首页 > 代码库 > C++ 常函数长函数
C++ 常函数长函数
常函数的意义对与普通函数来说,因为const关键字的增加,体现在对类成员的保护上,现在加以讲解:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Ctest
{
private:
int a;
public:
Ctest( int a = 2)
{
this->a = a;
}
int doubleA() const
{
return a*2;
}
};
int main()
{
Ctest * cts = new Ctest(2);
cout << cts->doubleA() << endl;
delete cts;
return 0;
}结果:
常函数->
int doubleA() const 就是在函数后加const
需要注意的是 :
①:构造函数和析构函数不可以是常函数
②:常函数不能对class的类成员进行修改(只能调用)如下面是不可以的:
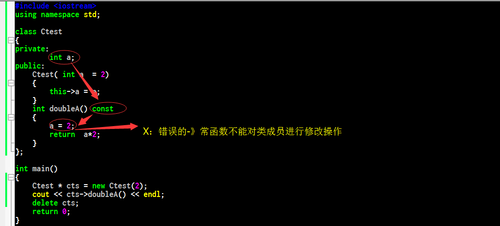
但是可以对本函数内部声明的参数进行修改
③:常函数的this指针,有别于普通函数的this指针
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Ctest
{
private:
int a;
public:
Ctest( int a = 2)
{
this->a = a;
}
int doubleA() const
{
return a*2;
}
const Ctest* my() const
{
return this;
}
Ctest* my1()
{
return this;
}
};
int main()
{
/*Ctest * cts = new Ctest(2);
cout << cts->doubleA() << endl;
delete cts;*/
Ctest cts(3);
cout << cts.my()->doubleA() << endl;
return 0;
}这里有个注意点:常对象只能调用常对象,如下面是不允许的:
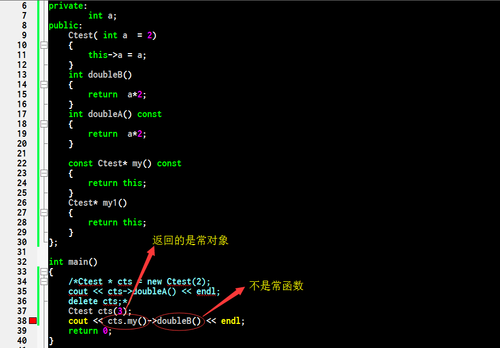
另外 :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Ctest
{
private:
int a;
public:
Ctest( int a = 2)
{
this->a = a;
}
int doubleB()
{
return a*2;
}
int doubleA() const
{
return a*2;
}
const Ctest* my() const
{
return this;
}
Ctest* my1()
{
return this;
}
};
int main()
{
/*Ctest * cts = new Ctest(2);
cout << cts->doubleA() << endl;
delete cts;*/
const Ctest cts(3);
cout << cts.doubleA() << endl;
return 0;
}用 const Ctest cts(3) 也是定义常对象
当然,下面的方案也行:
const Ctest * cts = new Ctest(3); cout << cts->doubleA() << endl;
总结 ,常函数具有保护类成员的作用。
本文出自 “Better_Power_Wisdom” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://aonaufly.blog.51cto.com/3554853/1922882
C++ 常函数长函数
声明:以上内容来自用户投稿及互联网公开渠道收集整理发布,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任,若内容有误或涉及侵权可进行投诉: 投诉/举报 工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
