首页 > 代码库 > Haproxy+Nginx实现负载均衡
Haproxy+Nginx实现负载均衡
一、什么是Haproxy
HAProxy提供高可用性、负载均衡以及基于TCP和HTTP应用的代理,支持虚拟主机,它是免费、快速并且可靠的一种解决方案。HAProxy特别适用于那些负载特大的web站点,这些站点通常又需要会话保持或七层处理。HAProxy运行在当前的硬件上,完全可以支持数以万计的并发连接。并且它的运行模式使得它可以很简单安全的整合进您当前的架构中, 同时可以保护你的web服务器不被暴露到网络上。
HAProxy实现了一种事件驱动, 单一进程模型,此模型支持非常大的并发连接数。多进程或多线程模型受内存限制 、系统调度器限制以及无处不在的锁限制,很少能处理数千并发连接。事件驱动模型因为在有更好的资源和时间管理的用户空间(User-Space) 实现所有这些任务,所以没有这些问题。此模型的弊端是,在多核系统上,这些程序通常扩展性较差。这就是为什么他们必须进行优化以 使每个CPU时间片(Cycle)做更多的工作。点击查看原文
二、负载均衡常用的调度算法
轮循(Round Robin)
这种方法会将收到的请求循环分配到服务器集群中的每台机器,即有效服务器。如果使用这种方式,所有的标记进入虚拟服务的服务器应该有相近的资源容量 以及负载形同的应用程序。如果所有的服务器有相同或者相近的性能那么选择这种方式会使服务器负载形同。基于这个前提,轮循调度是一个简单而有效的分配请求 的方式。然而对于服务器不同的情况,选择这种方式就意味着能力比较弱的服务器也会在下一轮循环中接受轮循,即使这个服务器已经不能再处理当前这个请求了。 这可能导致能力较弱的服务器超载。
最少连接数(Least Connection)
以上两种方法都没有考虑的是系统不能识别在给定的时间里保持了多少连接。因此可能发生,服务器B服务器收到的连接比服务器A少但是它已经超载,因为 服务器B上的用户打开连接持续的时间更长。这就是说连接数即服务器的负载是累加的。这种潜在的问题可以通过“最少连接数”算法来避免:传入的请求是根据每 台服务器当前所打开的连接数来分配的。即活跃连接数最少的服务器会自动接收下一个传入的请求。接本上和简单轮询的原则相同:所有拥有虚拟服务的服务器资源 容量应该相近。值得注意的是,在流量率低的配置环境中,各服务器的流量并不是相同的,会优先考虑第一台服务器。这是因为,如果所有的服务器是相同的,那么 第一个服务器优先,直到第一台服务器有连续的活跃流量,否则总是会优先选择第一台服务器。
源IP哈希(Source IP Hash)
这种方式通过生成请求源IP的哈希值,并通过这个哈希值来找到正确的真实服务器。这意味着对于同一主机来说他对应的服务器总是相同。使用这种方式,你不需要保存任何源IP。但是需要注意,这种方式可能导致服务器负载不平衡。
以上信息来自网络更多调度算法请点击该链接
三、案例环境
| 主机 | 操作系统 | IP地址 | 主要软件 |
| Haproxy | Centos 6.5 x86_x64 | 192.168.25.5 | haproxy-1.4.24.tar.gz |
| Nginx Server 1 | Centos 6.5 x86_x64 | 192.168.25.3 | nginx-1.6.0.tar.gz |
| Nginx Server 2 | Centos 6.5 x86_x64 | 192.168.25.4 | nginx-1.6.0.tar.gz |
| Client | Windows 7 | 192.168.25.6 | IE浏览器 |
这里服务器是托管在IDC中,公网访问使用的是防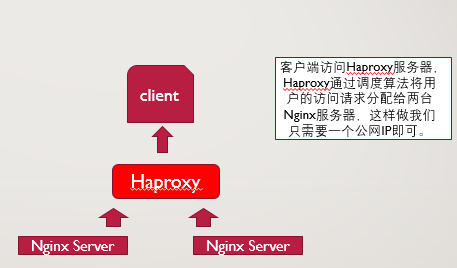 火墙NAT映射的公网IP,因此服务器端只需要配置一个内网IP即可。如果没有防火墙映射,建议在服务器端配置双网卡双IP,公网请求访问公网IP的网卡,Haproxy与各个节点间通信使用内网网卡。
火墙NAT映射的公网IP,因此服务器端只需要配置一个内网IP即可。如果没有防火墙映射,建议在服务器端配置双网卡双IP,公网请求访问公网IP的网卡,Haproxy与各个节点间通信使用内网网卡。
四、案例实施
1、编译安装Nginx服务器
1)安装一些必要组件
[root@localhost ~]#yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel gcc gcc-c++ make
2)创建nginx用户,并设置为禁止登陆
[root@localhost ~]#useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
3)解压并进入到nginx安装目录
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.6.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# cd nginx-1.6.0
4)编译安装nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module && make && make install
5)创建一个软连接,方便nginx的启动
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# ls /usr/local/nginx/
conf html logs sbin
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# ll /usr/local/sbin/nginx
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 27 12月 7 06:41 /usr/local/sbin/nginx -> /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
6)检查语句是否存在错误
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
7)启动nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# nginx
8)检查nginx启动情况
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# netstat -anpt | grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3465/nginx
9)测试nginx启动情况
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# killall -s HUP nginx
平滑重启nginx(reload)等同于下个命令
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]#killall -s QUIT nginx //正常停止nginx (stop) 等同于下个命令
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]#killall -3 nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]#killall -s USR1 nginx //用于nginx的日志切换,也就是重新打开一个日志文件,例如每天要生成一个日志文件时,可以使用这个信号来控制。
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]#killall -s USR2 nginx //用于平滑升级可执行程序。
10)编写nginx启动脚
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# vim /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/bash
# chkconfig: 2345 99 20
# description: Nginx ServerControl Scripts shell
PROG="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
PIDF="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
case "$1" in
start)
if [ -f $PIDF ]; then
echo "Nginx is running.. Start it is error"
else
$PROG
fi
;;
stop)
if [ -f $PIDF ]; then
kill -s QUIT $(cat $PIDF)
rm -rf $PIDF
else
echo "Nginx is stopping .. Stop it is error"
fi
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
if [ -f $PIDF ]; then
kill -s HUP $(cat $PIDF)
else
echo "Nginx is stopping . reload it is error"
fi
;;
status)
if [ -f $PIDF ]; then
echo "Nginx is running"
else
echo "Nginx is stopping"
fi
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 (start|stop|restart|reload|status)"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
给脚本执行权限
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# chkconfig --add nginx
添加为系统服务
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# chkconfig --list nginx
nginx 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:启用 3:启用 4:启用 5:启用 6:关闭
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# service nginx status
Nginx is running
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# service nginx stop
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# netstat -anpt | grep nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# service nginx start
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# netstat -anpt | grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3536/nginx
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# service nginx restart
[root@localhost nginx-1.6.0]# netstat -anpt | grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3551/nginx
测试nginx服务脚本是否可以正确使用
11)编辑nginx配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
[root@localhost conf]# vim nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘
‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘
‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘;
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name nginx1;
charset utf-8;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root
# concurs with nginx‘s one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
将nginx的配置文件改成和上面相同即可
[root@localhost conf]# mkdir -p /var/www/html
创建网页文件根目录
[root@localhost conf]# echo "nginx1" > /var/www/html/index.html
将网页的内容写到网页的根目录下
[root@localhost conf]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
nginx1
[root@localhost conf]# service nginx restart
12)测试nginx服务器是否搭建成功
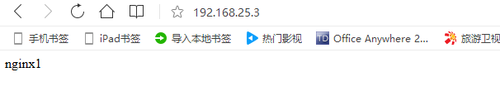
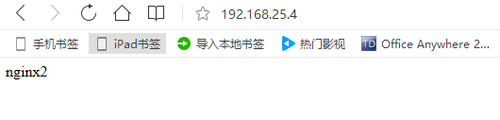
从图中可以看出两台nginx服务器已经可以正常访问,我们需要按照步(1)—(11)安装nginx server2 这里不再做过多赘述。
2、编译安装Haproxy
1)安装支持软件
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel bzip2-devel
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# yum -y install gcc* make
2)编译并安装Haproxy
[root@localhost ~]# tar xf haproxy-1.4.24.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# cd haproxy-1.4.24
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# make TARGET=linux26 ←指定linux系统位数
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# make install
3)修改Haproxy配置文件
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# mkdir /etc/haproxy
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# cp examples/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/ ←将haproxy.cfg文件复制到配置文件目录。
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
# this config needs haproxy-1.1.28 or haproxy-1.2.1
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0 ←配置日志记录,local0为日志设备,默认在系统日志
log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice ←notice为日志级别,通常有24个级别
#log loghost local0 info
maxconn 4096 ←最大连接数
# chroot /usr/share/haproxy ←禁锢目录
uid 99 ←用户UID
gid 99 ←用户GID
daemon ←守护模式
#debug
#quiet
defaults
log global
mode http ←工作在7层,tcp在四层
option httplog
option dontlognull
retries 3
# redispatch
maxconn 2000
contimeout 5000
clitimeout 50000
srvtimeout 50000
listen nginx-web 0.0.0.0:80 ←定义一个nginx-web的应用
option httpchk GET /index.html ←健康检查服务器的主页文件,方式为GET
option persist ←强制将请求发送到已经DOWN掉的服务器
balance roundrobin ←负载均衡调度算法为轮询。source是来源
server inst1 192.168.25.3:80 check inter 2000 fall 3 ←定义在线节点
server inst2 192.168.25.4:80 check inter 2000 fall 3 ←定义备份节点
4)创建自启动脚本
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# cp examples/haproxy.init /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# ln -s /usr/local/sbin/haproxy /usr/sbin/haproxy
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# /etc/init.d/haproxy start
-bash: /etc/init.d/haproxy: 权限不够
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/ha
halt haproxy
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# chkconfig --add /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# chkconfig haproxy on
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# chkconfig --list haproxy
haproxy 0:关闭 1:关闭 2:关闭 3:关闭 4:关闭 5:关闭 6:关闭
[root@localhost haproxy-1.4.24]# /etc/init.d/haproxy start
Starting haproxy: [确定]
5)测试负载均衡是否搭建成功
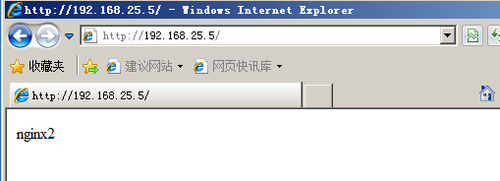
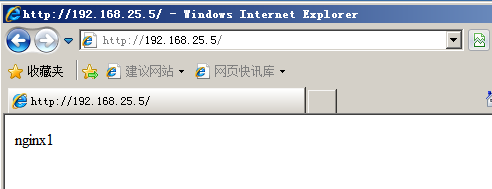
从图中我们可以看出访问同一个ip地址两次出现了两个不同的网页,所以我们的Haproxy负载均衡就搭建完了,但是大家需要注意的是windows的浏览器会有缓存,有时候会显示的不是特别及时,下面给大家看下linux下访问的结果
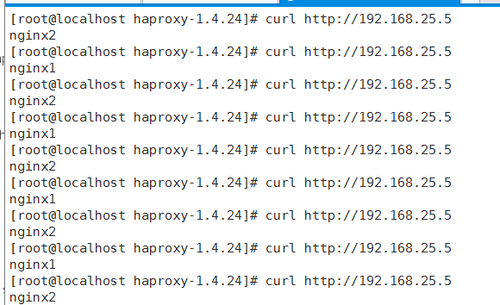
从图中可以看出linux的响应很及时,到这儿我们的服务就搭完了,后续我还会跟进其他调度算法的实验步骤,本次实验中如有哪里做的有错误或不对的地方请大家及时和探讨,以免给大家造成错误指导!
本文出自 “linux” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://bella41981.blog.51cto.com/10603572/1880200
Haproxy+Nginx实现负载均衡
