首页 > 代码库 > MariaDB 10 (MySQL DB) 多主复制并实现读写分离
MariaDB 10 (MySQL DB) 多主复制并实现读写分离
----本文大纲
-
简介
-
资源配置
-
拓扑图
-
实现过程
一、简介
MMM 即Master-Master Replication Manager for MySQL(mysql主主复制管理器)关于mysql主主复制配置的监控、故障转移和管理的一套可伸缩的脚本套件(在任何时候只有一个节点可以被写 入),这个套件也能对居于标准的主从配置的任意数量的从服务器进行读负载均衡,所以你可以用它来在一组居于复制的服务器启动虚拟ip,除此之外,它还有实 现数据备份、节点之间重新同步功能的脚本。MySQL本身没有提供replication failover的解决方案,通过MMM方案能实现服务器的故障转移,从而实现mysql的高可用。MMM不仅能提供浮动IP的功能,更可贵的是如果当前 的主服务器挂掉后,会将你后端的从服务器自动转向新的主服务器进行同步复制,不用手工更改同步配置。这个方案是目前比较成熟的解决方案。
优点:安全性、稳定性高,可扩展性好,高可用,当主服务器挂掉以后,另一个主立即接管,其他的从服务器能自动切换,不用人工干预。
缺点:至少三个节点,对主机的数量有要求,需要实现读写分离,对程序来说是个挑战。
主从复制原理:
第一步是在主库上记录二进制日志(稍后介绍如何设置)。在每次准备提交事务完成数 据更新前,主库将数据更新的事件记录到二进制日志中。MySQL会按事务提交的顺序 而非每条语句的执行顺序来记录二进制日志。在记录二进制日志后,主库会告诉存储引 擎可以提交事务了。 _
下一步,备库将主库的二进制日志复制到其本地的中继日志中。首先,备库会启动一个 工作线程,称为I/O线程,I/O线程跟主库建立一个普通的客户端连接,然后在主库上启 动一个特殊的二进制转储(binhg dump、线程(该线程没有对应的SQL命令),这个二 进制转储线程会读取主库上二进制日志中的事件。它不会对事件进行轮询。如果该线程 追赶上了主库,它将进入睡眠状态,直到主库发送信号量通知其有新的事件产生时才会 被唤醒,备库I/O线程会将接收到的事件记录到中继日志中。
备库的SQL线程执行最后一步,该线程从中继日志中读取事件并在备库执行,从而实现 备库数据的更新。当SQL线程追赶上I/O线程时,中继日志通常已经在系统缓存中,所 以中继日志的开销很低。SQL线程执行的事件也可以通过配置选项来决定是否写入其自 己的二进制日志中,它对于我们稍后提到的场景非常有用。这种复制架构实现了获取事件和重放事件的解耦,允许这两个过程异步进行。也就是说 I/o线程能够独立于SQL线程之外工作。但这种架构也限制了复制的过程,其中最重要 的一点是在主库上并发运行的査询在备库只能串行化执行,因为只有一个SQL线程来重 放中继日志中的事件。后面我们将会看到,这是很多工作负载的性能瓶颈所在。虽然有 一些针对该问题的解决方案,但大多数用户仍然受制于单线程。
二、资源配置
-
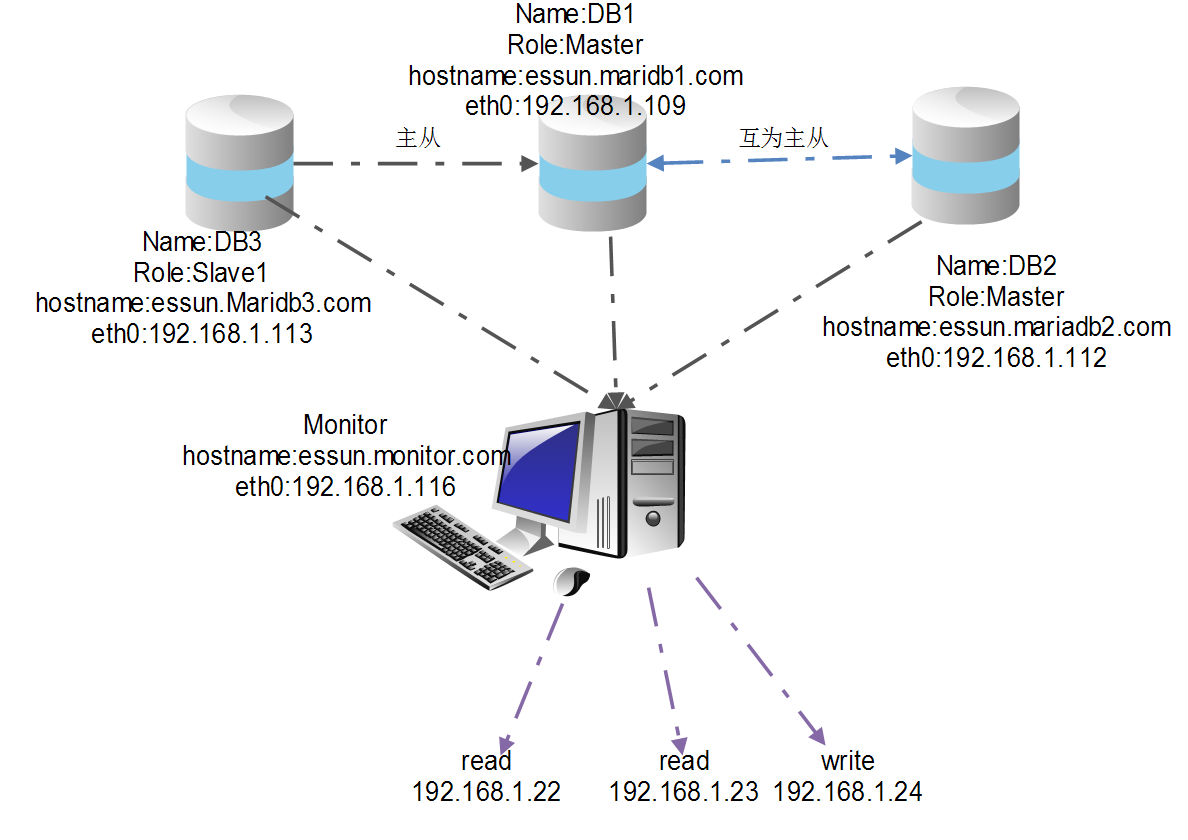
主机属性
| 系统 | 名字 | 角色 | 主机名 | ip地址 | 关系 |
| Centos6.5x86_64 | DB1 | Master | essun.mariadb1.com | 192.168.1.109 | 与DB2互为主从 |
| Centos6.5x86_64 | DB2 | Master | essun.mariadb2.com | 192.168.1.112 | 与DB1互为主从 |
| Centos6.5x86_64 | DB3 | Slave | essun.mariadb3.com | 192.168.1.113 | DB1的从库 |
| Centos6.5x86_64 | Monitor | Monitor | essun.monitor.com | 192.168.1.116 | 监控所有主机 |
-
虚拟ip(VIP)
DB1 192.168.1.109 192.168.1.24
DB2 192.168.1.112 192.168.1.24,192.168.1.22
DB3 192.168.1.113 192.168.1.23
三、拓扑图
要在MySQL 5.6中使用复制功能,其服务配置段[mysqld]中于少应该定义如下选项:
binlog-format:二进制日志的格式,有row、statement和mixed几种类型;以下binlog-format的详细介绍: 从 MySQL 5.1.12 开始,可以用以下三种模式来实现:基于SQL语句的复制(statement-based replication, SBR),基于行的复制(row-based replication, RBR),混合模式复制(mixed-based replication, MBR)。相应地,binlog的格式也有三种:STATEMENT,ROW,MIXED。MBR 模式中,SBR 模式是默认的。 在运行时可以动态低改变binlog的格式,除了以下几种情况: 存储过程或者触发器中间 启用了NDB 当前会话试用 RBR 模式,并且已打开了临时表 如果binlog采用了 MIXED 模式,那么在以下几种情况下会自动将binlog的模式由 SBR 模式改成 RBR 模式。 当DML语句更新一个NDB表时 当函数中包含 UUID() 时 2个及以上包含 AUTO_INCREMENT 字段的表被更新时 行任何 INSERT DELAYED 语句时 用 UDF 时 视图中必须要求使用 RBR 时,例如创建视图是使用了 UUID() 函数 设定主从复制模式的方法非常简单,只要在以前设定复制配置的基础上,再加一个参数: binlog_format="STATEMENT" #binlog_format="ROW" #binlog_format="MIXED" 当然了,也可以在运行时动态修改binlog的格式。例如 mysql> SET SESSION binlog_format = ‘STATEMENT‘; mysql> SET SESSION binlog_format = ‘ROW‘; mysql> SET SESSION binlog_format = ‘MIXED‘; mysql> SET GLOBAL binlog_format = ‘STATEMENT‘; mysql> SET GLOBAL binlog_format = ‘ROW‘; mysql> SET GLOBAL binlog_format = ‘MIXED‘; 现在来比较以下 SBR 和 RBR 2中模式各自的优缺点: SBR 的优点: 历史悠久,技术成熟 binlog文件较小 binlog中包含了所有数据库更改信息,可以据此来审核数据库的安全等情况 binlog可以用于实时的还原,而不仅仅用于复制 主从版本可以不一样,从服务器版本可以比主服务器版本高 SBR 的缺点: 不是所有的UPDATE语句都能被复制,尤其是包含不确定操作的时候。 调用具有不确定因素的 UDF 时复制也可能出问题 使用以下函数的语句也无法被复制: * LOAD_FILE() * UUID() * USER() * FOUND_ROWS() * SYSDATE() (除非启动时启用了 --sysdate-is-now 选项) INSERT ... SELECT 会产生比 RBR 更多的行级锁 复制需要进行全表扫描(WHERE 语句中没有使用到索引)的 UPDATE 时,需要比 RBR 请求更多的行级锁 对于有 AUTO_INCREMENT 字段的 InnoDB表而言,INSERT 语句会阻塞其他 INSERT 语句 对于一些复杂的语句,在从服务器上的耗资源情况会更严重,而 RBR 模式下,只会对那个发生变化的记录产生影响 存储函数(不是存储过程)在被调用的同时也会执行一次 NOW() 函数,这个可以说是坏事也可能是好事 确定了的 UDF 也需要在从服务器上执行 数据表必须几乎和主服务器保持一致才行,否则可能会导致复制出错 执行复杂语句如果出错的话,会消耗更多资源 RBR 的优点: 任何情况都可以被复制,这对复制来说是最安全可靠的 和其他大多数数据库系统的复制技术一样 多数情况下,从服务器上的表如果有主键的话,复制就会快了很多 复制以下几种语句时的行锁更少: * INSERT ... SELECT * 包含 AUTO_INCREMENT 字段的 INSERT * 没有附带条件或者并没有修改很多记录的 UPDATE 或 DELETE 语句 执行 INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE 语句时锁更少 从服务器上采用多线程来执行复制成为可能 RBR 的缺点: binlog 大了很多 复杂的回滚时 binlog 中会包含大量的数据 主服务器上执行 UPDATE 语句时,所有发生变化的记录都会写到 binlog 中,而 SBR 只会写一次,这会导致频繁发生 binlog 的并发写问题 UDF 产生的大 BLOB 值会导致复制变慢 无法从 binlog 中看到都复制了写什么语句 当在非事务表上执行一段堆积的SQL语句时,最好采用 SBR 模式,否则很容易导致主从服务器的数据不一致情况发生 另外,针对系统库 mysql 里面的表发生变化时的处理规则如下: 如果是采用 INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE 直接操作表的情况,则日志格式根据 binlog_format 的设定而记录 如果是采用 GRANT,REVOKE,SET PASSWORD 等管理语句来做的话,那么无论如何都采用 SBR 模式记录 注:采用 RBR 模式后,能解决很多原先出现的主键重复问题。 需要注意的是:当设置隔离级别为READ-COMMITED必须设置二进制日志格式为ROW,现在MySQL官方认为STATEMENT这个已经不再适合继续使用;但mixed类型在默认的事务隔离级别下,可能会导致主从数据不一致; log-slave-updates、gtid-mode、enforce-gtid-consistency、report-port和report-host:用于启动GTID及满足附属的其它需求; master-info-repository和relay-log-info-repository:启用此两项,可用于实现在崩溃时保证二进制及从服务器安全的功能; sync-master-info:启用之可确保无信息丢失; slave-paralles-workers:设定从服务器的SQL线程数;0表示关闭多线程复制功能; binlog-checksum、master-verify-checksum和slave-sql-verify-checksum:启用复制有关的所有校验功能; binlog-rows-query-log-events:启用之可用于在二进制日志记录事件相关的信息,可降低故障排除的复杂度; log-bin:启用二进制日志,这是保证复制功能的基本前提;如果主服务器运行时没有启用--logs-bin,SHOW MASTER STATUS或mysqldump --master-data显示的日 志名和位置值为空。在这种情况下,当以后指定从服务器的日志文件和位置时需要使用的值为空字符串(‘‘) server-id:同一个复制拓扑中的所有服务器的id号必须唯一;这些ID值能唯一识别复制服务器群集中的每个服务器实例
四、实现过程
1、配置DB1
修改配置文件/etc/my.cnf,添加如下语句
server-id=1 log_bin=/mariadb/data/mysql-bin binlog_format=row log-slave-updates sync_binlog=1 auto_increment_increment=2 # 默认地,AUTO_INCREMENT 的开始值是 1,每条新记录递增 1。 auto_increment_offset=1
授权用户
MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to ‘repluser‘@‘192.168.1.112‘ identified by ‘replpass‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.12 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to ‘repluser‘@‘192.168.1.113‘ identified by ‘replpass‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
查看binlog日志标记
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mysql-bin.000003 | 756 | | | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2、配置DB2
修改配置文件/etc/my.cnf,添加如下语句
log-bin=mysql-bin binlog_format=ROW log-slave-updates sync_binlog=1 auto_increment_increment=2 auto_increment_offset=2 server-id=2
授权用户
MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to ‘repluser‘@‘192.168.1.109‘ identified by ‘replpass‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.15 sec)
查看binlog日志标记
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mysql-bin.000007 | 548 | | | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
连接DB1
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mysql-bin.000007 | 548 | | | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3、配置DB3
修改配置文件/etc/my.cnf添加如下语句
server-id=3 log-bin=mysql-bin log-slave-updates
relay-log=relay-log-bin
连接DB1
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host=‘192.168.1.109‘,master_user=‘repluser‘,master_password=‘replpass‘,master_log_file=‘mysql-bin.000003‘,master_log_pos=756; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> start slave; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: 192.168.1.109 Master_User: repluser Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000003 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 756 Relay_Log_File: relay-log-bin.000002 Relay_Log_Pos: 535 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000003 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes Replicate_Do_DB: Replicate_Ignore_DB: Replicate_Do_Table: Replicate_Ignore_Table: Replicate_Wild_Do_Table: Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table: Last_Errno: 0 Last_Error: Skip_Counter: 0 Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 756 Relay_Log_Space: 830 Until_Condition: None Until_Log_File: Until_Log_Pos: 0 Master_SSL_Allowed: Yes Master_SSL_CA_File: /etc/slave/cacert.pem Master_SSL_CA_Path: Master_SSL_Cert: /etc/slave/mysql.crt Master_SSL_Cipher: Master_SSL_Key: /etc/slave/mysql.key Seconds_Behind_Master: 0 Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: No Last_IO_Errno: 0 Last_IO_Error: Last_SQL_Errno: 0 Last_SQL_Error: Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids: Master_Server_Id: 1 Master_SSL_Crl: /etc/slave/cacert.pem Master_SSL_Crlpath: Using_Gtid: No Gtid_IO_Pos: 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
DB1连接DB2
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host=‘192.168.1.112‘,master_user=‘repluser‘,master_password=‘replpass‘,master_log_file=‘mysql-bin.000007‘,master_log_pos=548; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> start slave; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: 192.168.1.112 Master_User: repluser Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000007 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 548 Relay_Log_File: essun-relay-bin.000002 Relay_Log_Pos: 535 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000007 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes Replicate_Do_DB: Replicate_Ignore_DB: Replicate_Do_Table: Replicate_Ignore_Table: Replicate_Wild_Do_Table: Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table: Last_Errno: 0 Last_Error: Skip_Counter: 0 Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 548 Relay_Log_Space: 832 Until_Condition: None Until_Log_File: Until_Log_Pos: 0 Master_SSL_Allowed: No Master_SSL_CA_File: Master_SSL_CA_Path: Master_SSL_Cert: Master_SSL_Cipher: Master_SSL_Key: Seconds_Behind_Master: 0 Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: No Last_IO_Errno: 0 Last_IO_Error: Last_SQL_Errno: 0 Last_SQL_Error: Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids: Master_Server_Id: 2 Master_SSL_Crl: Master_SSL_Crlpath: Using_Gtid: No Gtid_IO_Pos: 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4、测试
在DB2中建立一个数据库testdb
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host=‘192.168.1.112‘,master_user=‘repluser‘,master_password=‘replpass‘,master_log_file=‘mysql-bin.000007‘,master_log_pos=548; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> start slave; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G *************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: 192.168.1.112 Master_User: repluser Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000007 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 548 Relay_Log_File: essun-relay-bin.000002 Relay_Log_Pos: 535 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000007 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes Replicate_Do_DB: Replicate_Ignore_DB: Replicate_Do_Table: Replicate_Ignore_Table: Replicate_Wild_Do_Table: Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table: Last_Errno: 0 Last_Error: Skip_Counter: 0 Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 548 Relay_Log_Space: 832 Until_Condition: None Until_Log_File: Until_Log_Pos: 0 Master_SSL_Allowed: No Master_SSL_CA_File: Master_SSL_CA_Path: Master_SSL_Cert: Master_SSL_Cipher: Master_SSL_Key: Seconds_Behind_Master: 0 Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: No Last_IO_Errno: 0 Last_IO_Error: Last_SQL_Errno: 0 Last_SQL_Error: Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids: Master_Server_Id: 2 Master_SSL_Crl: Master_SSL_Crlpath: Using_Gtid: No Gtid_IO_Pos: 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
在DB1中对testdb,插入一条数据
MariaDB [testdb]> insert t1 values (‘tom‘,24); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
在DB3中查看结果
MariaDB [(none)]> select * from testdb.t1; +------+-----+ | name | age | +------+-----+ | tom | 24 | | king | 24 | +------+-----+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]>
5、安装mysql-mmm-agent
在DB1~3上安装mysql-mmmo-agent
注:mysql-mmm-agent是在epel源中,所以要下载EPEL源安装包即可http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/repoview/epel-release.html
下载对应的版本就可以的。
#rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm yum -y install mysql-mmm-agent
每一个节点都要安装
在每一个节点上要给Monitor授权用户
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT SUPER, REPLICATION CLIENT, PROCESS ON *.* TO ‘mmm_agent‘@‘192.168.1.116‘ IDENTIFIED BY ‘123456‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO ‘mmm_monitor‘@‘192.168.1.116‘ IDENTIFIED BY ‘123456‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO ‘repluser‘@‘192.168.1.116‘ IDENTIFIED BY ‘replpass‘; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
6、在Monitor节点上要安装
#yum -y install mysql-mmm*
此包同样也在epel源中
7、在Monitor端的设置/etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_common.conf
active_master_role writer <host default> cluster_interface eth0 pid_path /var/run/mysql-mmm/mmm_agentd.pid bin_path /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm/ replication_user repluser #复制用户 replication_password replpass #复制密码 agent_user mmm_agent #代理用户 agent_password 123456 #代理用户的密码 </host> <host db1> ip 192.168.1.109 mode master peer db2 </host> <host db2> ip 192.168.1.112 mode master peer db1 </host> <host db3> ip 192.168.1.113 mode slave </host> <role writer> hosts db1, db2 ips 192.168.1.24 mode exclusive #排它 </role> <role reader> hosts db2, db3 ips 192.168.1.22, 192.168.1.23 mode balanced #均衡 </role>
将此文件分发到各DB1~3中的/etc/mysql-mmm/下
8、每一个DB中都会有mmm_agent的配置文件,编辑mmm_agent.conf
在数据库服务器上,还有一个mmm_agent.conf需要修改,其内容是:
include mmm_common.conf # The ‘this‘ variable refers to this server. Proper operation requires # that ‘this‘ server (db1 by default), as well as all other servers, have the # proper IP addresses set in mmm_common.conf. this db2
第一行表示:将之前Monitor中的mmm_common.conf文件载入到此文件中,供此文件中的参数设用。
最后一行标记此主机的角色(引用mmm_common.conf中的host段)在不同的数据库服务器上要分别改为db1和db3否则代理就会无法启动。
9、编辑mmm_mon.confg
在Monitor上,修改mmm_mon.conf文件,修改后内容为:
include mmm_common.conf <monitor> ip 192.168.1.116 #当前monitor主机地址 pid_path /var/run/mysql-mmm/mmm_mond.pid bin_path /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm status_path /var/lib/mysql-mmm/mmm_mond.status ping_ips 192.168.1.109, 192.168.1.112 #真实DB地址 auto_set_online 10 # The kill_host_bin does not exist by default, though the monitor will # throw a warning about it missing. See the section 5.10 "Kill Host # Functionality" in the PDF documentation. # # kill_host_bin /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm/monitor/kill_host # </monitor> <host default> monitor_user mmm_monitor #监控DB的用户名 monitor_password 123456 #密码 </host> debug 0 #关闭debug功能,如果程序无法监控得到,可以使用debug 1查错
10、启动MMM
在各DB端启动mmm-agent
#cd /etc/init.d/ # chkconfig mysql-mmm-monitor on # service mysql-mmm-monitor start
在Monitor端启动监控程序
#cd /etc/init.d/ # chkconfig mysql-mmm-monitor on # service mysql-mmm-monitor start
过几秒钟,就可以使用mmm_control show查看在线监控端(DB)了
[root@essun ~]# service mysql-mmm-monitor status mmm_mond (pid 5395) is running... [root@essun ~]# mmm_control show db1(192.168.1.109) master/ONLINE. Roles: db2(192.168.1.112) master/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.1.22), writer(192.168.1.24) db3(192.168.1.113) slave/ONLINE. Roles: reader(192.168.1.23)
注:可以使用
[root@essun ~]# mmm_control --help Invalid command ‘--help‘ Valid commands are: help - show this message ping - ping monitor show - show status checks [<host>|all [<check>|all]] - show checks status set_online <host> - set host <host> online set_offline <host> - set host <host> offline mode - print current mode. set_active - switch into active mode. set_manual - switch into manual mode. set_passive - switch into passive mode. move_role [--force] <role> <host> - move exclusive role <role> to host <host> (Only use --force if you know what you are doing!) set_ip <ip> <host> - set role with ip <ip> to host <host>
查看mmm_control的可用参数
11、模拟DB2下线
Monitor当前状态

让DB2下线,当前可写主机是db1,db3
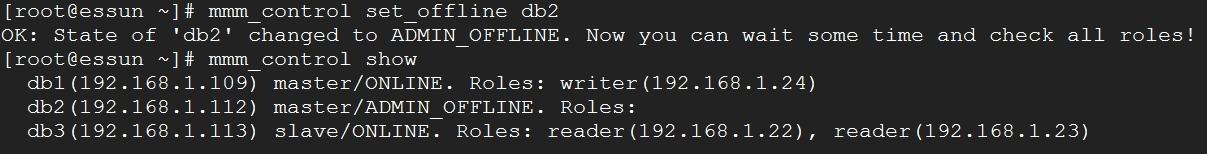
db2没有下线之前还可以读写,当下线之后,可写的切换到DB1上了,所有读的都到了db3上了
当DB2重新上线后的情况如下
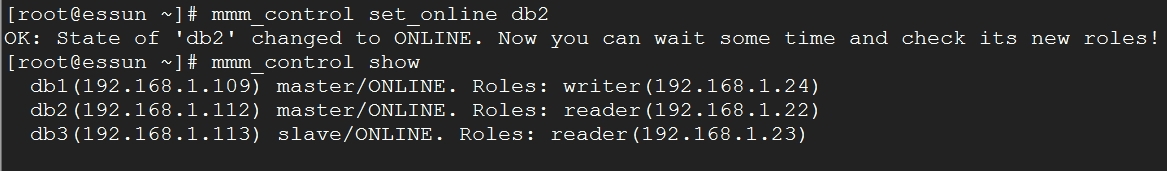
注:DB1、DB同时只能一有个写,一个读!
========================================== Mariadb高可用演示完毕========================
