首页 > 代码库 > Hadoop初学指南(6)--MapReduce的简单实例及分析
Hadoop初学指南(6)--MapReduce的简单实例及分析
本文在上一节的基础上通过一个简单的MR示例对MapReduce的运行流程进行分析。
假设有两行数据,分别是hello you,hello me,我们要统计其中出现的单词以及每个单词出现的次数。
所得的结果为
hello 2
you 1
me 1
(1)大致运行流畅
1.解析成2个<k,v>,分别是<0, hello you><10, hello me>。调用2次map函数。
2.执行map任务
3.map输出后的数据是:<hello,1>,<you,1>,<hello,1>,<me,1>
4.排序后是:<hello,1>,<hello,1>,<me,1>,<you,1>
5.分组后是:<hello,{1,1}>,<me,{1}>,<you,{1}>
6.执行reduce任务,reduce函数被调用的次数是3
7.输出
(2)相关代码
所有的项目依旧为以前所用的myhadoop项目
①在src下新建org.apache.hadoop.fs包,把FileUtil这个类文件拷贝到这个包,FileUtil在附件中给出,只需新建一个FileUtil类,将内容拷贝至其中。(这一步主要是为了给权限的)
②在myhadoop项目下建立一个mapreduce包,在这个包下建立一个名为WordCountApp的java类。
1.重写map类,代码如下:
static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>{
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws java.io.IOException ,InterruptedException {
final String[] splited = v1.toString().split(" ");
for (String word : splited) {
context.write(new Text(word), new LongWritable(1));
}
};
}其中Mapper泛型中的四个类型分别表示KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT。
KEYIN即k1,表示行的偏移量
VALUEIN即v1,表示行文本内容
KEYOUT即k2,表示行中出现的单词
VALUEOUT即v2,表示行中出现的单词的次数,这里为固定值1。
2.重写Reducer类,代码如下:
static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable>{
protected void reduce(Text k2, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> v2s, Context ctx) throws java.io.IOException ,InterruptedException {
long times = 0L;
for (LongWritable count : v2s) {
times += count.get();
}
ctx.write(k2, new LongWritable(times));
};
}其中Reducer泛型中的四个类型也表示KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT。
KEYIN即k2,表示行中出现的单词
VALUEIN即v2,表示行中出现的单词的次数
KEYOUT即k3,表示文本中出现的不同单词
VALUEOUT即v3,表示文本中出现的不同单词的总次数1。
3.写main方法,代码如下:
static final String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://myhadoop:9000/hello";
static final String OUT_PATH = "hdfs://myhadoop:9000/out";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI(INPUT_PATH), conf);
Path outPath = new Path(OUT_PATH);
if(fileSystem.exists(outPath)){
fileSystem.delete(outPath, true);
}
Job job = new Job(conf , WordCountApp.class.getSimpleName());
//1.1指定读取的文件位于哪里
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, INPUT_PATH);
//指定如何对输入文件进行格式化,把输入文件每一行解析成键值对
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
//1.2 指定自定义的map类
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
//map输出的<k,v>类型。如果<k3,v3>的类型与<k2,v2>类型一致,则可以省略
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
//1.3 分区
job.setPartitionerClass(HashPartitioner.class);
//有一个reduce任务运行
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);
//1.4 TODO 排序、分组
//1.5 TODO 规约
//2.2 指定自定义reduce类
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
//指定reduce的输出类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
//2.3 指定写出到哪里
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outPath);
//指定输出文件的格式化类
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
//把job提交给JobTracker运行
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}相关代码的所有内容,已经在附件中。
(3)运行查看结果
编写完代码后运行即可:

运行完成后,可以去HDFS中进行查看:
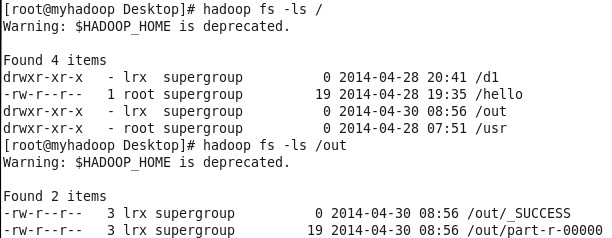
可以看到HDFS中有了/out文件夹,文件夹中多了两个文件。
查看其中的part-r-00000文件,内容如下:
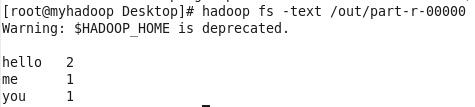
这就是我们想要得到的内容。
本文出自 “Xlows” 博客,转载请与作者联系!
