首页 > 代码库 > python基础知识(集合)
python基础知识(集合)
在python中集合set是一种基本数据的类型,它有可变集合(set())和不可变集合(frozenset)两种。创建集合set、集合set添加、集合删除、交集、并集、差集的操作都是非常实用的方法,接下来将介绍结合的相关知识。
一、集合特点
1、类似字典dict,但是只有key却没有value值;
2、集合的存储没有固定的顺序
3、由于集合里面的元素不能重复所以集合一般用来去重
二、集合的定义
常见的有两种方法
1、直接定义类似字典但是没有value值,例如
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
2、创建一个set,提供一个list作为输入集合
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set"])
两个的输出结果
{‘openatck‘, ‘list‘, ‘and‘, ‘set‘, ‘dict‘}
{‘openatck‘, ‘list‘, ‘and‘, ‘set‘, ‘dict‘}三、集合元素的操作
1、 增加元素可以使用add()方法增加元素
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set"])
set2.add("winnerlook")
print (set1,set2)
结果:
{‘set‘, ‘openatck‘, ‘and‘, ‘dict‘, ‘list‘}
{‘openatck‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘list‘, ‘and‘, ‘dict‘, ‘set‘}2、集合元素的增加update()方法
update()是把要传入的元素拆分,做为个体传入到集合中
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
set2.update("winnerlook","MYSQlDBA")
print (set2)
结果:
{‘B‘, ‘M‘, ‘r‘, ‘S‘, ‘Y‘, ‘e‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘set‘, ‘i‘, ‘Q‘, ‘
and‘, ‘o‘, ‘w‘, ‘n‘, ‘dict‘, ‘k‘,t}
这时我们发现将我们更新传入的值全部按每个字符当做一个元素插入到当前的集合里面了3、集合的删除
在前面列表的学习里面我们学习了clear()、pop()、remove()、del等方法可以删除列表中的元素,接下来我们分析一下集合删元素的方法。
clear()方法
clear()方法还是和列表中的一样直接会清空集合中的所有元素,例如:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
#set2.update("winnerlook","MYSQlDBA")
set2.clear()
print (set1,set2)
结果:
{‘set‘, ‘dict‘, ‘openatck‘, ‘list‘, ‘and‘} set()
返回结果和是一个空的集合,而列表使用clear()方法后是返回空的列表remove()方法
remove()方法是移除集合中的某个元素,但是元素必须存在,不然会报错
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
list=["openatck","and","list","dict","set"]
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
#set2.update("winnerlook","MYSQlDBA")
set2.remove("winnerlook")
list.remove("and")
print (list,set2)
结果:
[‘openatck‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘, ‘set‘] {‘openatck‘, ‘and‘, ‘dict‘, ‘list‘, ‘set‘}pop()方法
集合的pop()方法和列表的pop()方法是不一样的,列表的可以带下标的去删除,列表是默认删除最后一个元素,由于集合的存储是没有固定顺序的所以删除的元素时随机的。我们看一下下面的示例,相同的程序多次执行结果却是不一致。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
list=["openatck","and","list","dict","set"]
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
#set2.update("winnerlook","MYSQlDBA")
set2.pop()
list.pop()
print (list,set2)
结果1:
[‘openatck‘, ‘and‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘] {‘dict‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘and‘, ‘set‘, ‘list‘}#删除openstack
结果2:
[‘openatck‘, ‘and‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘] {‘list‘, ‘set‘, ‘and‘, ‘openatck‘, ‘dict‘} #删除winnerlook
结果3:
[‘openatck‘, ‘and‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘] {‘list‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘openatck‘, ‘set‘, ‘and‘}#删除dict
结果4:
[‘openatck‘, ‘and‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘] {‘openatck‘, ‘dict‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘and‘, ‘list‘}#删除set
这里为什么是随机删除的,个人猜想是因为集合里面存储顺序不是固定的原因吧,这样就会出现随机
删除的现象。del 删除
在删除某个定义的集合时,我们还可以采用del方法,这样就可以将一个集合删除,但是这种删除会报没有定义这个集合的错。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
list=["openatck","and","list","dict","set"]
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openatck","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
#set2.update("winnerlook","MYSQlDBA")
del set2
list.pop()
print (list,set2)
结果:
print (list,set2)
NameError: name ‘set2‘ is not defined4、集合的访问
由于集合本身是无序的,所以不能为集合创建索引或切片操作,只能循环遍历或使用in、not in来访问或判断集合元素。
5、元素与集合、集合与集合的关系
在我们高中学习集合相关的知识时,我们就学习到集合的交际、并集、补集等概念,而这部分概念在其python编程的数据类型集合里面还是适用的。
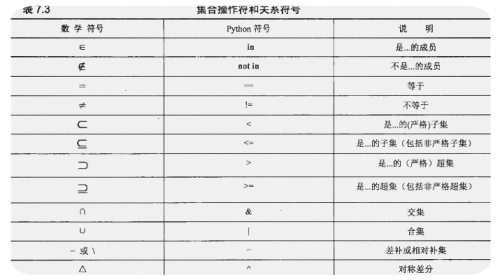
下面简单的演示以下上面的集合关系和相关的操作:
元素与集合的关系:
in 一般是用来表示某个元素是否在某个集合里面,返回值为Ture和False
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
list=["openatck","and","list","dict","set"]
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
print ("openstack" in set2)
print ("docker" in set2)
结果:
True
False
由于set2中包含openstack元素但是不包含docker元素,所以判断一个返回Ture,一个返回Falsenot in 其实和in表达的意思差不多
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
list=["openatck","and","list","dict","set"]
set1={"openatck","and","list","dict","set"}
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
print ("openstack" not in set2)
print ("docker" not in set2)
结果:
False
True== 等于关系
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
set3={"openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
print(set2==set3)
结果:
True 表示两个集合相等
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
print(set1==set3)
结果:
True 表示两个集合相等 表达式和结果一样!= 不等于关系 表示两个集合的元素不一样
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
print(set1!=set2)
print(set1!=set3)
结果:
True
False集合与集合的关系
子集(<)与真子集(<=)
子集表示一个集合里面的元素被另一个集合包含,而真子集是说的一个集合的元素恰好和另一个集合相等。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
print(set1<=set3)
print(set4< set1)
print(set4<=set3)
结果:
True
True
True严格超集(>)和非严格超集(>=)
这里的关系和上面的字迹关系是一样的,只不过是用的表示相反的关系
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","and","list","dict","set","winnerlook"])
set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
print(set1>=set3)
print(set4>set1)
print(set4>=set3)
结果:
True
False
False交集(&)或者用intersection()
表示两个集合中相同的元素
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","list","dict","winnerlook",99,100,0.99])
#set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
print(set1&set2)
print(set1.intersection(set2))
结果:
{‘openstack‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘, ‘winnerlook‘}
{‘openstack‘, ‘list‘, ‘dict‘, ‘winnerlook‘}并集 (|)或者用union()表示
表示两个集合中一共包含的元素
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","list","dict","winnerlook",99,100,0.99])
#set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#print(set1&set2)
#print(set1.intersection(set2))
print(set1|set2)
print(set1.union(set2))
结果:
{0.99, 99, 100, ‘dict‘, ‘set‘, 17, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘list‘, ‘openstack‘}
{0.99, 99, 100, ‘dict‘, ‘set‘, 17, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘list‘, ‘openstack‘}差补(-)或者difference()
相对补集
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","list","dict","winnerlook",99,100,0.99])
#set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#print(set1&set2)
#print(set1.intersection(set2))
print(set1-set2)
print(set1.difference(set2))
结果:
{17, ‘set‘}
{17, ‘set‘}
set2相对sst1的补集即set2中有,但是set1中是没有的对称差分(^)或者symmetric_difference()
对称差分是集合的XOR(‘异或’),取得的元素属于set1,set2但不同时属于set1和set2
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","list","dict","winnerlook",99,100,0.99])
#set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#print(set1&set2)
#print(set1.intersection(set2))
print(set1^set2)
print(set1.symmetric_difference(set2))
结果:
{0.99, 17, 99, 100, ‘set‘}
{0.99, 17, 99, 100, ‘set‘}6、集合之间的and与or关系
注意and关系是取值set2 or关系是取值set1
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","list","dict","winnerlook",99,100,0.99])
#set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#print(set1&set2)
#print(set1.intersection(set2))
print(set1 and set2)
print(set1 or set2)
{0.99, 99, 100, ‘dict‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘list‘, ‘openstack‘}
{‘dict‘, ‘set‘, ‘winnerlook‘, 17, ‘list‘, ‘openstack‘}7、集合、列表、元组、字符串之间转换
我们可以将集合根据不同的数据类型转换成其他的格式
list(set1)将集合转换成列表
tuple(set1)将集合转换成元组
str(set1) 将集合转换成字符串
#!/usr/bin/env python
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
set1={"openstack",9+8,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
set2=set(["openstack","list","dict","winnerlook",99,100,0.99])
#set3={"openstack",17,"list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#set4={"openstack","list","dict","set","winnerlook"}
#print(set1&set2)
#print(set1.intersection(set2))
print(str(set1),type(str(set1)))
print(list(set1),type(list(set1)))
print(tuple(set1),type(tuple(set1)))
结果:
{‘set‘, ‘list‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘dict‘, 17, ‘openstack‘} <class ‘str‘>
[‘set‘, ‘list‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘dict‘, 17, ‘openstack‘] <class ‘list‘>
(‘set‘, ‘list‘, ‘winnerlook‘, ‘dict‘, 17, ‘openstack‘) <class ‘tuple‘>8、集合的简单应用
由于集合的元素不能重复,所以可以用来去重
list2=[2,-3,-8,0,100,5005,737737,10010,-3,-8,0,100,10010]
set222=set(list2)
print(set222)
结果:
{0, 2, 100, 737737, 5005, -8, 10010, -3}四、集合的内建函数与内建方法
1、len():返回集合元素个数
2、set()、frozenset()工厂函数
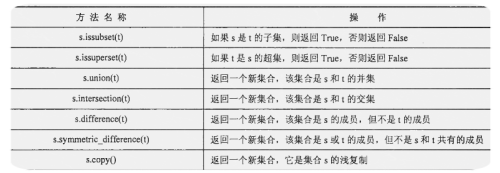
3、所有集合方法:
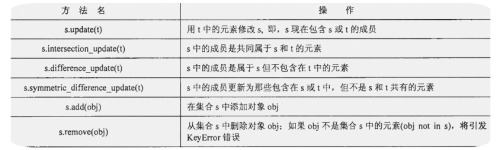
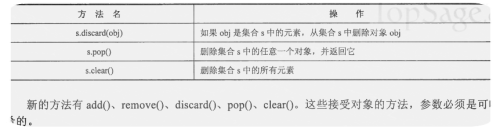
4、仅适合可变集合的
参考文档:http://www.cnblogs.com/BeginMan/p/3160565.html
本文出自 “坚持梦想” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://dreamlinux.blog.51cto.com/9079323/1910566
python基础知识(集合)
