首页 > 代码库 > RHEL7.0 防火墙入门
RHEL7.0 防火墙入门
最近手痒,翻出来新出的(其实已经下载了很长时间的)RHEL7.0鼓捣了一下。
7.0有啥更新,自己问度娘了。
我今天要扯扯的是防火墙的部分,没办法,谁叫他常用来着。当然,如果你从来就是disabled,那绕行,省着浪费时间。
安装
如果系统您老人家是下一步、下一步安装的话,恭喜你,你是最小化安装的滴,没桌面环境(我刚开始也是没注意),当然,防火墙也是默认安上了,只是没有图形的配置工具filewall-cofig。
如果干脆安装的时候就没选,也没关系,请yum来帮忙。
安装firewalld
yum install firewalld yum install firewall-config 这是桌面下的配置工具
这就行了,就是这么任性。
禁用
问题来了,你就是不想学,非得要用iptables
那也没问题。
首先停用 systemctl disable firewalld systemctl stop firewalld
然后安装iptables服务 yum install iptables-services
启用iptables systemctl start iptables systemctl start ip6tables systemctl enable iptables systemctl enable ip6tables
关于systemctl(新的管理系统的工具集),有时间再吐槽。
好了,iptables回来了,当然我还是希望你别这么做,其实firewall的底层还是基于iptables的。
如下图
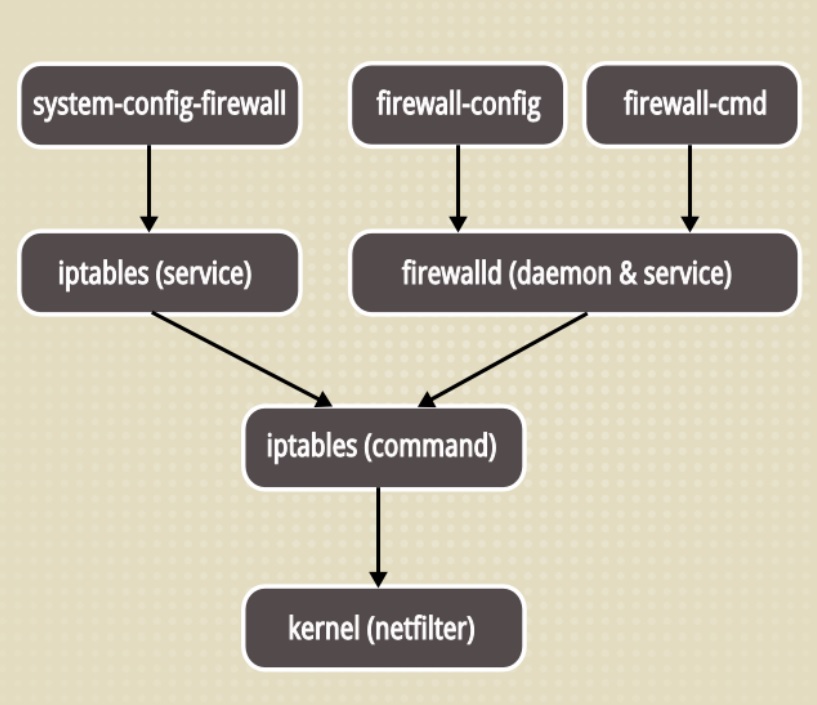
再罗嗦两句,如果要启用,那你就
systemctl start firewalld systemctl enable firewalld
如果想看看到底是啥状态,那就
[root@localhost zones]# systemctl is-active firewalld active 或者 [root@localhost zones]# systemctl status firewalld 这里就能看到systemctl工具牛B的地方了。 firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2014-11-03 01:57:52 CST; 1 weeks 1 days ago Main PID: 1845 (firewalld) CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service └─1845 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid Nov 03 01:57:51 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon... Nov 03 01:57:52 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon. 或者 [root@localhost zones]# firewall-cmd --state running
配置方式
有3种:
1、命令行方式
firewall-cmd,只要你装的firewall软件包,就已经集成了此工具,推荐方式。
2、图形方式
firewall-config,这个就不多说了,安装了桌面环境默认就有了。
3、直接编辑配置文件。
新的firewall的配置都是以xml文件的形式存在。
系统模板文件保存在/usr/lib/firewalld目录
[root@localhost firewalld]# ls icmptypes services zones 三个目录 [root@localhost services]# ls 下面是一堆内置的配置 amanda-client.xml ipp-client.xml mysql.xml rpc-bind.xml bacula-client.xml ipp.xml nfs.xml samba-client.xml bacula.xml ipsec.xml ntp.xml samba.xml dhcpv6-client.xml kerberos.xml openvpn.xml smtp.xml dhcpv6.xml kpasswd.xml pmcd.xml ssh.xml dhcp.xml ldaps.xml pmproxy.xml telnet.xml dns.xml ldap.xml pmwebapis.xml tftp-client.xml ftp.xml libvirt-tls.xml pmwebapi.xml tftp.xml high-availability.xml libvirt.xml pop3s.xml transmission-client.xml https.xml mdns.xml postgresql.xml vnc-server.xml http.xml mountd.xml proxy-dhcp.xml wbem-https.xml imaps.xml ms-wbt.xml radius.xml
用户创建或是系统修改的配置保存在/etc/firewalld/目录下面。如果你发现这个目录下面啥也没有,不要惊讶,你使用的是默认设置。
[root@localhost firewalld]# ls .conf那个文件是主配置文件 firewalld.conf icmptypes lockdown-whitelist.xml services zones [root@localhost services]# ls 看到了没,下面毛线都没有 [root@localhost services]# [root@localhost zones]# ls 这个目录就有东东,因为我把ipv6客户端的连接给默认禁用了。忘了说了,系统默认安装完成,只开了ssh与ipv6连接 public.xml public.xml.old
cat /etc/firewalld/firewalld.conf 主配置文件是这个样子滴 # firewalld config file # default zone # The default zone used if an empty zone string is used. # Default: public DefaultZone=public 这块是默认区域,下面马上说这块。 # Minimal mark # Marks up to this minimum are free for use for example in the direct # interface. If more free marks are needed, increase the minimum # Default: 100 MinimalMark=100 # Clean up on exit # If set to no or false the firewall configuration will not get cleaned up # on exit or stop of firewalld # Default: yes CleanupOnExit=yes # Lockdown # If set to enabled, firewall changes with the D-Bus interface will be limited # to applications that are listed in the lockdown whitelist. # The lockdown whitelist file is lockdown-whitelist.xml # Default: no Lockdown=no # IPv6_rpfilter # Performs a reverse path filter test on a packet for IPv6. If a reply to the # packet would be sent via the same interface that the packet arrived on, the # packet will match and be accepted, otherwise dropped. # The rp_filter for IPv4 is controlled using sysctl. # Default: yes IPv6_rpfilter=yes
啥是区域(zone)
zone这概念windows7开始也有,没发现的,自己找找。
比如你可以指定,从网卡A来的访问,一律都不响应;从网卡B来的访问,只返回ping请求。。。
说白了,就是内置的一些规则配置文件,用来给懒人们用的。
系统默认的zone有9个(从不信任到信任的顺序排序),列表如下:
drop
出去行,进来不行,即使你手工开放了访问,也不行。
block
和上面差不多,虽然也是拒绝访问,但至少告诉人家一声(返回 IPv4 的 icmp-host-prohibited 报文或者 IPv6 的 icmp6-adm-prohibited 报文)。当然,仅仅由系统初始化的网络连接才行。
public(默认)
这是默认的,看上一节的配置文件。
要是用了这个配置,就是告诉人家,你们都是坏人,只有我说你是好人,才是好人。
external
官方文档说这个是用在路由器等启用伪装的外部网络。
dmz
这个区域是说,你相信你们这群人中,还是有几个好人的,但都得听我指挥哈。
work
这个区域是说,我相信你们大多数人都是好同志哈,一号取款机不用密码,连过来吧。
home
和上面的类似
internal
和上面的类似
trusted
啥也不管,谁想进,想出都成。
你要问我细节上有啥区域,真没详细研究过,我只是觉得,相信所有人都是坏人吧,不需要开放的,一率不开放。
配置zone
查看zone设置
要想什么,当前是用的啥子zone,2招
查看/etc/firewalld/firewalld.conf配置文件里面的DefaultZone设置项,见上面的内容
或者用下面的命令
[root@localhost zones]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone 这种命令,喜欢啊,好记 public
当然还可以用图形工具firewall-config,我推荐还是用firewall-cmd,那样显示啥牛B啊,嘿嘿
修改zone设置
2种方式,或者说3种,图形不再费话了(以下说的都是命令哈)。
第1种,还是改那个配置文件。
第2种,下面这样
[root@localhost zones]# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=work success [root@localhost zones]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone work
服务与端口
这可能是我们配防火墙做的最多的事啦。
那,下回再说吧。。。
待续
本文出自 “@” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://moyung.blog.51cto.com/3154631/1576984
RHEL7.0 防火墙入门
