%d" , &x) 17 #define SFI64(x) scanf("%I64d" , &x) 18 #define PFF(x) printf("%f" , x) 19 #define PFD(x) printf("%lf" , x) 20 #define PFI(x) printf("%d" , x) 21 #define PFC(x) printf("%c" , x) 22 #define PFS(x) printf("%s" , x) 23 #define PFI64(x) printf("%I64d" , x) 24 #define SPACE printf(" ") 25 #define PUT puts("") 26 #define LPUP(i , j , k) for(int i = j ; i <= k ; ++i) 27 #define LPDW(i , j , k) for(int i = j ; i >= k ; --i) 28 #define PB(x) push_back(x) 29 #define ALL(A) A.begin(), A.end() 30 #define SZ(A) int((A).size()) 31 #define LBD(A, x) (lower_bound(ALL(A), x) - A.begin()) 32 #define UBD(A, x) (upper_bound(ALL(A), x) - A.begin()) 33 #define LOCAL 34 static const double PI = acos(-1.0); 35 static const double EPS = 1e-8; 36 static const int INF = 0X3fffffff; 37 typedef __int64 LL; 38 typedef double DB; 39 template<class T> inline 40 T read(T &x) 41 { 42 x = 0; 43 int f = 1 ; char ch = getchar(); 44 while (ch < ‘0‘ || ch > ‘9‘) {if (ch == ‘-‘) f = -1; ch = getchar();} 45 while (ch >= ‘0‘ && ch <= ‘9‘) {x = x * 10 + ch - ‘0‘; ch = getchar();} 46 x *= f; 47 } 48 49 /************************Little Pea****************************/ 50 51 static const int MAXN = 3e5 + 10; 52 char a[MAXN]; 53 int n , m; 54 int ans; 55 int main() 56 { 57 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE 58 freopen("D:\\系统优化\\Desktop\\littlepea\\in.data" , "r" , stdin); 59 #endif 60 read(n);read(m); 61 SFS(a + 1); 62 LPUP(i , 2 , n) 63 { 64 if(a[i] == ‘.‘ && a[i - 1] == ‘.‘) 65 { 66 ++ans; 67 } 68 } 69 int p; 70 while(m--) 71 { 72 SFI(p); 73 char ch[5] = {‘\0‘}; 74 scanf("%s" , ch + 1); 75 if((a[p] == ‘.‘ && ch[1] == ‘.‘) || (a[p] != ‘.‘ && ch[1] != ‘.‘)); 76 else 77 { 78 if(ch[1] == ‘.‘) 79 { 80 if(p != 1 && a[p-1] == ‘.‘) 81 ans++; 82 if(p != n && a[p+1] == ‘.‘) 83 ans++; 84 } 85 else 86 { 87 if(p != 1 && a[p-1] == ‘.‘) 88 ans--; 89 if(p != n && a[p+1] == ‘.‘) 90 ans--; 91 } 92 } 93 a[p] = ch[1]; 94 PFI(ans);PUT; 95 } 96 97 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE 98 fclose(stdin), fclose(stdout); 99 #endif100 }
2017-4-30-Train:Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2)

