首页 > 代码库 > MySQL简单查询详解
MySQL简单查询详解
MySQL的查询操作
单表查询:简单查询
多表查询:连接查询
联合查询
布尔条件表达式操作符
= 等值比较 <=>:跟空值比较不会产生额外信息的等值比较 <>:不等值 <: <=: > >= IS NULL IS NOT NULL LIKE: 支持的通配符: %(任意长度的任意字符),_(任意单个字符) RLIKE,REGEXP: 支持使用正则表达式 IN: 判断指定字段的值是否在给定在列表中; BETWEEN ... AND ...: 位于指定的范围之间(x>=10 and x<=40 --> x BETWEEN 10 AND 20)
示例
新创建一个表 mysql> create table tests (sid int unsigned auto_increment not null unique key,name char(30) not null,age tinyint unsigned not null,gender enum(‘F‘,‘M‘) not null,tutor char(30));

添加几个用户 mysql> insert into tests values (1,‘Guo Jing‘,27,‘M‘,‘Song Jiang‘), (2,‘Yang Guo‘,28,‘M‘,‘Hu Sanniang‘),(3,‘Guo Polu‘,21,‘M‘,‘Jia Baoyu‘); mysql> insert into tests values (4,‘Xue Baochai‘,‘19‘,‘F‘,‘Rong Momo‘), (5,‘Xia Yuhe‘,37,‘F‘,‘Shi Qian‘),(6,‘Wu Yong‘,51,‘M‘,‘Lin Daiyu‘);
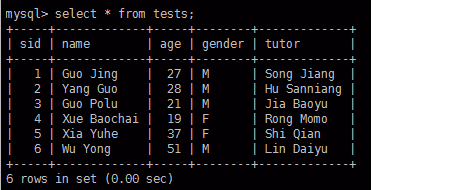
BETWEEN...AND...语法演示 mysql> select name,age from tests where age between 25 and 40;
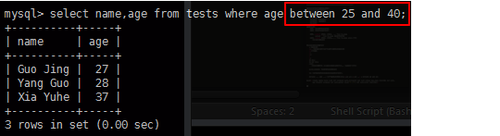
IN 语法演示 mysql> select name,age from tests where age in (25,26,27,28,29);
LIKE 语法演示 mysql> select name from tests where name like ‘x%‘;

RLIKE 语法演示 mysql> select name from tests where name rlike ‘^x.*‘;

//添加两行新的数据 //NULL不是字符串 不需要加引号 mysql> insert into tests values (7,‘tom‘,11,‘M‘,‘jerry‘),(8,‘tomy‘,13,‘M‘,NULL);

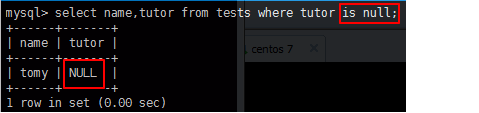
IS NULL mysql> select name,tutor from tests where tutor is null;
NOT NULL mysql> select name,tutor from tests where tutor is not null;
组合条件测试
NOT, ! AND, && OR, ||
示例
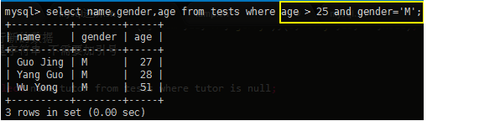
mysql> select name,gender,age from tests where age > 25 and gender=‘M‘;
排序
order by ‘排序字段’ 默认为升序:ASC 降序:DESC
示例
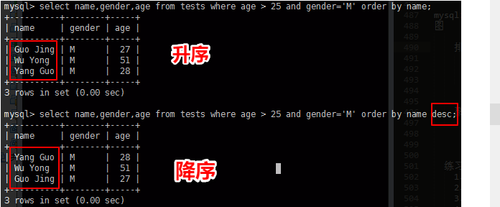
mysql> select name,gender,age from tests where age > 25 and gender=‘M‘ order by name; mysql> select name,gender,age from tests where age > 25 and gender=‘M‘ order by name desc;
聚合函数
SUM(), AVG(), MAX(), MIN(), COUNT()
示例
mysql> select sum(age) from tests; mysql> select avg(age) from tests; mysql> select max(age) from tests; mysql> select count(age) from tests;

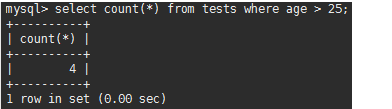
mysql> select count(*) from tests where age > 25; //年龄大于25的有4个
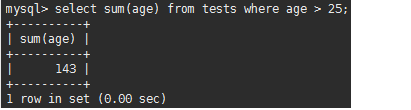
mysql> select sum(age) from tests where age > 25; //年龄大于25的所有年龄之和
分组
group by
示例
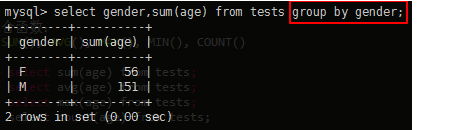
mysql> select gender,sum(age) from tests group by gender;
mysql> alter table tests add classid tinyint unsigned; //为表新添加一个字段
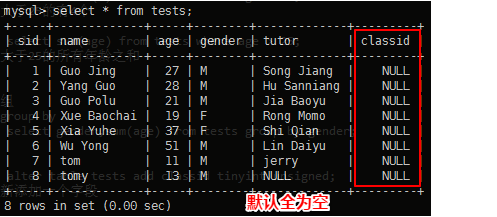
插入数据 mysql> update tests set classid=1 where sid=1; ... ...

mysql> select classid,count(*) from tests group by classid; 或者 mysql> select classid,count(name) from tests group by classid; //按班级分类 每班有多少人

mysql> select classid,count(name),sum(age) from tests group by classid; 每个班的人的年龄之和
对分组(group by)的条件过滤
having 注意:使用having和不是使用where
示例
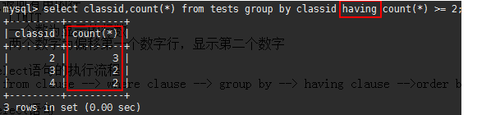
mysql> select classid,count(*) from tests group by classid having count(*) >= 2;
mysql> select classid,count(*),sum(age) from tests group by classid having sum(age) <= 50;

mysql> select classid,count(name),sum(age) from tests where classid in (1,2) group by classid havingsum(age) <= 50; //注意where过滤和having过滤 分别出现的位置
只返回有用的行
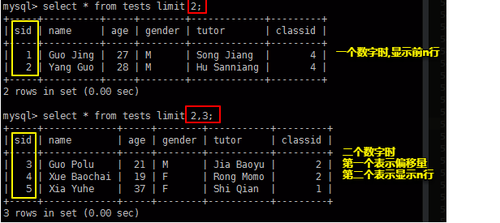
LIMIT 一个数为显示的行数 两个数字为偏移第一个数字行,显示第二个数字
示例
mysql> select * from tests limit 2; mysql> select * from tests limit 2,3;
select语句
distinct 重复的只显示一次 SQL_CACHE 缓存查询结果 SQL_NO_CACHE 不缓存查询结果
示例
mysql> select age from tests order by age; mysql> select distinct age from tests order by age;
总结
select语句的执行流程
from clause --> where clause --> group by --> having clause -->order by -->
select -->limit
常见用法
select from order by
select from group by having
select from where
select -->调用内部函数
select from where group by limit
本文出自 “似水流年” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://sixijie123.blog.51cto.com/11880770/1883224
MySQL简单查询详解
声明:以上内容来自用户投稿及互联网公开渠道收集整理发布,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任,若内容有误或涉及侵权可进行投诉: 投诉/举报 工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
