首页 > 代码库 > 通过Powershell远程管理Windows Azure上的虚拟机
通过Powershell远程管理Windows Azure上的虚拟机
Windows Azure上连接虚拟机想必不是件难事尤其是连接Windows操作系统简单点几下鼠标通过远程桌面RDPWindows Azure虚拟机会帮助你自动创建远程连接RDP的Profile你就能体验到公有云带来的便利。由于虚拟机外部连接都是通过端口映射连接的。当然基于区域网络目前Azure.CN中新创建的虚拟网络已经都是区域网络了当然你目前仍然可以创建基于地缘组的虚拟网络虽然并不推荐后可以创建虚拟机实例级别的公共IP地址所以你也可以跳过通过"云服务"端口映射的RDP而直接连接虚拟机公共IP的3389端口。好吧说了这么多都是通过远程桌面对远程虚拟机进行管理的如果需要批量对虚拟机进行管理有什么方法呢在全球运营的Microsoft Azure上已经提供了自动化as a Service的自动化云服务 通过Powershell工作流运行手册批量定时管理虚拟机服务当然听上去很酷不过目前国内的自动化服务还要等等呢。
可是如果我们希望通过Powershell脚本批量管理在国内Azure公有云上的虚拟机该如何操作呢这里把我用于演示的脚本和大家分享一下。
首先下载并安装最新的 Azure Powershell 注意本脚本只是在Powershell 4.0环境测试通过Azure中创建的Windows服务器虚拟机自动provision部署的时候后台会自动帮助启用Powershell基于https的WINRM访问而用到的证书正是"云服务FQDN"证书这个可以通过以下方式验证在Azure管理门户云服务证书中查看

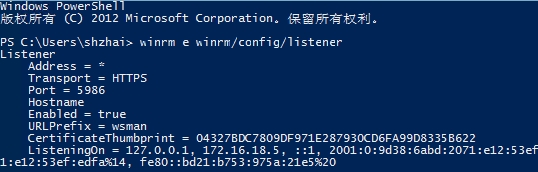
来到Azure虚拟机中查看配置的Powershell已经启用了基于https的访问并且配置了访问证书的指纹就是"云服务"配置的证书指纹因此想通过Powershell远程访问云中的Windows 服务器虚拟机则需要再访问客户端安装相应的证书文件到本地受信任证书列表 CurrentUser\My下面脚本中就是将该证书安装到远程管理客户机的该位置。
(*注意* 这里的脚本没有做"云服务"下的虚拟机操作系统判断因为演示环境中所有虚拟机均为Windows Server 2012 R2的虚拟机。)
演示脚本远程执行脚本Invoke-command 的scriptblock中主要用于在Azure虚拟机中添加配置用户体验服务可以根据需要进行修改,另外如果需要交互式的环境也可以通过Enter-PSSession URI连接虚拟机的URI管理。
实际演示中需要指定参数订阅名称云服务名称 Remote-configAzVM.ps -Subscriptionname "订阅名"-Servicename "云服务名"
Param
(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false,Position=0)]
[String]$SubscriptionName,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[String]$Servicename,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[String]$Path = (Get-Location)
)
# Elevate to admin
Write-Host "Checking for elevation... " -NoNewline
$CurrentUser = New-Object Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal $([Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent())
if (($CurrentUser.IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltinRole]::Administrator)) -eq$false) {
$ArgumentList= "-noprofile-noexit -file `"{0}`" -Path `"$Path`""
If($DeploymentOnly) {$ArgumentList = $ArgumentList +" -DeploymentOnly"}
Write-Host"elevating"
Start-Processpowershell.exe -VerbRunAs -ArgumentList($ArgumentList -f($myinvocation.MyCommand.Definition))
Exit
}
Select-AzureSubscription -SubscriptionName $SubscriptionName -Current
$Validate = $true
# Check Current PS Version
If ($PSVersionTable.PSVersion.Major -lt 4) {Write-Error "Only Supports PowerShell Version 4 or Higher!";$Validate =$false}
if ($Validate)
{
function Install-WinRmCertificate($ServiceName, $VMName)
{
$vm= Get-AzureVM-ServiceName $ServiceName-Name $VMName
$winRmCertificateThumbprint= $vm.VM.DefaultWinRMCertificateThumbprint
$winRmCertificate= Get-AzureCertificate-ServiceName $ServiceName`
-Thumbprint$winRmCertificateThumbprint -ThumbprintAlgorithm sha1
$installedCert= Get-Item Cert:\CurrentUser\My\$winRmCertificateThumbprint-ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if($installedCert -eq$null)
{
$certBytes= [System.Convert]::FromBase64String($winRmCertificate.Data)
$x509Cert= New-ObjectSystem.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate
$x509Cert.Import($certBytes)
$store= New-ObjectSystem.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Store"Root","LocalMachine"
$store.Open("ReadWrite")
$store.Add($x509Cert)
$store.Close()
}
}
$VMnames = (Get-AzureVM -ServiceName $ServiceName).HostName
foreach ($VMname in $VMnames)
{
Install-WinRmCertificate-ServiceName $ServiceName-VMName $VMname
$VMwinRmUri= Get-AzureWinRMUri-ServiceName $ServiceName-Name $VMname
$credential= Get-Credential
Start-Job-ScriptBlock{
Invoke-Command-URI $VMwinRmUri-Credential $credential-ScriptBlock {
Install-WindowsFeature -nameDesktop-Experience -IncludeAllSubFeature -Restart-Force}}
}
}通过Powershell远程管理Windows Azure上的虚拟机
