首页 > 代码库 > VC++编程之第二课笔记
VC++编程之第二课笔记
第二课 C++的继承封装多态
简单类型转换
int型转换为char型,会发生截断,丢失精度(3Bytes),有警告。
char型转换位int型,不会发生截断,没有警告。
父类子类的类型转换
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
public:
Animal(){} //构造函数重载
Animal(int height, int weight){} //构造函数有参数
void eat()
{
cout<<"Animal eat"<<endl;
}
void sleep()
{
cout<<"Animal sleep"<<endl;
}
void breathe()
{
cout<<"Animal breathe"<<endl;
}
};
class Fish : public Animal
{
public:
Fish():Animal(150,200),a(1){} //可以如此给类中常量赋初值以及传递基类构造函数的参数
void breathe() //函数的覆盖(子类父类间)
{
// Animal::breathe(); //可通过此种方式继续调用父类函数
cout<<"Fish bubble"<<endl;
}
private:
const int a;
};
void fun(Animal* pAn)
{
pAn->breathe();
}
void main()
{
Fish fh;
Animal* pAn;
pAn = &fh; //父类子类类型转换
fun(pAn);
}运行结果(调用父类的breathe()函数):
Animal breathe Press any key to continue
Fish对象内存布局:


由此可知:Fish对象的指针转换为Animal对象的指针时,会发生截断,后面的“Fish继承部分”内存丢失。
虚函数(多态性)
此时,若想显示结果为Fish的呼吸,可以在以前的代码基础上,在Animal的breathe()函数前面加上Virtual标识符:
virtual void breathe()
{
cout<<"Animal breathe"<<endl;
}结果:
Fish bubble Press any key to continue
注意:子类继承父类时,不管前面有没有加virtual,breathe()这个函数都是虚函数。
多态性
当C++编译器在编译的时候,发现Animal类的
breathe()函数是虚函数,这个时候C++就会采用迟绑定(late binding)的技术,在运行时,依据对象的类型(在程序中,我们传递的Fish类对象的地址)来确认调用的哪一个函数,这种能力就叫做C++的多态性。
纯虚函数与抽象类
如果将再修改一下上面的代码:
virtual void breathe()=0;
那么这个函数就是纯虚函数,而与此对应的Animal类就是抽象类。
抽象类不能实例化对象,只能作为基类为派生类服务。
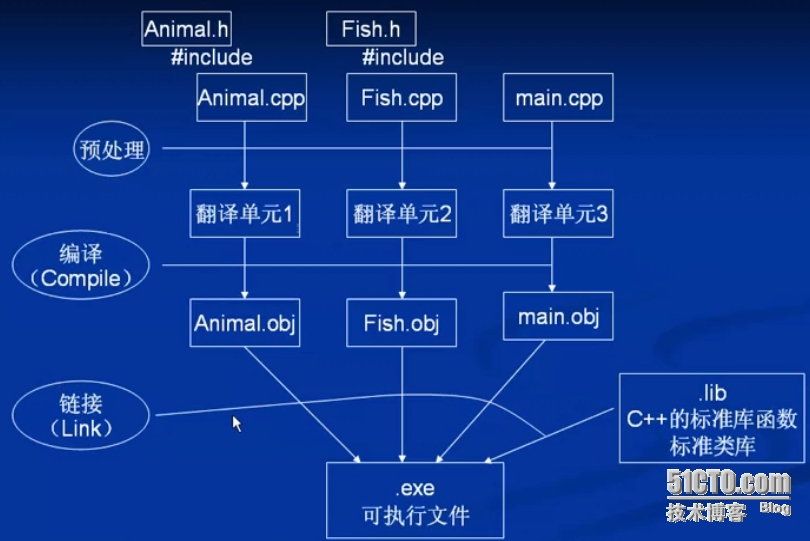
VC++程序编译链接原理及过程
图示:
本文出自 “zero4eva” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://zero4eva.blog.51cto.com/7558298/1581244
VC++编程之第二课笔记
声明:以上内容来自用户投稿及互联网公开渠道收集整理发布,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任,若内容有误或涉及侵权可进行投诉: 投诉/举报 工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
