首页 > 代码库 > QT开发(十二)——QT事件处理机制
QT开发(十二)——QT事件处理机制
QT开发(十二)——QT事件处理机制
一、QT事件简介
QT程序是事件驱动的, 程序的每个动作都是由内部某个事件所触发。QT事件的发生和处理成为程序运行的主线,存在于程序整个生命周期。
常见的QT事件类型如下:
键盘事件: 按键按下和松开
鼠标事件: 鼠标移动,鼠标按键的按下和松开
拖放事件: 用鼠标进行拖放
滚轮事件: 鼠标滚轮滚动
绘屏事件: 重绘屏幕的某些部分
定时事件: 定时器到时
焦点事件: 键盘焦点移动
进入和离开事件: 鼠标移入widget之内,或是移出
移动事件: widget的位置改变
大小改变事件: widget的大小改变
显示和隐藏事件: widget显示和隐藏
窗口事件: 窗口是否为当前窗口
QT将系统产生的消息转化为QT事件,QT事件被封装为对象,所有的QT事件均继承抽象类QEvent,用于描述程序内部或外部发生的动作,任意的QObject对象都具备处理QT事件的能力。
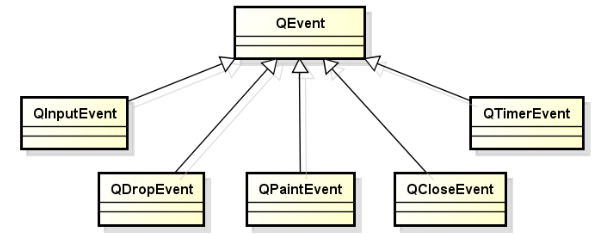
二、QT事件的产生
1、操作系统产生
操作系统将获取的事件,比如鼠标按键,键盘按键等keyPressEvent,keyReleaseEvent,mousePressEvent,mouseReleaseEvent事件, 放入系统的消息队列中,Qt事件循环的时候读取消息队列中的事件,转化为QEvent,再依次处理。
2、QT应用程序程序自己产生
程序产生事件有两种方式, 一种是调用QApplication::postEvent(), 例如QWidget::update()函数,当需要重新绘制屏幕时,程序调用update()函数,new出来一个paintEvent,调用 QApplication::postEvent(),将其放入Qt的消息队列中,等待依次被处理;另一种方式是调用sendEvent()函数,事件不会放入队列, 而是直接被派发和处理, QWidget::repaint()函数用的就是这种方式。
三、QT事件的处理
1、调度方式
事件有两种调度方式,同步和异步。
Qt的事件循环是异步的,当调用QApplication::exec()时,就进入了事件循环,先处理Qt事件队列中的事件, 直至为空,再处理系统消息队列中的消息, 直至为空, 处理系统消息的时候会产生新的Qt事件, 需要对其再次进行处理。
调用QApplication::sendEvent的时候, 消息会立即被处理,是同步的。实际上QApplication::sendEvent()是通过调用QApplication::notify(), 直接进入了事件的派发和处理环节。
2、事件的派发和处理
事件过滤器是Qt中一个独特的事件处理机制, 功能强大而且使用起来灵活方便。通过事件过滤器, 可以让一个对象侦听拦截另外一个对象的事件。事件过滤器实现如下: 在所有Qt对象的基类QObject中有一个类型为QObjectList的成员变量,名字为eventFilters,当某个QObject(A)给另一个QObject(B)安装了事件过滤器后, B会把A的指针保存在eventFilters中。在B处理事件前,会先去检查eventFilters列表, 如果非空, 就先调用列表中对象的eventFilter()函数。一个对象可以给多个对象安装过滤器,一个对象能同时被安装多个过滤器, 在事件到达之后, 事件过滤器以安装次序的反序被调用。事件过滤器函数( eventFilter() ) 返回值是bool型, 如果返回true, 则表示事件已经被处理完毕, Qt将直接返回, 进行下一事件的处理。如果返回false, 事件将接着被送往剩下的事件过滤器或是目标对象进行处理。
QT中,事件的派发是从 QApplication::notify()开始的, 因为QAppliction也是继承自QObject, 所以先检查QAppliation对象, 如果有事件过滤器安装在qApp上, 先调用事件过滤器,接下来QApplication::notify() 会过滤或合并一些事件(比如失效widget的鼠标事件会被过滤掉, 而同一区域重复的绘图事件会被合并),事件被送到reciver::event()处理。
在reciver::event()中, 先检查有无事件过滤器安装在reciever上。若有, 则调用之。然后根据QEvent的类型, 调用相应的特定事件处理函数。常见的事件都有特定事件处理函数, 比如:mousePressEvent(), focusOutEvent(), resizeEvent(), paintEvent(), resizeEvent()等等。在实际应用中, 经常需要重载特定事件处理函数处理事件。对于不常见的事件, 没有相对应的特定事件处理函数,如果要处理这些事件, 就需要使用别的办法, 比如重载event() 函数, 或是安装事件过滤器。
3、事件的转发
对于某些类别的事件,如果在整个事件的派发过程结束后还没有被处理, 那么这个事件将会向上转发给它的父widget, 直到最顶层窗口。Qt中和事件相关的函数通过两种方式相互通信,一种是QApplication::notify(), QObject::eventFilter(), QObject::event()通过返回bool值来表示是否已处理;另一种是调用QEvent::ignore() 或 QEvent::accept() 对事件进行标识,只用于event()函数和特定事件处理函数之间的沟通,而且只有用在某些类别事件上是有意义的, 这些事件就是上面提到的那些会被转发的事件, 包括: 鼠标, 滚轮, 按键等事件。
4、事件的处理、过滤
QT提供了五种不同级别的事件处理和过滤:
A、重写特定事件处理函数.
最常见的事件处理办法就是重写mousePressEvent(), keyPressEvent(), paintEvent() 等特定事件处理函数。
B、重写event()函数.
重写event()函数时, 需要调用父类的event()函数来处理不需要处理或是不清楚如何处理的事件。
return QWidget::event(event);
C、在Qt对象上安装事件过滤器
安装事件过滤器有两个步骤: (假设要用A来监视过滤B的事件)
首先调用B的installEventFilter( const QOject *obj ), 以A的指针作为参数,所有发往B的事件都将先由A的eventFilter()处理。然后, A要重写QObject::eventFilter()函数, 在eventFilter() 中对事件进行处理。
D、给QAppliction对象安装事件过滤器
如果给QApplication对象装上过滤器,那么所有的事件在发往任何其他的过滤器时,都要先经过当前eventFilter()。在QApplication::notify() 中, 是先调用qApp的过滤器, 再对事件进行分析, 以决定是否合并或丢弃。
E、继承QApplication类,并重载notify()函数
Qt是用QApplication::notify()函数来分发事件的,要在任何事件过滤器查看任何事件之前先得到这些事件,重写notify()函数是唯一的办法。通常来说事件过滤器更好用一些, 因为不需要去继承QApplication类,而且可以给QApplication对象安装任意个数的事件过滤器。
GUI应用程序的事件处理:
A、QT事件产生后会被立即发送到QWidget对象
B、QWwidget中的event(QEvent *)进行事件处理
C、event(QEvent *)根据事件类型调用不同的事件处理函数
D、在事件处理函数中发送QT预定义的信号
E、调用信号关联的槽函数
四、源码分析QT事件处理机制
QT源码中事件梳理过程中调用函数如下:
QApplication::exec() QCoreApplication::exec() QEventLoop::exec(ProcessEventsFlags ) QEventLoop::processEvents(ProcessEventsFlags ) QEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents(QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlags) QT_WIN_CALLBACK QtWndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) bool QETWidget::translateMouseEvent(const MSG &msg) bool QApplicationPrivate::sendMouseEvent(...) inline bool QCoreApplication::sendSpontaneousEvent(QObject *receiver, QEvent *event) bool QCoreApplication::notifyInternal(QObject *receiver, QEvent *event) bool QApplication::notify(QObject *receiver, QEvent *e) bool QApplicationPrivate::notify_helper(QObject *receiver, QEvent * e) bool QWidget::event(QEvent *event)
1、进入Qpplication事件循环
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication app(argc, argv);
Widget window; // Widget 继承自QWidget
window.show();
return app.exec(); // 进入Qpplication事件循环
}2、进入QCoreApplication事件循环
int QApplication::exec()
{
#ifndef QT_NO_ACCESSIBILITY
QAccessible::setRootObject(qApp);
#endif
//简单的交给QCoreApplication来处理事件循环
return QCoreApplication::exec();
}3、进入QEventLoop事件队列循环
int QCoreApplication::exec()
{
if (!QCoreApplicationPrivate::checkInstance("exec"))
return -1;
//得到当前Thread数据
QThreadData *threadData = self->d_func()->threadData;
if (threadData != QThreadData::current()) {
qWarning("%s::exec: Must be called from the main thread", self->metaObject()->className());
return -1;
}
//检查event loop是否已经创建
if (!threadData->eventLoops.isEmpty()) {
qWarning("QCoreApplication::exec: The event loop is already running");
return -1;
}
threadData->quitNow = false;
QEventLoop eventLoop;
self->d_func()->in_exec = true;
self->d_func()->aboutToQuitEmitted = false;
//委任QEventLoop 处理事件队列循环
int returnCode = eventLoop.exec();
threadData->quitNow = false;
if (self) {
self->d_func()->in_exec = false;
if (!self->d_func()->aboutToQuitEmitted)
emit self->aboutToQuit();
self->d_func()->aboutToQuitEmitted = true;
sendPostedEvents(0, QEvent::DeferredDelete);
}
return returnCode;
}4、进入QEventLoop::processEvents
int QEventLoop::exec(ProcessEventsFlags flags)
{
Q_D(QEventLoop); //访问QEventloop私有类实例d
//we need to protect from race condition with QThread::exit
QMutexLocker locker(&static_cast<QThreadPrivate *>(QObjectPrivate::get(d->threadData->thread))->mutex);
if (d->threadData->quitNow)
return -1;
if (d->inExec) {
qWarning("QEventLoop::exec: instance %p has already called exec()", this);
return -1;
}
d->inExec = true;
d->exit = false;
++d->threadData->loopLevel;
d->threadData->eventLoops.push(this);
locker.unlock();
// remove posted quit events when entering a new event loop
QCoreApplication *app = QCoreApplication::instance();
if (app && app->thread() == thread())
QCoreApplication::removePostedEvents(app, QEvent::Quit);
//这里的实现代码不少,最为重要的是以下几行
#if defined(QT_NO_EXCEPTIONS)
while (!d->exit)
processEvents(flags | WaitForMoreEvents | EventLoopExec);#else
try {
while (!d->exit) //只要没有遇见exit,循环派发事件
processEvents(flags | WaitForMoreEvents | EventLoopExec);
} catch (...) {
qWarning("Qt has caught an exception thrown from an event handler. Throwing\n"
"exceptions from an event handler is not supported in Qt. You must\n"
"reimplement QApplication::notify() and catch all exceptions there.\n");
// copied from below locker.relock();
QEventLoop *eventLoop = d->threadData->eventLoops.pop();
Q_ASSERT_X(eventLoop == this, "QEventLoop::exec()", "internal error");
Q_UNUSED(eventLoop); // --release warning
d->inExec = false;
--d->threadData->loopLevel;
throw;
}#endif
// copied above locker.relock();
QEventLoop *eventLoop = d->threadData->eventLoops.pop();
Q_ASSERT_X(eventLoop == this, "QEventLoop::exec()", "internal error");
Q_UNUSED(eventLoop); // --release warning
d->inExec = false;
--d->threadData->loopLevel;
return d->returnCode;
}5、事件处理QEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents
bool QEventLoop::processEvents(ProcessEventsFlags flags)
{
Q_D(QEventLoop);
if (!d->threadData->eventDispatcher)
return false;
if (flags & DeferredDeletion)
QCoreApplication::sendPostedEvents(0, QEvent::DeferredDelete);
//将事件派发给与平台相关的QAbstractEventDispatcher子类
return d->threadData->eventDispatcher->processEvents(flags);
}6、将获取的事件打包为消息,传递给操作系统
AbstractEventDispatcher的子类QEventDispatcherWin32获得用户的输入事件,并将其打包成message后,通过标准的Windows API传递给Windows OS
bool QEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents(QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlags flags)
{
Q_D(QEventDispatcherWin32);
if (!d->internalHwnd)
createInternalHwnd();
d->interrupt = false;
emit awake();
bool canWait;
bool retVal = false;
bool seenWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS = false;
bool needWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS = false;
do {
DWORD waitRet = 0;
HANDLE pHandles[MAXIMUM_WAIT_OBJECTS - 1];
QVarLengthArray<MSG> processedTimers;
while (!d->interrupt) {
DWORD nCount = d->winEventNotifierList.count();
Q_ASSERT(nCount < MAXIMUM_WAIT_OBJECTS - 1);
MSG msg;
bool haveMessage;
if (!(flags & QEventLoop::ExcludeUserInputEvents) && !d->queuedUserInputEvents.isEmpty()) {
// process queued user input events
haveMessage = true;
msg = d->queuedUserInputEvents.takeFirst(); //从处理用户输入队列中取出一条事件,处理队列里面的用户输入事件
} else if(!(flags & QEventLoop::ExcludeSocketNotifiers) && !d->queuedSocketEvents.isEmpty()) {
// process queued socket events
haveMessage = true;
msg = d->queuedSocketEvents.takeFirst(); // 从处理socket队列中取出一条事件,处理队列里面的socket事件
} else {
haveMessage = PeekMessage(&msg, 0, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE);
if (haveMessage && (flags & QEventLoop::ExcludeUserInputEvents)
&& ((msg.message >= WM_KEYFIRST
&& msg.message <= WM_KEYLAST)
|| (msg.message >= WM_MOUSEFIRST
&& msg.message <= WM_MOUSELAST)
|| msg.message == WM_MOUSEWHEEL
|| msg.message == WM_MOUSEHWHEEL
|| msg.message == WM_TOUCH
#ifndef QT_NO_GESTURES
|| msg.message == WM_GESTURE
|| msg.message == WM_GESTURENOTIFY#endif
|| msg.message == WM_CLOSE)) {
// queue user input events for later processing
haveMessage = false;
d->queuedUserInputEvents.append(msg); // 用户输入事件入队列,待以后处理 }
if (haveMessage && (flags & QEventLoop::ExcludeSocketNotifiers)
&& (msg.message == WM_QT_SOCKETNOTIFIER && msg.hwnd == d->internalHwnd)) {
// queue socket events for later processing
haveMessage = false;
d->queuedSocketEvents.append(msg); // socket 事件入队列,待以后处理 }
}
if (!haveMessage) {
// no message - check for signalled objects
for (int i=0; i<(int)nCount; i++)
pHandles[i] = d->winEventNotifierList.at(i)->handle();
waitRet = MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx(nCount, pHandles, 0, QS_ALLINPUT, MWMO_ALERTABLE);
if ((haveMessage = (waitRet == WAIT_OBJECT_0 + nCount))) {
// a new message has arrived, process it
continue;
}
}
if (haveMessage) {
#ifdef Q_OS_WINCE
// WinCE doesn‘t support hooks at all, so we have to call this by hand :(
(void) qt_GetMessageHook(0, PM_REMOVE, (LPARAM) &msg);#endif
if (d->internalHwnd == msg.hwnd && msg.message == WM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS) {
if (seenWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS) {
// when calling processEvents() "manually", we only want to send posted
// events once
needWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS = true;
continue;
}
seenWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS = true;
} else if (msg.message == WM_TIMER) {
// avoid live-lock by keeping track of the timers we‘ve already sent
bool found = false;
for (int i = 0; !found && i < processedTimers.count(); ++i) {
const MSG processed = processedTimers.constData()[i];
found = (processed.wParam == msg.wParam && processed.hwnd == msg.hwnd && processed.lParam == msg.lParam);
}
if (found)
continue;
processedTimers.append(msg);
} else if (msg.message == WM_QUIT) {
if (QCoreApplication::instance())
QCoreApplication::instance()->quit();
return false;
}
if (!filterEvent(&msg)) {
TranslateMessage(&msg); //将事件打包成message调用Windows API派发出去
DispatchMessage(&msg); //分发一个消息给窗口程序。消息被分发到回调函数,将消息传递给windows系统,windows处理完毕,会调用回调函数 => section 7 }
} else if (waitRet < WAIT_OBJECT_0 + nCount) {
d->activateEventNotifier(d->winEventNotifierList.at(waitRet - WAIT_OBJECT_0));
} else {
// nothing todo so break
break;
}
retVal = true;
}
// still nothing - wait for message or signalled objects
canWait = (!retVal
&& !d->interrupt
&& (flags & QEventLoop::WaitForMoreEvents));
if (canWait) {
DWORD nCount = d->winEventNotifierList.count();
Q_ASSERT(nCount < MAXIMUM_WAIT_OBJECTS - 1);
for (int i=0; i<(int)nCount; i++)
pHandles[i] = d->winEventNotifierList.at(i)->handle();
emit aboutToBlock();
waitRet = MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx(nCount, pHandles, INFINITE, QS_ALLINPUT, MWMO_ALERTABLE | MWMO_INPUTAVAILABLE);
emit awake();
if (waitRet < WAIT_OBJECT_0 + nCount) {
d->activateEventNotifier(d->winEventNotifierList.at(waitRet - WAIT_OBJECT_0));
retVal = true;
}
}
} while (canWait);
if (!seenWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS && (flags & QEventLoop::EventLoopExec) == 0) {
// when called "manually", always send posted events
QCoreApplicationPrivate::sendPostedEvents(0, 0, d->threadData);
}
if (needWM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS)
PostMessage(d->internalHwnd, WM_QT_SENDPOSTEDEVENTS, 0, 0);
return retVal;
}7、操作系统将事件发回给QT平台
extern "C" LRESULT QT_WIN_CALLBACK QtWndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
...
//将消息重新封装成QEvent的子类QMouseEvent ==> Section 8
result = widget->translateMouseEvent(msg);
...
}8、将操作系统打包的事件解包、翻译为QApplication可识别的事件
bool QETWidget::translateMouseEvent(const MSG &msg)
{
......
res = QApplicationPrivate::sendMouseEvent(target, &e, alienWidget, this, &qt_button_down, qt_last_mouse_receiver);
}9、根据事件类型发送事件
bool QApplicationPrivate::sendMouseEvent(QWidget *receiver, QMouseEvent *event,
QWidget *alienWidget, QWidget *nativeWidget,QWidget **buttonDown, QPointer<QWidget> &lastMouseReceiver,bool spontaneous)
{
...
if (spontaneous)
result = QApplication::sendSpontaneousEvent(receiver, event);
else
result = QApplication::sendEvent(receiver, event);
...
return result;
}10、发送事件
inline bool QCoreApplication::sendSpontaneousEvent(QObject *receiver, QEvent *event)
{
//将event标记为自发事件
//进一步调用 2-5 QCoreApplication::notifyInternal
if (event)
event->spont = true;
return self ? self->notifyInternal(receiver, event) : false;
}11、线程内事件的处理
bool QCoreApplication::notifyInternal(QObject *receiver, QEvent *event)
{
...
// 以下代码主要意图为Qt强制事件只能够发送给当前线程里的对象,也就是说receiver->d_func()->threadData应该等于QThreadData::current()。
//注意,跨线程的事件需要借助Event Loop来派发
QObjectPrivate *d = receiver->d_func();
QThreadData *threadData = d->threadData;
++threadData->loopLevel;
QT_TRY {
returnValue = notify(receiver, event);
} QT_CATCH (...) {
--threadData->loopLevel;
QT_RETHROW;
}
...
return returnValue;
}12、事件的派发
任何线程的任何对象的所有事件在发送时都会调用notify函数。
bool QCoreApplication::notify(QObject *receiver, QEvent *event)
{
Q_D(QCoreApplication);
// no events are delivered after ~QCoreApplication() has started
if (QCoreApplicationPrivate::is_app_closing)
return true;
if (receiver == 0) { // serious error
qWarning("QCoreApplication::notify: Unexpected null receiver");
return true;
}
#ifndef QT_NO_DEBUG
d->checkReceiverThread(receiver);#endif
return receiver->isWidgetType() ? false : d->notify_helper(receiver, event);
}13、使用事件过滤器对发送的事件进行处理
bool QCoreApplicationPrivate::notify_helper(QObject *receiver, QEvent * event)
{
// send to all application event filters
if (sendThroughApplicationEventFilters(receiver, event))
return true;
// 向事件过滤器发送该事件,这里介绍一下Event Filters. 事件过滤器是一个接受即将发送给目标对象所有事件的对象。
//如代码所示它开始处理事件在目标对象行动之前。过滤器的QObject::eventFilter()实现被调用,能接受或者丢弃过滤
//允许或者拒绝事件的更进一步的处理。如果所有的事件过滤器允许更进一步的事件处理,事件将被发送到目标对象本身。
//如果他们中的一个停止处理,目标和任何后来的事件过滤器不能看到任何事件。
if (sendThroughObjectEventFilters(receiver, event))
return true;
return receiver->event(event);
}14、事件派发至QObject的子类-QWidget
bool QWidget::event(QEvent *event)
{
...
switch (event->type()) {
case QEvent::MouseMove:
mouseMoveEvent((QMouseEvent*)event);
break;
case QEvent::MouseButtonPress:
#if 0
resetInputContext();
#endif
mousePressEvent((QMouseEvent*)event);
break;
...
}五、自定义事件与事件处理
1、手动发送事件的流程
A、构造事件对象
QEvent *event = new QEvent(QEvent::Close);
B、发送事件给指定对象
QApplication::sendEvent(this, event);
2、定制某个组件的事件处理
A、确定要对组件的哪些事件进行处理, 如close、key、keyboard 事件
B、重写对象的 event() 函数
QEvent中的主要成员函数
void ignore();接收者忽略当前事件,事件可能传递给父组件
void accept();接收者期望处理当前事件
bool isAccepted();判断当前事件是否被处理
3、事件过滤流程
A、确定需要过滤处理哪些对象的哪些事件
B、构造自己的事件过滤类: 重写类的eventFilter函数
C、在主程序中实例化一个过滤类对象
D、调用过滤类对象的installEventFilter(receiver, QEvent *event)函数,
在目标对象上安装过滤器。
事件过滤器可以对其他组件接收到的事件进行监控,任意的QObject对象都可以作为事件过滤器使用,事件过滤器对象需要重写eventFilter函数。
组件通过installEventFilter函数安装事件过滤器,事件过滤器在组件之前接收到事件,能够决定是否将事件转发到组件对象。
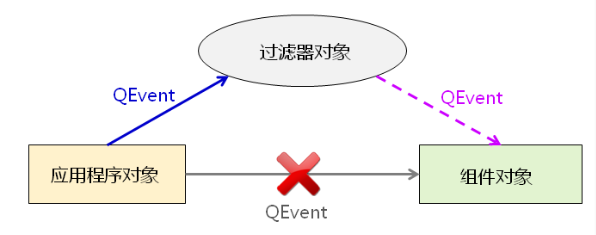
2、事件的发送
sendEvent()立即同步处理要发送的event。当sendEvent()返回的时候, 表示相关的事件过滤器或目标对象处理完了event。对于多数的event类, 有一个成员函数 isAccepted() 可以用来判别event事件是已被接受处理或被拒绝处理。
postEvent()将event提交到一个事件队列中等待调度。在下一次 Qt 的主 event loop 运行的时候,主 event loop 就会调度所有提交到队列中的 event, 以某种优化的方式. 例如, 如果有几个 resize event, 他们就会被压缩成一个事件. 同样适用于 paint events: QWidget::update() 调用postEvent(), 以避免多次重画来避免闪烁以及提高速度.
postEvent()也被用于对象的初始化过程, 因为提交过的 event 通常在相应对象初始化完毕后极短的 时间内就会被调度. 在实现一个控件的时候, 在自定义控件的 constructor 中尽早支持事件机制是非常重要的, 在可能接受到任何事件之前,确保尽早初始化成员变量。
事件和信号不同,事件由具体对象进行处理,信号由具体对象产生,改写事件处理函数可能导致程序行为发生改变。
六、自定义QDropEvent拖放事件实例
1、QDropEvent拖放事件
拖放一个文件进入窗口时将触发拖放事件,每一个QWidget对象都可以处理拖放事件。
拖放事件的处理函数
void dragEnterEvent(QDragEnterEvent *e)
void dragEvent(QDropEvent *)
拖放事件中的QMimeData,QMimeData是QT中的多媒体数据类,拖放事件通过QMimeData对象传递数据,QMimeData支持多种不同类型的多媒体数据。
常用QMimeData数据处理函数
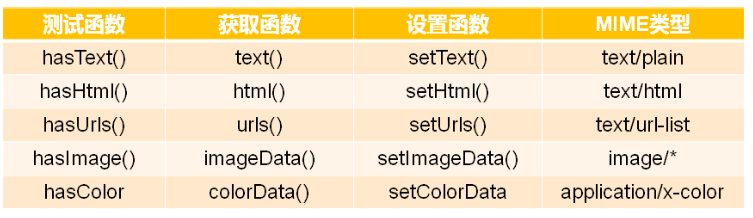
2、自定义拖放事件
自定义拖放事件的流程:
A、对接收拖放事件的对象调用setAcceptDrops成员函数
B、重写dragEnterEvent函数并判断MIME类型
期望类型数据:e->acceptProposedAction();
其他数据类型:e->ignore();
C、重写dragEvent函数并判断MIME类型
期望数据类型:从事件对象中获取MIME数据并处理
其他数据类型:e->ignore();
//在窗口类构造函数中设置拖放事件生效
setAcceptDrops(true);
//重写窗口类的dropEvent函数
void MainWindow::dropEvent(QDropEvent* e)
{
if( e->mimeData()->hasUrls() )
{
QList<QUrl> list = e->mimeData()->urls();
QString path = list[0].toLocalFile();
QFileInfo fi(path);
if( fi.isFile() )
{
saveOldFile();
if( !m_isTextChanged )
{
showFile(path);
}
}
else
{
showErrorMessage("Cannot open a folder!");
}
}
else
{
e->ignore();
}
}
//重写窗口类的dragEnterEvent函数
void MainWindow::dragEnterEvent(QDragEnterEvent* e)
{
if( e->mimeData()->hasUrls() )
{
e->acceptProposedAction();
}
else
{
e->ignore();
}
}本文出自 “生命不息,奋斗不止” 博客,谢绝转载!
QT开发(十二)——QT事件处理机制
