首页 > 代码库 > HDU - 2604 Queuing (矩阵快速幂)
HDU - 2604 Queuing (矩阵快速幂)
Description
Queues and Priority Queues are data structures which are known to most computer scientists. The Queue occurs often in our daily life. There are many people lined up at the lunch time.

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
Input
Input a length L (0 <= L <= 10 6) and M.
Output
Output K mod M(1 <= M <= 30) where K is the number of E-queues with length L.
Sample Input
3 8 4 7 4 8
Sample Output
6 2 1
题意:n个人排队,f表示女,m表示男,形成的2^n个序列中,有多少个序列不包含子串‘fmf’和‘fff’.
思路:用f(n)表示n个人满足条件的结果,那么如果最后一个人是m的话,那么前n-1个满足条件即可,就是f(n-1);
如果最后一个是f那么这个还无法推出结果,那么往前再考虑一位:那么后三位可能是:mmf, fmf, mff, fff,其中fff和fmf不满足题意所以我们不考虑,但是如果是
mmf的话那么前n-3可以找满足条件的即:f(n-3);如果是mff的话,再往前考虑一位的话只有mmff满足条件即:f(n-4)
所以f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-3)+f(n-4),为了达到效率的要求我们应用矩阵快速幂
构造一个矩阵:借用一张图来表达
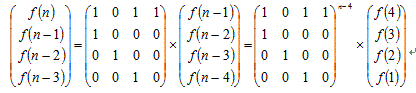
写出一次相乘的矩阵结果是: f(n-1)+f(n-3)+f(n-4)
f(n-1)
f(n-2)
f(n-3), 那么就可以递推出结果是在矩阵的第一项
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 4;
struct Matrix {
int v[maxn][maxn];
Matrix() {
memset(v, 0, sizeof(v));
}
};
int n, m;
Matrix Mul(Matrix a, Matrix b) {
Matrix c;
for (int i = 0; i < maxn; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < maxn; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < maxn; k++)
c.v[i][j] = (c.v[i][j]+a.v[i][k]*b.v[k][j])%m;
return c;
}
Matrix powMul(Matrix a, int k) {
Matrix tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < maxn; i++)
tmp.v[i][i] = 1;
while (k) {
if (k & 1)
tmp = Mul(a, tmp);
k >>= 1;
a = Mul(a, a);
}
return tmp;
}
int main() {
Matrix a, b, c;
a.v[0][0] = 9;
a.v[1][0] = 6;
a.v[2][0] = 4;
a.v[3][0] = 2;
b.v[0][0] = b.v[0][2] = b.v[0][3] = b.v[1][0] = b.v[2][1] = b.v[3][2] = 1;
while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {
if (n <= 4) {
if (n == 0)
printf("0\n");
else printf("%d\n", a.v[4-n][0]%m);
}
else {
c = powMul(b, n-4);
c = Mul(c, a);
printf("%d\n", c.v[0][0]%m);
}
}
return 0;
}
声明:以上内容来自用户投稿及互联网公开渠道收集整理发布,本网站不拥有所有权,未作人工编辑处理,也不承担相关法律责任,若内容有误或涉及侵权可进行投诉: 投诉/举报 工作人员会在5个工作日内联系你,一经查实,本站将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。
