首页 > 代码库 > docker run命令详解及示例(二)
docker run命令详解及示例(二)
docker run
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Run a command in a new container
上接博文:docker run命令详解及示例(一)
--link
--link=[] Add link to another container
用于连接两个容器。
启动容器1:web
docker run --name web -d -p 22 -p 80 -itwebserver:v1
启动容器2:ap1连接到web,并命名为apache
docker run --name ap1 --link=web:apache -d-p 22 -p 80 -it webserver:v1
--log-driver
--log-driver= Logging driver for container
--log-opt=[] Log driver options
--lxc-conf
--lxc-conf=[] Add custom lxc options
设置lxc配置项。
示例:
docker run--lxc-conf="lxc.network.type=veth"--lxc-conf="lxc.network.ipv4=192.168.1.10/24"--lxc-conf="lxc.network.ipv4.gateway=192.168.1.1"--lxc-conf="lxc.network.link=docker0"--lxc-conf="lxc.network.name=eth0" --lxc-conf="lxc.network.flags=up" -it --net=none ubuntu:14.04/bin/bash
--mac-address
--mac-address= Container MAC address (e.g.92:d0:c6:0a:29:33)
设置容器的mac地址。
-m, --memory
-m, --memory= Memory limit
设置容器使用的最大内存上限。默认单位为byte,可以使用K、G、M等带单位的字符串。
默认情况下,容器可以使用主机上的所有空闲内存。
设置容器的内存上限,参考命令如下所示:
docker run -tid —name mem1 —memory 128mubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
默认情况下,除了–memory指定的内存大小以外,docker还为容器分配了同样大小的swap分区,也就是说,上面的命令创建出的容器实际上最多可以使用256MB内存,而不是128MB内存。如果需要自定义swap分区大小,则可以通过联合使用–memory–swap参数来实现控制。
对上面的命令创建的容器,可以查看到在cgroups的配置文件中,查看到容器的内存大小为128MB (128×1024×1024=134217728B),内存和swap加起来大小为256MB(256×1024×1024=268435456B)。
#cat /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/docker/<容器的完整ID>/memory.limit_in_bytes 134217728 #cat /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/docker/<容器的完整ID>/memory.memsw.limit_in_bytes 268435456 |
注意:执行上述命令时,命令行可能会输出下面的警告:
WARNING: Your kerneldoes not support swap limit capabilities, memory limited without swap.
这是因为主机上默认不启用cgroup来控制swap分区,可以参考docker官方的相应文档,修改grub启动参数。
在容器中,依次使用下面的stress命令,即可对容器的内存进行压力测试,确认内存。
stress –vm 1–vm-bytes 256M –vm-hang 0 &
stress –vm 1 –vm-bytes 250M–vm-hang 0 &
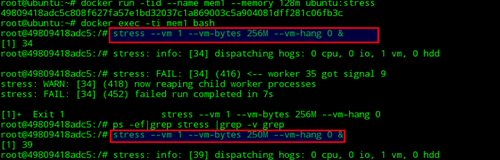
可以发现,使用256MB进行压力测试时,由于超过了内存上限(128MB内存+128MB swap),进程被OOM杀死。使用250MB进行压力测试时,进程可以正常运行,并且通过docker stats可以查看到容器的内存已经满负载了。

--memory-reservation
--memory-reservation= Memory soft limit
启用弹性的内存共享,当宿主机资源充足时,允许容器尽量多地使用内存,当检测到内存竞争或者低内存时,强制将容器的内存降低到memory-reservation所指定的内存大小。按照官方说法,不设置此选项时,有可能出现某些容器长时间占用大量内存,导致性能上的损失。
--memory-swap
--memory-swap= Total memory (memory + swap), ‘-1‘ todisable swap
等于内存和swap分区大小的总和,设置为-1时,表示swap分区的大小是无限的。默认单位为byte,可以使用K、G、M等带单位的字符串。如果–memory-swap的设置值小于–memory的值,则使用默认值,为–memory-swap值的两倍。
--memory-swappiness
--memory-swappiness=-1 Tuning container memory swappiness (0 to 100)
控制进程将物理内存交换到swap分区的倾向,默认系数为60。系数越小,就越倾向于使用物理内存。值范围为0-100。当值为100时,表示尽量使用swap分区;当值为0时,表示禁用容器 swap 功能(这点不同于宿主机,宿主机 swappiness 设置为 0 也不保证 swap 不会被使用)。
--name
--name= Assign a name to the container
为容器指定一个名字。
# docker run -it --name=web ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash

--net
--net=default Set the Network for the container
以下是网络设置中常用的参数:
none 关闭container内的网络连接:
将网络模式设置为none时,这个container将不允许访问任何外部router。这个container内部只会有一个loopback接口,而且不存在任何可以访问外部网络的router。
bridge 通过veth接口来连接contianer默认选项:
Docker默认是将container设置为bridge模式。此时在host上面讲存在一个docker0的网络接口,同时会针对container创建一对veth接口。其中一个veth接口是在host充当网卡桥接作用,另外一个veth接口存在于container的命名空间中,并且指向container的loopback。Docker会自动给这个container分配一个IP,并且将container内的数据通过桥接转发到外部。
host 允许container使用host的网络堆栈信息:
当网络模式设置为host时,这个container将完全共享host的网络堆栈。host所有的网络接口将完全对container开放。container的主机名也会存在于host的hostname中。这时,container所有对外暴露的port和对其它container的link,将完全失效。
Container:
当网络模式设置为Container时,这个container将完全复用另外一个container的网络堆栈。同时使用时这个container的名称必须要符合下面的格式:--net container:<name|id>.
比如当前有一个绑定了本地地址localhost的redis container。如果另外一个container需要复用这个网络堆栈,则需要如下操作:
#docker run -d --name redis example/redis--bind 127.0.0.1
$ # use the redis container‘s network stackto access localhost
#sudo docker run --rm -ti --netcontainer:redis example/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1
--oom-kill-disable
--oom-kill-disable=false Disable OOM Killer
-P, --publish-all
-P, --publish-all=false Publish all exposed ports to random ports
对外映射所有端口。
-p, --publish
-p, --publish=[] Publish a container‘s port(s) to the host
对外映射指定端口,如不指定映射后的端口将随机指定。
#docker run –d -p 10022:22 -p 10080:80 -itwebserver:v1
使用docker run来启动我们创建的容器。-d让容器以后台方式运行。使用多个-p来映射多个端口,将容器的22端口映射为本地的10022,80映射为10080。
--pid
--pid= PID namespace to use
设置容器的PID模式。两种:
host: use the host‘s PID namespace insidethe container.
Note: the host mode gives the containerfull access to local PID and is therefore considered insecure.
--privileged
--privileged=false Give extended privileges to this container
默认情况下container是不能访问任何其他设备的。但是通过"privileged",container就拥有了访问任何其他设备的权限。
当操作者执行docker run --privileged时,Docker将拥有访问host所有设备的权限
# docker run -it --rm --privilegedubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
--read-only
--read-only=false Mount the container‘s root filesystem asread only
启用后,容器的文件系统将为只读。
# docker run -it --rm --read-onlyubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
root@d793e24f0af1:/# touch a
touch:cannot touch ‘a‘: Read-only file system
--restart
--restart=no Restart policy to apply when a containerexits
当容器退出或宿主机重启的时候,容器接着会重启操作。
重启策略:
no - 不重启
on-failure - container推出状态非0时重启
always - 始终重启
示例:
#docker run -it--restart=always ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
当退出容器时,再查看容器的状态为UP
--rm
--rm=false Automatically remove the container whenit exits

--security-opt
--security-opt=[] Security Options
安全选项。
--sig-proxy
--sig-proxy=true|false
Proxy received signals to the process(non-TTY mode only). SIGCHLD, SIGSTOP, and SIGKILL are not proxied. The defaultis true.
--stop-signal
--stop-signal=SIGTERM Signal to stop a container, SIGTERM bydefault
-t, --tty
-t, --tty=false Allocate a pseudo-TTY
分配一个模拟终端,常和-i一块使用.
-u, --user
-u, --user= Username or UID (format:<name|uid>[:<group|gid>])
Sets the username or UID used andoptionally the groupname or GID for the specified command.
The followings examples are all valid:
--user [user | user:group | uid | uid:gid |user:gid | uid:group ]
Without this argument the command will berun as root in the container.
--ulimit
--ulimit=[] Ulimit options
--default-ulimit,dockerdaemon的启动参数,能够指定默认container ulimit配置。如果此参数没配置,则默认从docker daemon继承;
--ulimit,docker run的参数,能够覆盖dockerdaemon指定的ulimit默认值。如果此参数没配置,则默认从default-ulimit继承;
# docker run -it -d --ulimitnofile=20480:40960 ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
--uts
--uts= UTS namespace to use
-v, --volume
-v, --volume=[] Bind mount a volume
可以使用带有 -v 参数的 docker run 命令给容器添加一个数据卷.
1.添加数据卷/data1,会自动创建目录
# docker run -it --name web -v /data1ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
root@fac11d44de3e:/# df -h
/dev/disk/by-uuid/1894172f-589b-4e8b-b763-7126991c7fbb 29G 2.6G 25G 10% /data1
root@fac11d44de3e:/# cd /data1
2.将宿主机的目录添加到容器
将宿主机的/data_web加载为容器/data目录
# docker run -it --name web -v/data_web:/data ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
--volume-driver
--volume-driver= Optional volume driver for the container
--volumes-from
--volumes-from=[] Mount volumes from the specifiedcontainer(s)
从其他容器挂载目录。
1.创建dbdata容器,并含有/data数据卷
# docker run -it -v /data --name dbdataubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
2.创建webserver1挂载dbdata的数据卷
# docker run -it --volumes-from dbdata--name webserver1 ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
-w, --workdir
-w, --workdir= Working directory inside the container
设置容器的工作目录。
# docker run -it--workdir="/data" ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash
root@7868da4d2846:/data#
本文出自 “老书生” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://showing.blog.51cto.com/11976328/1843182
docker run命令详解及示例(二)
