首页 > 代码库 > jasypt与Spring结合使用说明
jasypt与Spring结合使用说明
jasypt既然是以简单的方式来解决java开发中的加密问题,自然使用起来难度不是很大。加密是从系统安全性方面考虑的,因此jasypt更像是面向方面的解决办法,不管你的系统中配置文件,敏感信息是否已经加密或者没有加密,jasypt都能够轻松的嵌入其中,开发人员就不用专门考虑加密算法和代码的编写。
要想深入了解jasypt是如何将加密解密和摘要算法组织起来,轻松的解决开发中加密问题以及和第三方组件集成,查看它的源代码是不错的选择。
下面主要说说如何在Spring框架中如何轻松使用jasypt。(下面的加密机是对jasypt中的加密解密,摘要算法的统称)
第一种方式:以bean的形式将加密机(即:加密类的实例对象)交给Spring托管
第二种方式:以配置XML的形式将加密机与Spring集成。
第一种方式:
1.托管一个StandardPBEStringEncryptor加密机
<!-- 加密机 -->
<bean id="strongEncryptor" class="org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEStringEncryptor">
<property name="algorithm">
<value>PBEWithMD5AndTripleDES</value>
</property>
<property name="password">
<value>${user.home}</value>
</property>
</bean>这里的属性"password"的值为系统属性的值,实际开发中在对某一个数据进行加密的时候这个password是要进行记录的,如果password在这里设置之后将默认提供了一个password的取值。
其它的属性设置可以参见:http://aiilive.blog.51cto.com/1925756/1420837 这篇文章中关于jasypt命令行工具的介绍。
在程序中使用strongEncrypt加密机对象:
@Test
public void test1() {
StandardPBEStringEncryptor spe = (StandardPBEStringEncryptor) context
.getBean("strongEncryptor");
String src = "admin@123";
String encrypt = spe.encrypt(src);
System.out.println("src=http://www.mamicode.com/‘#/‘" //加密解密
Assert.assertEquals(decrypt, src);
}2.托管一个StandardStringDigester加密机
<!-- 摘要算法 --> <bean id="digestEncryptor" class="org.jasypt.digest.StandardStringDigester"> <property name="algorithm"> <value>MD5</value> </property> </bean>
在程序中使用digestEncryptor加密机对象
@Test
public void test7() {
StandardStringDigester ssd = (StandardStringDigester) context
.getBean("digestEncryptor");
String rs1 = ssd.digest("admin");
String rs2 = ssd.digest("admin");
System.out.println(rs1 + " [vs] " + rs2);
//判断是否匹配
Assert.assertTrue(ssd.matches("admin", rs1));
}StrandardStringDigester类提供了matches方法用来检测原始数据和进行摘要计算后的数据是否匹配。
1,2介绍了数据的处理,下面3讲介绍使用jasypt对配置文件进行处理.
3.使用jasypt对配置文件进行处理
比如数据库连接的属性值一般要进行加密处理,然后在程序运行时对其进行解密连接数据库,这样就保证了在程序代码已经配置中数据库的连接相关敏感数据不至于明文暴露。
jasypt是如何处理这一过程的呢?
首先,配置环境变量(这里指用来加解密的环境),
然后,通过环境变量来装载加密机,
最后,使用jasypt对Spring的org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer类的子类来配置属性文件替换配置。
下面是具体的配置信息:
<!-- 基于环境变量,配置加密机 -->
<bean id="environmentVariablesConfiguration"
class="org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.EnvironmentStringPBEConfig">
<property name="algorithm" value="http://www.mamicode.com/PBEWithMD5AndDES" />
<!-- <property name="passwordEnvName" value=""/> -->
<!-- <property name="passwordSysPropertyName" value=""></property> -->
<property name="password" value="http://www.mamicode.com/sa" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置加密器,将用于解密 -->
<bean id="configurationEncryptor" class="org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEStringEncryptor">
<property name="config" ref="environmentVariablesConfiguration" />
</bean>
<!-- 外部属性文件配置 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.jasypt.spring31.properties.EncryptablePropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<constructor-arg ref="configurationEncryptor" />
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:db.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!--数据源配置, jasypt的EncryptedPropertyPlaceholderConfigurer将确保${dataSource.password}是解密 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName">
<value>${dataSource.driver}</value>
</property>
<property name="url">
<value>${dataSource.url}</value>
</property>
<property name="username">
<value>${dataSource.username}</value>
</property>
<property name="password">
<value>${dataSource.password}</value>
</property>
</bean>说明:
EnvironmentStringPBEConfig 中的属性
passwordEnvName, passwordSysPropertyName,password
三者的区别是:
passwordEnvName的值直接设置为环境变量,比如value="http://www.mamicode.com/APP_PASSWORD", APP_PASSWORD则是系统环境变量,在实际生产环境中建议使用这个属性,具体使用步骤如:配置环境变量APP_PASSWORD --> 启动应用程序 --> 应用程序启动完成 --> 删除环境变量APP_PASSWORD。
passwordSysPropertyName的值就是用 System.getProperties() 获取的属性值,比如:value="http://www.mamicode.com/${user.home}"
password和使用jasypt命令行工具时的password参数用法一致。
属性配置文件加密
dataSource.driver=org.postgresql.Driver dataSource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/dbname dataSource.username=postgres #dataSource.password=postgres dataSource.password=ENC(lzRg3F8s4sfJPQ96m5YqDz50VeY85YGX)
这里将password的加密结果放置在ENC(机密结果)中,注意这样的写法是jasypt的规定,可以查看源代码,在解密过程中会根据这个标志对属性配置文件中的加密数据进行解密。
属性配置文件中的机密结果产生则需要用jasypt的命令行工具(具体使用可以参见:http://aiilive.blog.51cto.com/1925756/1420837 ),这里要注意的是加密过程中的算法,password参数值需要和Spring配置文件中的environmentVariablesConfiguration(bean)的属性取值保持一致。
数据源中使用属性配置信息中的值
以前Spring中怎么使用,现在就怎么使用。
jasypt和Spring集成的依赖
jasypt.jar+jasypt-springx-x.jar , x表示一些版本信息。
第二种方式
第一种方式将jasypt中的类作为bean的形式在Spring中应用,第二种方式则更加强大,有独立的XML配置命名空间,更像是Spring的一部分。
首先需要在Spring的配置文件中添加jasypt的命名空间。
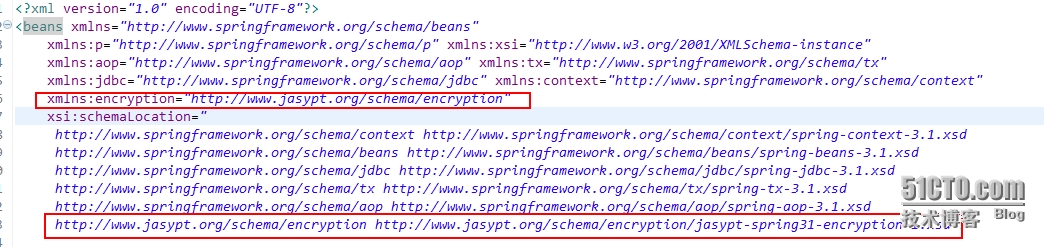
配置完成jasypt的命名空间就可以在Spring的配置文件中直接进行加密机,加密机参数配置,下面是一个示例:
<!-- 基本的密码加密机 --> <encryption:basic-password-encryptor id="bpe" scope="singleton" /> <!-- 摘要配置 --> <encryption:digester-config id="digester-config" algorithm="SHA-256" algorithm-env-name=""/> <!-- 字符串摘要机 --> <encryption:string-digester id="sd" algorithm="MD5" config-bean="digester-config"/> <!-- 加密机配置 --> <encryption:encryptor-config id="encryptor-config" algorithm="PBEWITHMD5ANDTRIPLEDES"/> <!-- 字符串加密机 --> <encryption:string-encryptor id="se" algorithm="PBEWITHMD5ANDDES" config-bean="encryptor-config"/> <!-- 加密的属性占位符 --> <encryption:encryptable-property-placeholder encryptor="se" location="classpath:db.properties"/>
第二种方式同样可以实现方式一中的功能。
通过介绍了jasypt和Spring集成的两种方式可以看出使用jasypt能够比较轻松自定义加密的参数,配置文件的加解密,整个过程对于应用程序的代码侵入性是很小的,可以在程序中使用jasypt提供的加密算法和方法来实现对需要加密的数据进行处理。
此外jasypt与Hibernate集成则以一个完全对程序逻辑透明的方式可以在ORM映射中对数据进行加解密。
最后jasypt也是开放的,它开放了JCE Provider API,允许开发者使用任何存在的JCE Provider在jasypt中进行消息摘要和加密处理。
本文出自 “野马红尘” 博客,谢绝转载!
