首页 > 代码库 > Django 入门学习(2)
Django 入门学习(2)
在上一篇的基础上,我已经成功地获取了用户的输入信息,下面我希望将用户的值进行处理之后然后返回一个页面给用户
urls.py和前面一样
""" from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from MyApp1 import views urlpatterns = [ # url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls), url(r‘^index/‘, views.index), ]
views.py里面我新创建一个列表,把字典结构的数据放进去,然后通过render发送回去
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
USERLIST=[]
def index(request):
if request.method == ‘POST‘:
u=request.POST.get(‘user‘)
e=request.POST.get(‘email‘)
print(u,e)
temp={‘user‘:u,‘email‘:e}
USERLIST.append(temp)
return render(request,‘index.html‘,{‘data‘:USERLIST})index.html 这里有一个特殊的for使用,他其实是转换为对应的python命令,执行之后,然后把渲染后的html页面发回给用户
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is 4th Example!</h1>
<form action="/index/" method="post">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="email" name="email">
<input type="submit" value="http://www.mamicode.com/Submit">
</form>
<table border="1">
<th>用户名</th>
<th>邮箱</th>
<tr>
{% for item in data %}
<td> {{ item.user }}</td>
<td> {{ item.email }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>结果如下所示。
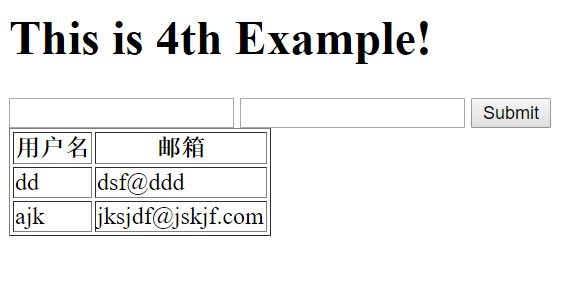
因为目前所有的数据都保存在内存里,如果重启Django,这些数据都会丢失。
如果需要长久保存,我们需要把数据保存在数据库了。
本文出自 “麻婆豆腐” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://beanxyz.blog.51cto.com/5570417/1918853
Django 入门学习(2)
声明:以上内容来自用户投稿及互联网公开渠道收集整理发布,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任,若内容有误或涉及侵权可进行投诉: 投诉/举报 工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
