首页 > 代码库 > Hadoop初学指南(8)--MapReduce中的Combiner操作
Hadoop初学指南(8)--MapReduce中的Combiner操作
本文主要介绍了MapReduce中的Combiner操作。
在MapReduce的执行步骤中,我们一共分了8步,其中Map中的最后一步规约操作就是今天要讲的Combiner。
首先看一下前文中的计数器:
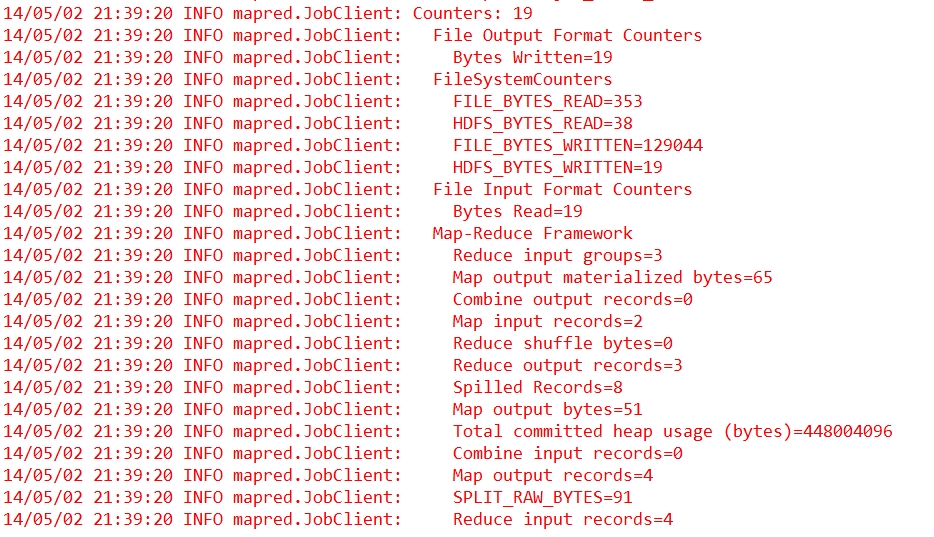
我们可以发现,其中有两个计数器:Combine output records和Combine input records,他们的计数都是0,这是因为我们在代码中没有进行规约操作。
现在我们加入规约操作。
在前文代码(参看http://xlows.blog.51cto.com/5380484/1405212)的main方法中的1.5不后,加入如下一行代码:
//1.5规约 job.setCombinerClass(MyReducer.class);
那么,为什么要用MyReducer的类呢,因为Combine和Reduce一样,其实就是对数据的统计,因此Reduce的内容同样可以用于Combine。
执行后控制台输出如下:
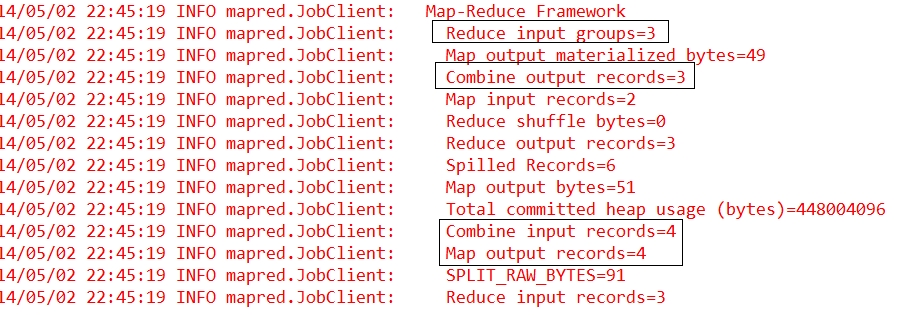 我们看到map的输出和combine的输入统计是一致的,而combine的输出与reduce的输入统计是一样的。由此可以看出规约操作成功,而且执行在map的最后,reduce之前。
我们看到map的输出和combine的输入统计是一致的,而combine的输出与reduce的输入统计是一样的。由此可以看出规约操作成功,而且执行在map的最后,reduce之前。
那么对比原来的计数,规约到底进行了什么呢?
我们可以在自定义的类中加入输出语句来进行查看:
static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable>{
protected void map(LongWritable k1, Text v1, Context context) throws java.io.IOException ,InterruptedException {
String[] splited = v1.toString().split(" ");
for (String word : splited) {
context.write(new Text(word), new LongWritable(1));
System.out.println("Mapper输出<"+word+","+1+">");
}
};
}static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable>{
protected void reduce(Text k2, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> v2s, Context ctx) throws java.io.IOException ,InterruptedException {
//显示次数表示redcue函数被调用了多少次,表示k2有多少个分组
System.out.println("MyReducer输入分组<"+k2.toString()+",...>");
long times = 0L;
for (LongWritable count : v2s) {
times += count.get();
//显示次数表示输入的k2,v2的键值对数量
System.out.println("MyReducer输入键值对<"+k2.toString()+","+count.get()+">");
}
ctx.write(k2, new LongWritable(times));
};
}static class MyCombiner extends Reducer<Text, LongWritable, Text, LongWritable>{
protected void reduce(Text k2, java.lang.Iterable<LongWritable> v2s, Context ctx) throws java.io.IOException ,InterruptedException {
//显示次数表示redcue函数被调用了多少次,表示k2有多少个分组
System.out.println("Combiner输入分组<"+k2.toString()+",...>");
long times = 0L;
for (LongWritable count : v2s) {
times += count.get();
//显示次数表示输入的k2,v2的键值对数量
System.out.println("Combiner输入键值对<"+k2.toString()+","+count.get()+">");
}
ctx.write(k2, new LongWritable(times));
//显示次数表示输出的k2,v2的键值对数量
System.out.println("Combiner输出键值对<"+k2.toString()+","+times+">");
};
}在main方法中改为
job.setCombinerClass(MyCombiner.class);
执行之后,控制台输出如下:



从输出我们可以发现,其实combine只是把两个相同的hello进行的规约,由此输入给reduce的就变成了<hello,2>。其实在实际的集群操作中,我们是由多台主机一起进行MR的,那么如果加入规约操作,每一台主机会在reduce之前进行一次对本机数据的规约,然后在通过集群进行reduce操作,这样就会大大节省reduce的时间,从而加快MR的处理速度。
本文出自 “Xlows” 博客,转载请与作者联系!
