首页 > 代码库 > Linux的ntp常用配置整理
Linux的ntp常用配置整理
ntp介绍:
NTP是网络时间协议(Network Time Protocol),它是用来同步网络中各个计算机的时间的协议;
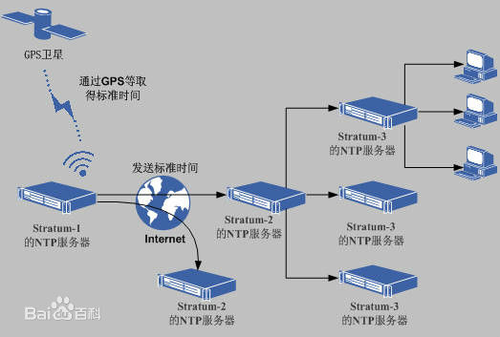
在NTP中,定义了时间按照服务器的等级传播,按照离外部UTC源远近将所有的服务器归入不同的Stratum(层)中,例如把通过GPS(Global Positioning System,全球定位系统)取得发送标准时间的服务器叫Stratum-1的NTP服务器,而Stratum-2则从Stratum-1获取时间,Stratum-3从Stratum-2获取时间,以此类推,但Stratum层的总数限制在15以内。所有这些服务器在逻辑上形成阶梯式的架构相互连接,而Stratum-1的时间服务器是整个系统的基础;
架构示意图,如下:
那么下一步就要进入正题了
1.允许防火墙通过ntp的数据
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=123/udp firewall-cmd --list-all
public (active)
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces: eth0
sources:
services: dhcpv6-client ssh
ports: 123/udp #我还开启了其他的端口,这里我就不显示啦
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports:
sourceports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
2.安装ntp服务
yum -y install ntp
3.配置ntp
ntp服务的主要配置文件为“/etc/ntp.conf”,没有修改过的配置文件如下所示
egrep -v "^#|^$" /etc/ntp.conf
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw
keys /etc/ntp/keys
disable monitor
下面解释经常能用到的参数意思
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift #系统时间与BIOS时间的偏差记录
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
restrict default nomodify notrap nopeer noquery #控制相关权限
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
-------------------------------------------------- #语法为: restrict ip地址 子网掩码 参数
参数有一下几个:
ignore 拒绝所有类型的ntp连接;
nomodify 客户端不能使用ntpc与ntpq这两个程序来修改服务器的时间参数;但是客户端任可以通过该服务端进行网络校时
notrust 拒绝没有认证的客户端;
noquery 不提供客户端的时间查询(拒绝客户端的所有查询操作),用户端不能使用ntpq,ntpc等命令来查询ntp服务器
notrap 不提供trap这个远端事件登录(remote event logging)的功能
注意:如果没有在restrict 参数的地方加上任何参数的话,将表示“ip、网段地址不受任何限制”
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
server 0.centos.pool.ntp.org prefer #指定ntp服务器地址
server 1.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 2.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
server 3.centos.pool.ntp.org iburst
-------------------------------------------------- #语法为:server ip地址 prefer/iburst
-------------------------------------------------- #prefer 表示:优先的ntp服务器地址
正常配置ntp服务的话,只需要将server 后的地址修改为自己想要的ntp地址就可以啦,不需要其他的配置;如下
vim /etc/ntp.conf
restrict 192.168.100.254 #想要为其同步时间的客户端地址(自己充当ntp服务器) server 192.168.100.254 #ntp服务器地址
4.启动ntp,并查看ntp端口
systemctl start ntpd.service
检查ntp是否运行
pgrep ntpd 或者
ps -ef | grep ntpd 或者
systemctl status ntpd.service 或者
netstat -anptu | grep ntp
udp 0 0 10.0.0.143:123 0.0.0.0:* 10466/ntpd
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:123 0.0.0.0:* 10466/ntpd
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:123 0.0.0.0:* 10466/ntpd
udp6 0 0 fe80::f816:3eff:feb:123 :::* 10466/ntpd
udp6 0 0 ::1:123 :::* 10466/ntpd
udp6 0 0 :::123 :::* 10466/ntpd
这样就表示ntp服务已经起来啦,但是它有没有去连接ntp服务器,怎么看?
5.查看ntp是否与上层ntp连通
ntpstat
synchronised to NTP server (85.199.214.101) at stratum 2
time correct to within 112 ms
polling server every 512 s
这个指令可以列出客户机是否与ntp服务器进行连接,通过上面可以知道我们的机器处于地3层,因为我们是从第二层去同步的时间
那么咱们继续,我们处于第三层,我们肯定想要知道第一层是谁
6.查看ntp与上层的状态
ntpq -p

下面解释一下:
remote #ntp主机的ip,左边‘ * ’表示当前引用;
------- #‘ + ’表示 优先选择,或者下一个候选; 顺序为 ‘ * + - ‘
refid 参考上一层ntp主机地址
st 层, 第一层为GPS卫星,不明白可以看最上边的图
when 多少秒之间做的时间同步;
poll 下一次更新时间在几秒之后;
reach 向上层更新的次数
delay 网络过程中的延迟时间
offset 时间补偿
jitter linux系统时间与BIOS的时间差
查看ntpd进程状态 按 Ctrl + c 停止
watch ‘ntpq -p‘
Every 2.0s: ntpq -p Wed Mar 1 17:50:18 2017
remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
==============================================================================
+marla.ludost.ne 131.188.3.220 2 u 872 1024 177 214.437 24.742 6.540
*85.199.214.101 .GPS. 1 u 11 64 377 216.950 0.123 5.755
+188-39-37-91.st .GPS. 1 u 15 64 355 231.056 -0.961 19.068
-biisoni.miuku.n 207.224.49.219 2 u 395 1024 367 177.958 32.780 39.127
7.ntpdate 同步时间
用法: ntpdate ntp服务器地址
ntpdate 0.asia.pool.ntp.org
这样更新时间的话,server/client之间的时间不允许超过1000秒,超过,则不会去同步;
强制同步的话,可以使用 -u 选项,-u 会采用一个非特权端口来同步时间;如下所示:
ntpdate -u 0.asia.pool.ntp.org
8.将时间写入BIOS
hwclock -r 查看BIOS时间
hwclock -w 将系统时间写入到BIOS
底下做一个总结:
ntpd、ntpdate
1.ntpd 时间同步服务器,同步时是平滑同步
2.ntpdate 同步时间时需要依赖ntp服务,并且是立即同步,不会管之前的时间是多少,会立马同步到与ntp服务器一样的时间;
参考文档:
http://linux.vbird.org/linux_server/0440ntp.php
http://www.cnblogs.com/kerrycode/archive/2015/08/20/4744804.html
本文出自 “RSLinux” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://readshlinux.blog.51cto.com/9322509/1902432
Linux的ntp常用配置整理
